Network Security
Decryption Log Errors and Error Indexes
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Network Security Docs
Decryption Log Errors and Error Indexes
Learn, troubleshoot, and resolve certificate, cipher, protocol, version, and other
TLS handshake errors you might find in a decryption log.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
No separate license required for decryption when using NGFWs or
Prisma Access.
Note: The features and capabilities available to you in
Strata Cloud Manager depend on your active license(s).
|
The Error Index and Error
columns in decryption logs list error categories and details. You can also see error and
error index information in the Handshake Details section of the Detailed Log View (click
![]() for any log entry). The Error Index
column displays one of eight types of errors:
for any log entry). The Error Index
column displays one of eight types of errors:
If no suitable error category exists for an error, the default message is
General TLS protocol error.
- Certificate—Errors such as invalid certificates, expired certificates, unsupported client certificates, certificate revocation status check failures, and untrusted issuer CAs (sessions signed by an untrusted root, which includes incomplete certificate chains).
- Cipher—Unsupported cipher errors where:
- The client tries to negotiate a cipher that the NGFW supports but the decryption profile applied to the traffic doesn’t support.
- The client tries to negotiate a cipher that the NGFW doesn’t support.
- (Rare) Inbound Inspection is enabled and the server’s capabilities don’t match the decryption profile settings.
- The error message includes the supported client cipher bitmask value and the supported decryption profile cipher bitmask value. You can use these values to identify the cipher the client tried to use and the ciphers that the decryption profile supports.
- Feature—Errors such as oversized TLS handshakes or unknown handshakes, oversized certificate chains (more than five certificates), and other unsupported features.
- HSM—Hardware storage module (HSM) errors such as unknown requests, items not found in the configuration, request timeouts, and other HSM errors and failures.
- Protocol—Errors such as TLS handshake failures, private and public key mismatches, Heartbleed errors, TLS key exchange failures, and other TLS protocol errors. Protocol errors show when the server doesn’t support the protocols that the client supports, the server uses certificate types that the NGFW doesn’t support, and general TLS protocol errors.
- Resource—Errors such as lack of sufficient memory.
- Resume—Session resumption errors concerning resume session IDs and tickets, resume session entries in the NGFW cache, and other session resumption errors.
- Version—Errors regarding client and decryption profile version mismatches and client and server version mismatches. The error messages include bitmask values that identify the supported client and decryption profile versions. You can use these values to identify the protocol version the client tried to use and the versions that the decryption profile supports.
The following sections include a table that lists the specific errors for each error
category along with additional information and resources. For some errors, possible
remediation steps are shared. Finally, the Root Status “Uninspected” section describes why the Root Status
column in a decryption log may display "uninspected."
Certificate Errors
Certificate errors are raised for reasons including invalid certificates, expired
certificates, unsupported client certificates, Online Certificate Status Protocol
(OCSP) or certificate revocation list (CRL) check failures, and untrusted issuer CAs
(sessions signed by an untrusted root, which includes incomplete certificate
chains).
When the NGFW doesn’t have an intermediate
certificate because the site didn't send the full certificate chain, you can find
and install the missing certificate to repair an incomplete certificate
chain.
| Decryption Error Message | Additional Information and Resources |
|---|---|
| Invalid (client or server) certificate |
Description: The certificate presented by either a client
or server is invalid or cannot be verified.
Related Documentation:
Remediation:
|
| Expired (client or server) certificate |
Description: A certificate has expired or is not currently
valid.
RFC Information: This alert falls under the
certificate_expired error defined in RFC 5246, which is
applicable to TLSv1.1-TLSv1.3.
Related Documentation:Troubleshoot Expired
Certificates
Remediation:
|
| Unsupported client certificate |
Description: The client certificate was of an unsupported
type.
RFC Information: This alert falls under the
unsupported_certificate error defined in RFC 5246, which is
applicable to TLSv1.1-TLSv1.3.
|
| OCSP / CRL check: certificate revoked |
Description: A certificate was revoked by its signer.
RFC Information: This alert falls under the
certificate_revoked error defined in RFC 5246, which is
applicable to TLSv1.1-TLSv1.3.
Related Documentation:
Remediation:
|
| OCSP / CRL check failure |
Description: Sent by clients when an invalid or
unacceptable OCSP response is provided by the server through the
"status_request" extension.
