Next-Generation Firewall
Configure a DNS Proxy Object
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Next-Generation Firewall Docs
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- PAN-OS 12.1
- PAN-OS 11.2
- PAN-OS 11.1
- PAN-OS 11.0 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 10.2
- PAN-OS 10.1
- PAN-OS 10.0 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 9.1 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 9.0 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 8.1 (EoL)
-
- PAN-OS 12.1
- PAN-OS 11.2
- PAN-OS 11.1
- PAN-OS 10.2
- PAN-OS 10.1
Configure a DNS Proxy Object
Configure a DNS proxy object.
If your firewall is to act as a DNS proxy, perform this task to configure a DNS Proxy
Object. The proxy object can either be shared among all virtual systems
or applied to a specific virtual system.
When the firewall is enabled to act as a DNS proxy, evasion signatures that
detected crafted HTTP or TLS requests can alert to instances where a client
connects to a domain other than the domains specified in the original DNS query.
As a best practice, Enable Evasion Signatures after
configuring DNS proxy to trigger an alert if crafted requests are detected.
- Configure the basic settings for a DNS Proxy object.
- Select NetworkDNS Proxy and Add a new object.Verify that Enable is selected.Enter a Name for the object.For Location, select the virtual system to which the object applies. If you select Shared, you must specify at least a Primary DNS server address, and optionally a Secondary address.If you selected a virtual system, for Server Profile, select a DNS Server profile or else click DNS Server Profile to configure a new profile. See Configure a DNS Server Profile.For Inheritance Source, select a source from which to inherit default DNS server settings. The default is None.For Interface, click Add and specify the interfaces to which the DNS Proxy object applies.
- If you use the DNS Proxy object for performing DNS lookups, an interface is required. The firewall will listen for DNS requests on this interface, and then proxy them.
- If you use the DNS Proxy object for a service route, the interface is optional.
(Optional) Specify DNS Proxy rules.- On the DNS Proxy Rules tab, Add a Name for the rule.Turn on caching of domains resolved by this mapping if you want the firewall to cache the resolved domains.For Domain Name, Add one or more domains, one entry per row, to which the firewall compares FQDN queries. If a query matches one of the domains in the rule, the query is sent to one of the following servers to be resolved (depending on what you configured in the prior step):
- The Primary or Secondary DNS Server directly specified for this proxy object.
- The Primary or Secondary DNS Server specified in the DNS Server profile for this proxy object.
DNS Proxy Rule and FQDN Matching describes how the firewall matches domain names in an FQDN to a DNS proxy rule. If no match is found, default DNS servers resolve the query.Do one of the following, depending on what you set the Location to:- If you chose a virtual system, select a DNS Server profile.
- If you chose Shared, enter a Primary and optionally a Secondary address.
Click OK.(Optional) Supply the DNS Proxy with static FQDN-to-address entries. Static DNS entries allow the firewall to resolve the FQDN to an IP address without sending a query to the DNS server.- On the Static Entries tab, Add a Name.Enter the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN).For Address, Add the IP address to which the FQDN should be mapped.You can provide additional IP addresses for an entry. The firewall will provide all of the IP addresses in its DNS response and the client chooses which address to use.Click OK.(PAN-OS 11.2.1 and later releases) (Optional) Configure the DNS proxy to accept encrypted DNS queries from DNS clients and send encrypted DNS queries to DNS servers.
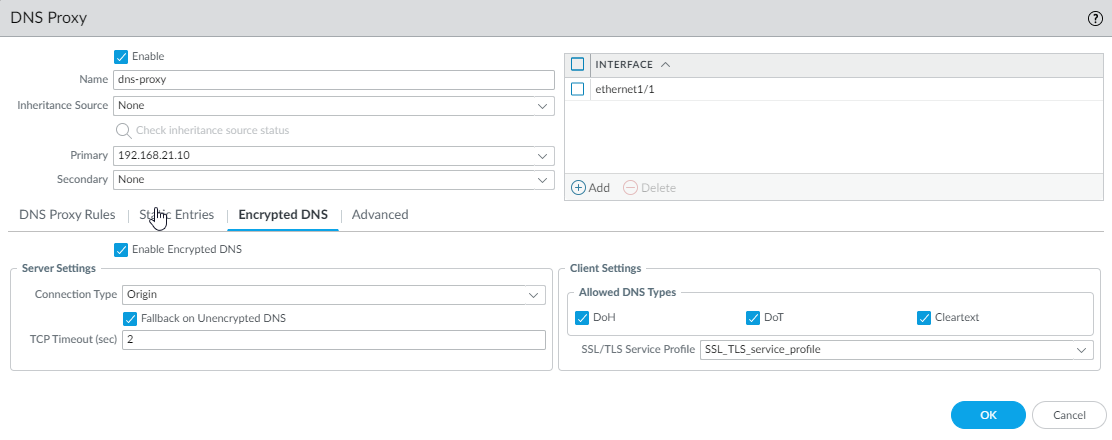
- On the Encrypted DNS tab, Enable Encrypted DNS.If Enable Encrypted DNS isn't selected, the DNS proxy sends cleartext DNS requests to DNS servers, whether the client DNS request is encrypted or not.For Server Settings, select one Connection Type that the firewall (DNS proxy) will use to communicate with DNS servers:
- DoH—DNS over HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer
Protocol Secure). DoH uses port 443. When encrypted DNS is
enabled and DoH is the connection type:
- A primary DNS address is required and the DNS proxy sends all DNS requests to the primary DNS server using DoH. If no response arrives from the primary DNS server, the DNS proxy sends DoH requests to the secondary DNS server.
