IoT Security
Set up IoT Security and XSOAR for Aruba Central Integration
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
IoT Security Docs
Set up IoT Security and XSOAR for Aruba Central Integration
Set up IoT Security and Cortex XSOAR to integrate with
Aruba Central.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
One of the following Cortex XSOAR setups:
|
You must configure Cortex XSOAR with
an Aruba Central integration instance and a job to import device
data from the Aruba Central server. You can set the job to run at
regular intervals or on demand. The configuration requires the following
information from the Aruba Central:
- Domain URL for a cloud-hosted Aruba Central instance, or an FQDN for an on-premises Aruba Central server.
- Username and password of the read/write user account that XSOAR uses when logging in to the Aruba Central API and obtaining a Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) token. This is the first of three steps to generate an access token and is part of the Open Authorization 2.0 (OAuth2) mechanism.
- Customer ID, which is used with the CSRF token to get an authorization code. This is the second step.
- Client ID and client secret, which in combination with the authorization code, XSOAR uses to acquire an access token. This is the third and final step.
To set up IoT Security
to integrate through a cloud-hosted Cortex XSOAR instance with an
on-premises Aruba Central server, you must also add a Cortex XSOAR
engine to your network.
Cortex XSOAR Engine Installation
An on-premises XSOAR engine facilitates communications between the Cortex XSOAR cloud and Aruba Central server. Although it's possible to install an XSOAR engine on machines running Windows, macOS, and Linux operating systems, only an engine on a Linux machine supports IoT Security integrations. For more information about operating system and hardware requirements, see the Cortex Administrator’s Guide.
We recommend downloading the Cortex XSOAR engine using the shell
installer script and installing it on a Linux machine. This simplifies the
deployment by automatically installing all required dependencies and also
enables remote engine upgrades.
When placing the XSOAR engine on your network, make sure it can form SSH connections to your Aruba Central server. By default, SSH uses TCP port 22.
The on-premises firewall must allow the Cortex XSOAR engine to form
HTTPS connections on TCP port 443 to the Cortex cloud at
https://<your-domain>.iot.demisto.live/. You can see the URL of your Cortex XSOAR instance when you log in to the IoT Security portal
and click Integrations and then click Launch
Cortex XSOAR. It’s visible in the address bar
of the web page displaying the Cortex XSOAR interface.
To create an Cortex XSOAR engine, access the Cortex XSOAR
interface (from the IoT Security portal, click
Integrations and then click Launch
Cortex XSOAR). In the Cortex XSOAR UI,
click SettingsEngines+ Create New Engine. Choose
Shell as the type.
For Cortex XSOAR engine installation instructions, see Engine Installation.
For help troubleshooting Cortex XSOAR engines, including installations,
upgrades, connectivity, and permissions, see Troubleshoot Engines and Troubleshoot Integrations Running on
Engines.
Configure IoT Security and Cortex XSOAR
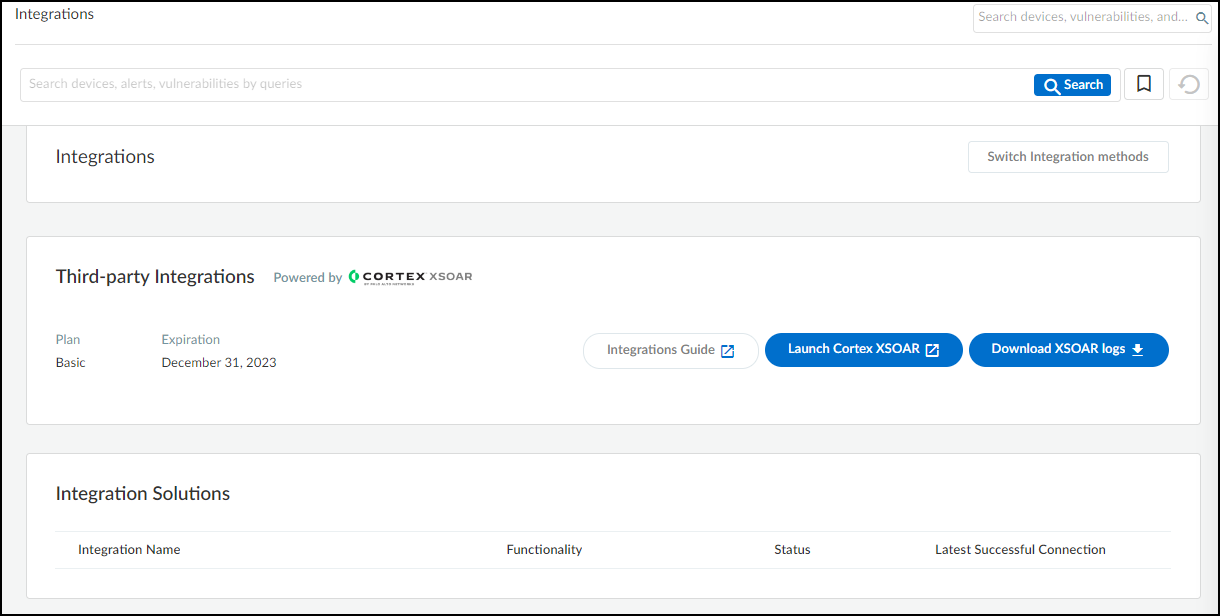
- Log in to IoT Security and from there access Aruba Central settings in Cortex XSOAR.