RFC Information: This alert falls under the
bad_certificate_status_response error defined in
RFC 8446, which is
applicable to TLSv1.3.
|
| Untrusted issuer CA |
Description: A valid certificate chain was received, but
the certificate authority (CA) certificate could not be matched
with a known trust anchor.
RFC Information: This alert falls under the
unknown_ca error defined in RFC 5246, which is
applicable to TLSv1.1-TLSv1.3.
Related Documentation:
Identify Untrusted CA
Certificates
Remediation: This error may be due to a configuration
issue. Use a certificate from a trusted external CA (rather than
an untrusted or self-signed CA). See Obtain a Certificate from an
External CA.
|
| Received fatal alert <error name> from (client or server) |
Description: The variable error has caused the connection
to fail.
|
| Server and firewall's certificate mismatch |
Description: The sender was unable to negotiate an
acceptable set of security parameters with the receiver. A few
possible causes are: incorrect certificates, a missing client
certificate, an untrusted server certificate, or a missing
server certificate.
RFC Information: This alert falls under the
handshake_failure error defined in RFC 5246, which is
applicable to TLSv1.1-TLSv1.3.
Remediation:
|
| SNI didn't match with subject name or SAN |
Related Documentation:
SSL Decryption and Subject
Alternative Names (SAN)
|
| General (client or server) certificate error | This message indicates that an error doesn't meet the criteria for any of the aforementioned certificate errors. |
Cipher Errors
Cipher errors are unsupported cipher errors where at least one of the following is
true:
- The client tries to negotiate a cipher that the NGFW supports but that the decryption profile applied to the traffic doesn’t support.
- The client tries to negotiate a cipher that the NGFW doesn’t support.
- (Rare) Inbound Inspection is enabled and the server’s capabilities don’t match the decryption profile settings.
- The error message includes the supported client cipher bitmask value and the supported decryption profile cipher bitmask value. You can convert these values to actual values using operational CLI commands to identify the cipher the client tried to use and to list the cipher values that the decryption profile supports.
| Decryption Error Message | Additional Information and Resources |
|---|---|
| Unsupported cipher |
Description: The sender was unable to negotiate an
acceptable set of security parameters with the receiver, likely
due to incompatible cipher suites.
RFC Information: This alert falls under the
handshake_failure error defined in RFC 5246, which is
applicable to TLSv1.1-TLSv1.3.
Remediation:
|
Feature Errors
Feature errors include oversized TLS handshakes or unknown handshakes, oversized
certificate chains (more than five certificates), and other unsupported
features.
| Decryption Error Message | Additional Information and Resources |
|---|---|
| Client certificate received |
Related Documentation:
|
| Oversized chain (>5 certificates) received |
Description: The certificate chain contains more than five
certificates.
Remediation:
|
| Oversized handshake received | N/A |
| Unknown handshake message received |
Description: A field in the handshake was incorrect or
inconsistent with other fields (albeit conforms to the formal
protocol syntax), likely causing an unrecognizable handshake
message.
RFC Information: This alert falls under the
illegal_parameter error defined in RFC 5246, which is
applicable to TLSv1.1-TLSv1.3.
|
| Unsupported feature | This message indicates that an error doesn't meet the criteria for any of the aforementioned feature errors. |
HSM Errors
Hardware storage module (HSM) errors include unknown requests, items not found in the
configuration, request timeouts, and other HSM errors and failures.
| Decryption Error Message | Additional Information and Resources |
|---|---|
| Unknown request | N/A |
| Certificate not found in configuration |
Remediation:
|
| Private key not found on HSM |
Remediation:
|
| Request to HSM timed out |
Troubleshooting:
Remediation:
|
| HSM is down |
Related Documentation:
|
| Could not send request to HSM |
Related Documentation:
Remediation: Restart the HSM.
|
| HSM server not found in configuration |
Related Documentation:
|
| General HSM failure | This message indicates that an error doesn't meet the criteria for any of the aforementioned HSM errors. |
Protocol Errors
Protocol errors include TLS handshake failures, private and public key mismatches,
Heartbleed errors, TLS key exchange failures, and other TLS protocol errors.
Protocol errors show when the server doesn’t support the protocols that the client
supports, the server uses certificate types that the NGFW doesn’t
support, and general TLS protocol errors.
| Decryption Error Message | Additional Information and Resources |
|---|---|
| TLS Handshake Failure |
Description: The sender was unable to negotiate an
acceptable set of security parameters with the receiver. A few
possible causes are: incompatible cipher suites, incompatible
SSL/TLS versions, incorrect certificates, missing client
certificate, untrusted server certificate, or a missing server
certificate.
