Prisma SD-WAN
Configure Branch HA for Devices with Software Cellular Bypass (1200-S-C-5G)
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma SD-WAN Docs
-
-
-
- CloudBlade Integrations
- CloudBlades Integration with Prisma Access
-
-
-
-
- 5.6
- 6.1
- 6.2
- 6.3
- 6.4
- 6.5
- New Features Guide
- On-Premises Controller
- Prisma SD-WAN CloudBlades
- Prisma Access CloudBlade Cloud Managed
- Prisma Access CloudBlade Panorama Managed
Configure Branch HA for Devices with Software Cellular Bypass (1200-S-C-5G)
Learn how to configure branch HA for devices with software cellular bypass in Prisma SD-WAN.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
The example showcases two ION 1200-S-C-5G devices, representing the next
generation of software-defined enterprise technology. These devices feature switch
ports, cellular 5G/LTE technologies, and 802.1x authentication capabilities. With
the implementation of software bypass, both cellular connections can be utilized
concurrently, enabling elastic WAN network connectivity.
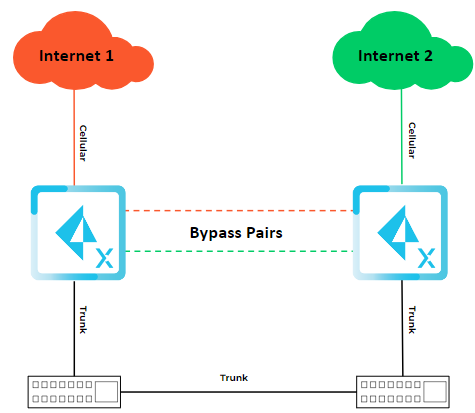
The topology has the following features:
- The active device has one cellular network. (Cellular Internet 1)
- The backup device has one cellular network. (Cellular Internet 2).
- The ION devices operate in an active/backup configuration, and through fail-to-wire functionality, the active ION device constantly maintains complete control and utilizes the full capacity of all the WAN circuits.
- The devices establish a connection with the LAN switch through a trunk, facilitating both data connectivity and enabling High Availability (HA) via device heartbeat monitoring.
- The LAN addressing is identical on both devices, permitting only the active device to use Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) and communicate with hosts and network devices in the LAN.
- The High Availability (HA) addressing is unique, enabling the backup device to communicate with the controller through the active device for connectivity.
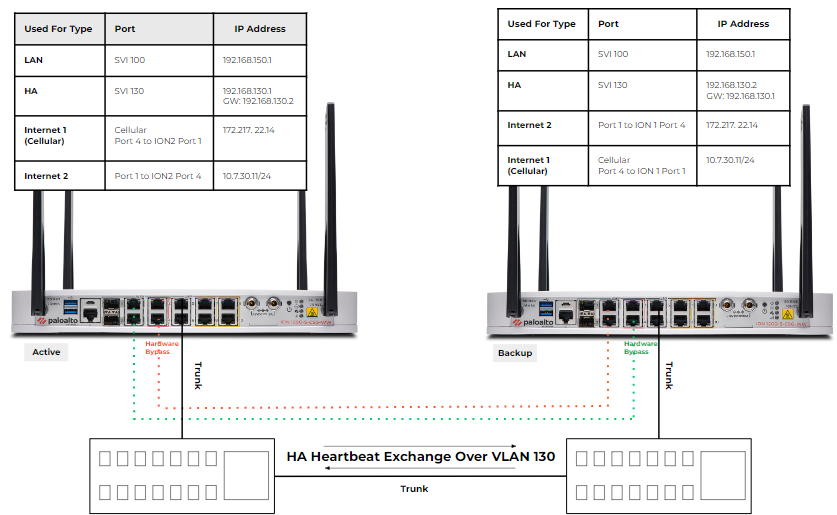
- Create software cellular bypass pairs between WAN and cellular interfaces of the same ION device.Software cellular bypass creates a software bridge between the ethernet and cellular interfaces of an ION device. When both the links are active, the active ION device employs a path selection algorithm to select the best path.The Ethernet link is omitted in this example as we are using the built-in cellular capabilities.