- No other HTTPS services are allowed on the interface that is acting as a DNS proxy.
- An SSL decryption policy must be configured from the DNS client to DNS server so that the DNS proxy can decrypt DoH traffic.
- DoT—DNS over TLS (Transport Layer
Security). DoT uses port 853, which is dedicated to DoT traffic.
When encrypted DNS is enabled and DoT is the connection type:
- A primary DNS address is required and the DNS proxy sends all DNS requests to the primary DNS server using DoT. If no response arrives from the primary DNS server, the DNS proxy sends DoT requests to the secondary DNS server.
- No other TLS services are allowed on the interface that is acting as a DNS proxy.
- Origin—DNS proxy sends all DNS requests to the primary DNS server using the same DNS type as that received from the client. A primary DNS address is required. If the DNS proxy receives no DNS response from the primary DNS server within the TCP timeout period, the DNS proxy sends the DNS request to the secondary DNS server.
- Cleartext—Plain, unencrypted DNS traffic.
Select Fallback on Unencrypted DNS to have the DNS proxy fall back to traditional DNS (cleartext) if the DNS server rejects encrypted DNS or times out (the DNS proxy receives no response of the configured connection type [DoH or DoT] from the primary or secondary DNS server within the configured TCP timeout period).Enter the TCP Timeout (sec) in seconds, the length of time by which the primary DNS server must respond before the DNS query goes to the secondary DNS server, and the length of time by which the secondary DNS server must respond before the DNS query falls back to cleartext DNS communications; range is 1 to 10; default is 1 second.For Client Settings, select one or more Allowed DNS Types that the DNS proxy will accept from the client:- DoH—DNS proxy must decrypt DoH traffic
and proxy DNS as specified for Server Settings:
- If Origin is the Server Setting, the DNS proxy sends DNS requests as DoH.
- If DoH is the Server Setting, the DNS proxy sends DNS requests as DoH.
- If DoT is the Server Setting, the DNS proxy sends DNS requests as DoT.
- DoT—DNS proxy must decrypt DoT traffic
and proxy DNS as specified for Server Settings:
- If Origin is the Server Setting, the DNS proxy sends DNS requests as DoT.
- If DoH is the Server Setting, the DNS proxy sends DNS requests as DoH.
- If DoT is the Server Setting, the DNS proxy sends DNS requests as DoT.
- Cleartext—DNS proxy must proxy DNS
requests as specified for Server Settings:
- If Origin is the Server Setting, the DNS proxy sends DNS requests as cleartext.
- If DoH is the Server Setting, the DNS proxy sends DNS requests as DoH.
- If DoT is the Server Setting, the DNS proxy sends DNS requests as DoT.
Select an SSL/TLS Service Profile or create a new SSL/TLS Service Profile to use for DNS encryption between the client and DNS proxy, or select None.Click OK.![]() Enable caching and configure other advanced settings for the DNS Proxy.
Enable caching and configure other advanced settings for the DNS Proxy.- On the Advanced tab, select TCP Queries to enable DNS queries using TCP.
- Max Pending Requests—Enter the maximum number of concurrent, pending TCP DNS requests that the firewall will support (range is 64 to 256; default is 64).
For UDP Queries Retries, enter:- Interval (sec)—Length of time (in seconds) after which another request is sent if no response has been received (range is 1 to 30; default is 2).
- Attempts—Maximum number of UDP query attempts (excluding the first attempt), after which the next DNS server is queried (range is 1 to 30; default is 5.)
Select Cache to enable the firewall to cache FQDN-to-address mappings that it learns. You must enable Cache (enabled by default) if this DNS proxy object is used for queries that the firewall generates (that is, under DeviceSetupServicesDNS, or under DeviceVirtual Systems and you select a virtual system and GeneralDNS Proxy.- Select Enable TTL to limit the length of time the firewall caches DNS resolution entries for the proxy object. Disabled by default.
- Enter Time to Live (sec), the number of seconds after which all cached entries for the proxy object are removed. After the entries are removed, new DNS requests must be resolved and cached again. Range is 60 to 86,400. There is no default TTL; entries remain until the firewall runs out of cache memory.
- Cache EDNS Responses—You must enable this setting if this DNS proxy object is used for queries that the firewall generates (that is, under DeviceSetupServicesDNS, or under DeviceVirtual Systems and you select a virtual system and GeneralDNS Proxy.
Commit your changes.Click OK and Commit.