RFC Information: This alert falls under the
handshake_failure error defined in RFC 5246, which is
applicable to TLSv1.1-TLSv1.3.
Remediation:
|
| Private key does not match public key |
Related Documentation:
|
| TLS Key Exchange Failure |
Description: The client and server are unable to exchange
the keys needed to secure communication. A few possible causes
are: incompatible cipher suites, incompatible SSL/TLS versions,
or an incomplete certificate chain.
Remediation:
|
| OpenSSL Error |
Description: An OpenSSL error was detected.
|
| Client only supports Post Quantum Algorithms |
Description: The TLS handshake failed because the client
does not support classical algorithms.
Related Documentation:
|
| General TLS Protocol Error |
This message indicates that an error doesn't meet the criteria
for any of the aforementioned protocol errors.
If no suitable error category exists for
any error, this is the default error message. |
Resource Errors
Resource errors point to a lack of sufficient memory.
| Decryption Error Message | Additional Information and Resources |
|---|---|
| Out of the firewall resources: memory |
Description: An internal error unrelated to the peer or
SSL/TLS protocol correctness (such as a memory allocation error)
makes it impossible to continue.
RFC Information: This alert falls under the
internal_errors error defined in RFC 5246, which is
applicable to TLSv1.1-TLSv1.3.
|
| Out of the firewall resources (general) | This message indicates that an error doesn't meet the criteria for any of the aforementioned resource errors. |
Resume Errors
Resume errors include session resumption errors concerning resume session IDs and
tickets, resumed session entries in the NGFW cache, and other session
resumption errors.
| Decryption Error Message | Additional Information and Resources |
|---|---|
| No resume entry in firewall cache |
Description: The NGFW tried to resume a session for
which a cache entry doesn't exist.
|
| General sessions resumption error | This message indicates that an error doesn't meet the criteria for any of the aforementioned resume errors. |
Version Errors
Version errors regard client and decryption profile version mismatches and client and
server version mismatches. The error messages include bitmask values that identify
the supported client and decryption profile versions. You can convert these values to actual values using operational CLI commands to
identify the cipher the client tried to use and to list the cipher values that the
decryption profile supports.
| Decryption Error Message | Additional Information and Resources |
|---|---|
| Client and decrypt profile version mismatch |
Description: The sender was unable to negotiate an
acceptable set of security parameters with the receiver given
the available options. This is likely due to incompatibility
between the SSL/TLS versions supported by the client and in the
decryption profile.
RFC Information: This alert falls under the
handshake_failure error defined in RFC 5246, which is
applicable to TLSv1.1-TLSv1.3.
Related Documentation:
Troubleshoot Unsupported
Cipher Suites
Remediation:
|
| Client and server version mismatch |
Description: The sender was unable to negotiate an
acceptable set of security parameters with the receiver given
the available options. This is likely due to incompatibility
between the SSL/TLS versions supported by the client and
server.
RFC Information: This alert falls under the
handshake_failure error defined in RFC 5246, which is
applicable to TLSv1.1-TLSv1.3.
Related Documentation:
Troubleshoot Unsupported
Cipher Suites
The troubleshooting topic uses the
"Client and decrypt profile version mismatch" search query. For
this error, use the (error contains ‘Client and
server version mismatch’) query. Remediation:
|
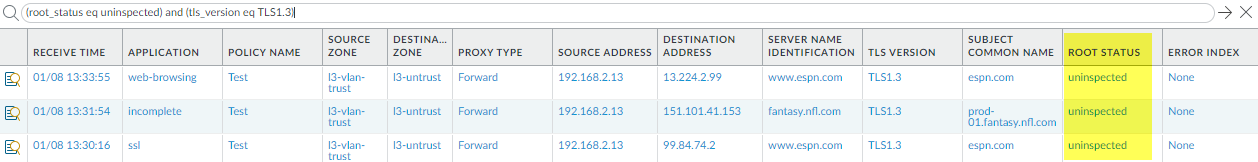
Root Status “Uninspected”
In some cases, the Root Status column displays the value
uninspected. Reasons why the
NGFW might not inspect the root status include:
- Session resumption
- A decryption policy rule with an action of no-decrypt controls the traffic
- A decryption failure occurs before the NGFW inspects the server certificate
Filter the decryption log (root_status eq uninspected) and (tls_version eq
TLS1.3) to see decryption sessions with a root status of
"uninspected."