- Create a cellular bypass pair between Cellular Port and Port 4 of ION 1.Create a cellular bypass pair between Cellular Port and Port 4 of ION 2.Create physical connections between the interfaces of the active and backup ION device.
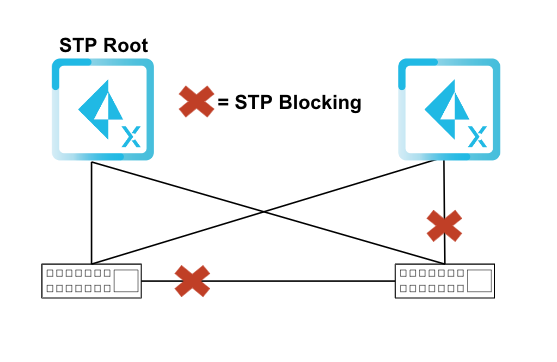
- Connect Port 4 of ION 1 to Port 1 of ION 2.Connect Port 4 of ION 2 to Port 1 of ION 1.This ensures that the cellular circuits are available to both the ION devices.Configure WAN (peer) interfaces on Port 1 for each ION device.The ION devices operate in an active/backup configuration, and through fail-to-wire functionality, the active ION device constantly maintains complete control and utilizes the full capacity of all the WAN circuits. As a result, you need to configure WAN circuits on both the ION devices.The initial step is to configure a cellular bypass pair and configure a WAN port (Port 4) on each ION device. The next step is to mirror the WAN configuration on the connected WAN port (Port 1) of the other ION device.Configure the High Availability (HA) (Used-for-HA) interface.In this example, we are configuring SVI 130 as the Used-for-HA interface for heartbeat exchange between the devices.The interface designated for handling High Availability (HA) will be responsible for establishing connections between the devices and the controller. Consequently, it is crucial that these interfaces possess external reachability (direct or via overlay) and are configured with DNS servers capable of resolving public addresses.Configure an SVI interface for LAN connectivity.In this example, we are configuring SVI 100 for LAN connectivity to enable data exchange between devices.This can involve a single SVI used as a transit to a layer 3 switch below, or alternatively, you can create multiple LAN SVIs to communicate directly with different host subnets.If using a transit LAN to a layer 3 switch, you must also set up routing accordingly.Configure a trunk port for the LAN and HA SVIs.In this instance, we are configuring a trunk port on port 5, where both the LAN (SVI 100) and HA SVI (SVI 130) are assigned. Both the Ports 5 on the ION devices will be directly connected to the LAN switch.The embedded Layer 2 switch on the ION 1200-S and 3200 operates via Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) when in layer 2 mode. When integrating these switches with neighboring LAN switches, it's crucial to note that the adjacent switches should not operate using Per VLAN Spanning-Tree (PVST). Instead, they should use MSTP (which is Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) backwards compatible).For redundancy purposes, trunk ports can be connected to redundant switches. With the implementation of MSTP, it ensures the creation of a loop-free topology, thus maintaining network stability.
![]() Add the ION Devices to the HA Groups.Enable Interface tracking for the trunk switch ports to ensure correct failover behavior if you're connecting them to a LAN switch below. Ensure that the tracking decrement value is the same as the existing device HA priority in order for the ION to decrement to zero under this failure condition. If you're connecting the ION devices back to back, this step is not required.
Add the ION Devices to the HA Groups.Enable Interface tracking for the trunk switch ports to ensure correct failover behavior if you're connecting them to a LAN switch below. Ensure that the tracking decrement value is the same as the existing device HA priority in order for the ION to decrement to zero under this failure condition. If you're connecting the ION devices back to back, this step is not required.