- Log in to IoT Security and then click Integrations.
![]()
- IoT Security uses Cortex XSOAR to integrate with Aruba Central, and the settings you must configure to integrate with it are in the XSOAR interface. To access these settings, click Launch Cortex XSOAR.The Cortex XSOAR interface opens in a new browser window.
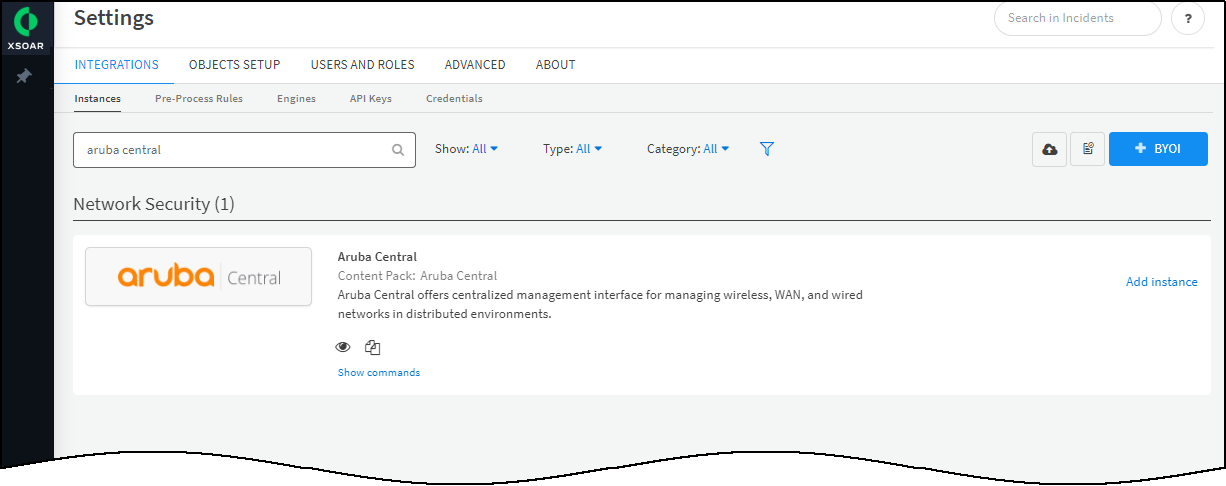
- Click Settings in the left navigation menu, search for aruba central to locate it among other instances.
![]()
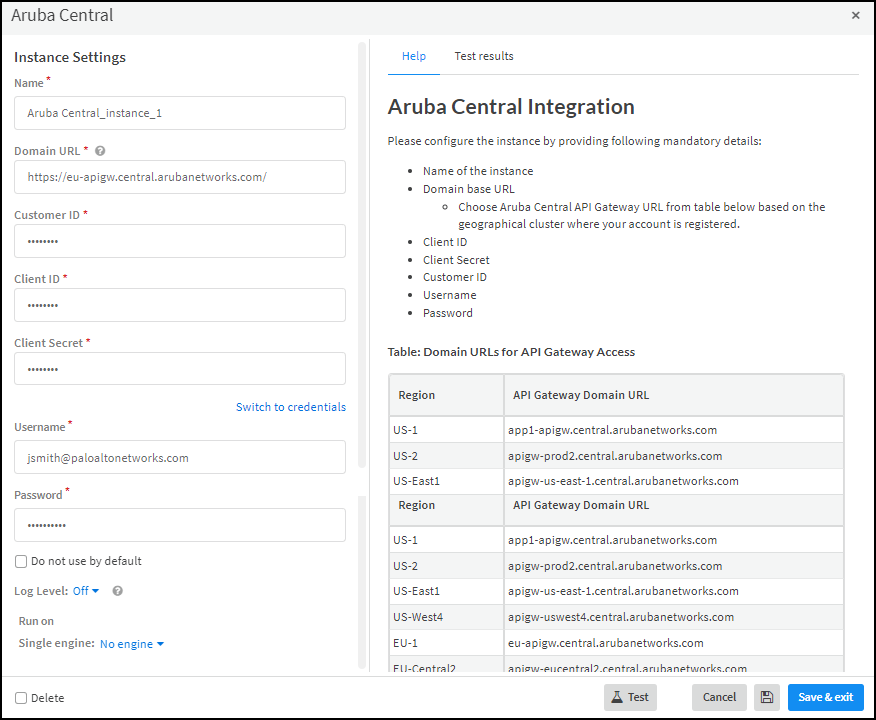
Configure the Aruba Central integration instance.- Click Add instance to open the settings panel.
- Enter the following settings:Name: Use the default name of the instance or enter a new one.Remember the instance name because you are going to use it again when creating a job that Cortex XSOAR will run to gather device data from the Aruba Central instance specified in this integration instance.Domain URL: Enter the domain URL of a cloud-hosted Aruba Central instance or the FQDN of an on-premises Aruba Central server.Customer ID: Copy and paste the customer ID that you copied from the Aruba Central UI and pasted and saved in a text file.Client ID: Copy and paste the client ID that you copied and saved from the Aruba Central UI.Client Secret: Copy and paste the customer ID that you copied and saved from the Aruba Central UI.Username: Type the name of the read-only user account that you previously created for the XSOAR engine to use when connecting to the Aruba Central API.Password: Type the password associated with the user account.Use single engine: When using a cloud-based XSOAR instance and an on-premises Aruba Central server, choose the XSOAR engine that you want to communicate with the Aruba Central server.
![]()
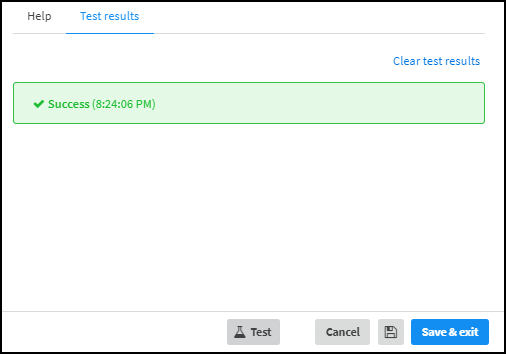
- When finished, click Run test or Test.If the test is successful, a Success message appears. If not, check that the settings were entered correctly and then test the configuration again.
![]()
- After the test succeeds, click Save & exit to save your changes and close the settings panel.
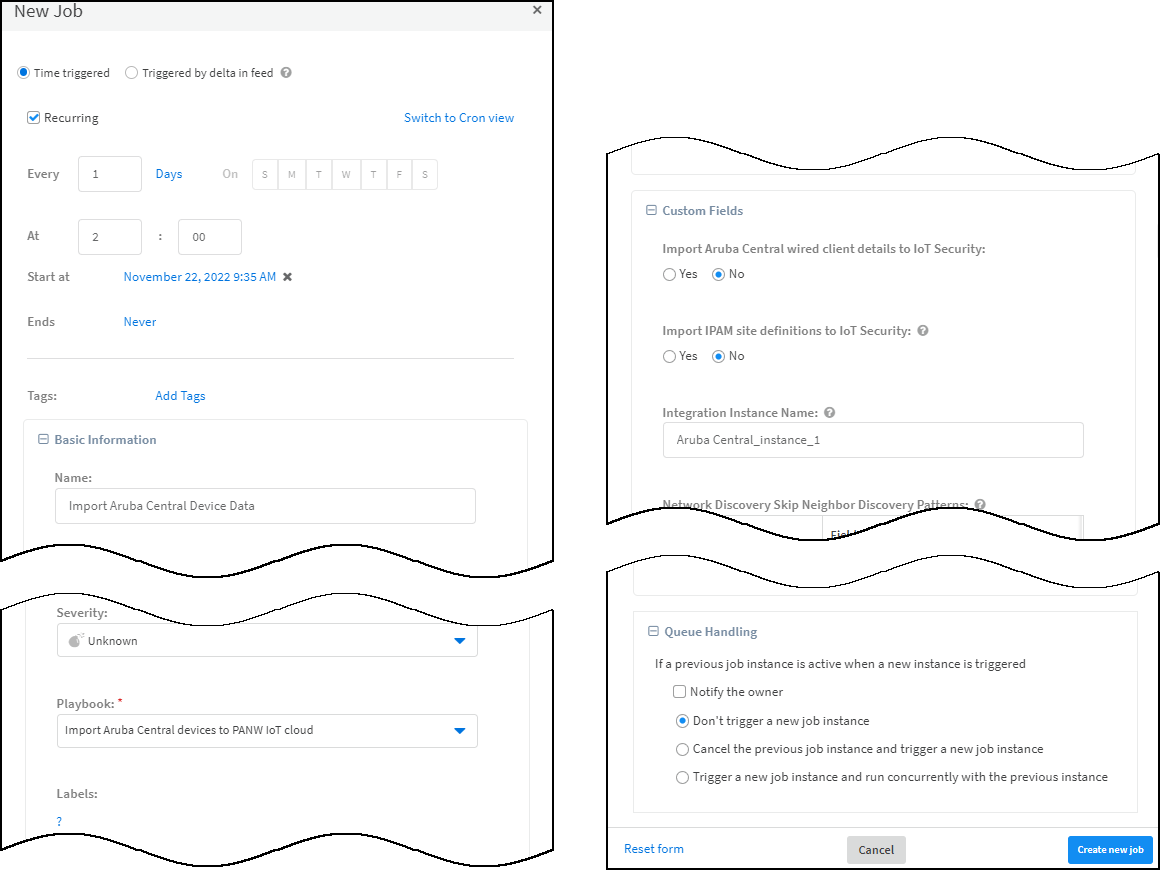
Create a job for XSOAR to query Aruba Central for device details and import them to IoT Security.IoT Security updates devices that are in its database and whose MAC address matches that returned by Aruba Central. If Aruba Central returns device information for a MAC address that’s not in the IoT Security database, then IoT Security creates a new entry and adds the imported MAC address to its database along with any associated device information about it.- Copy the name of the instance you just created, click Jobs near the bottom of the left navigation menu and then click New Job at the top of the page.
- In the New Job panel that appears, enter the following and leave the other settings at their default values:Recurring: Select this if you want to periodically import device information from Aruba Central. Clear it if you want to import data on demand.Every: If you select Recurring, enter a number and set the interval value (Minutes, Hours, Days, or Weeks) and select the days on which to run the job. (If you don’t select specific days, then the job will run everyday by default.) This determines how often XSOAR queries Aruba Central for information about its devices. For example, every day at 2:00 AM.Name: Enter a name for the job.Playbook: Choose Import Aruba Central Device Data.Import Aruba Central wired client details to IoT Security: Select to import device information for both wired and wireless devices. Clear to import device information for wireless devices only.Integration Instance Name: Paste the instance name you copied a few moments ago.
![]()
- Click Create new job.The job appears in the Jobs list.
Enable the job and run it.- Check the Job Status for the job you created. If it’s Disabled, select its check box and then click Enable.
- After you enable it, keep the check box selected and click Run now. The Run Status changes from Idle to Running.If you selected Recurring, XSOAR queries Aruba Central for device information at the defined interval and forwards imported information to IoT Security.If you cleared Recurring, XSOAR immediately queries Aruba Central and forwards imported device information to IoT Security.
If you created more integration instances for multiple on-premises Aruba Central servers, add more jobs as necessary.Each Aruba Central server requires a separate job.Run the job for each integration instance you create. The first time you run a job that references an integration instance, it triggers XSOAR to report the instance to IoT Security, which then displays the integration instance on the Integrations page.When done, return to the IoT Security portal and check the status of the Aruba Central integration.An integration instance can be in one of the following four states, which IoT Security displays in the Status column on the Integrations page:- Disabled means that either the integration was configured but intentionally disabled or it was never configured and a job that references it is enabled and running.
- Error means that the integration was configured and enabled but is not functioning properly, possibly due to a configuration error or network condition.
- Inactive means that the integration was configured and enabled but no job has run for at least the past 60 minutes.
- Active means that the integration was configured and enabled and is functioning properly.
When you see that the status of an integration instance is Active, its setup is complete.