Network Security
Set Up an IPSec Tunnel (Tunnel Mode) ()
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Network Security Docs
Set Up an IPSec Tunnel (Tunnel Mode) ()
Set up a Panorama Managed
Prisma Access IPSec tunnel for your service connection or a remote
network site.
With Prisma Access, Palo Alto Networks deploys and manages the security
infrastructure globally to secure your remote networks and mobile users.
- Service Connections—If your Prisma Access license includes it, you
have the option to establish IPSec tunnels to allow communication between
internal resources in your network and mobile users and users in your remote
network locations. You could, for example, create a service connection to an
authentication server in your organization’s HQ or data center. Even if you don’t require a service connection for your HQ or data center, we recommend that you create one to allow network communication between mobile users and remote network locations, and between mobile users in different geographical locations.
- Remote Networks—Use remote networks to secure remote network locations, such as branches, and users in those branches with cloud-based next-generation firewalls. You can enable access to the subnetworks at each remote network location using either static routes, dynamic routing using BGP, or a combination of static and dynamic routes. All remote network locations that you onboard are fully meshed.
See how to set up an IPSec tunnel for a service connection and a remote network.
Set up an IPSec Tunnel (Service Connection)
- Select or add a new IPSec Tunnel configuration to access the private apps at your data center or headquarters location:
- If you have added a template to the Service_Conn_Template_Stack (or modified the predefined Service_Conn_Template) that includes an IPSec Tunnel configuration, select that IPSec Tunnel from the drop-down. Note that the tunnel you are creating for each service connection connects Prisma Access to the IPSec-capable device at each corporate location. The peer addresses in the IKE Gateway configuration must be unique for each tunnel. You can, however, re-use some of the other common configuration elements, such as Crypto profiles.The IPSec Tunnel you select from a template must use Auto Key exchange and IPv4 only. In addition, make sure that the IPSec tunnel, IKE gateway, and crypto profile names are 31 characters or less.
- To
create a new IPSec Tunnel
configuration, click New IPSec Tunnel, give
it a Name and configure the
IKE Gateway,
IPSec Crypto
Profile, and
Tunnel Monitoring
settings.
- If the IPSec-capable device at your HQ or data center location uses policy-based VPN, on the Proxy IDs tab, Add a proxy ID that matches the settings configured on your local IPSec device to ensure that Prisma Access can successfully establish an IPSec tunnel with your local device.
- Leave Enable Replay Protection selected to detect and neutralize against replay attacks.
- Select Copy TOS Header to copy the Type of Service (TOS) header from the inner IP header to the outer IP header of the encapsulated packets in order to preserve the original TOS information.
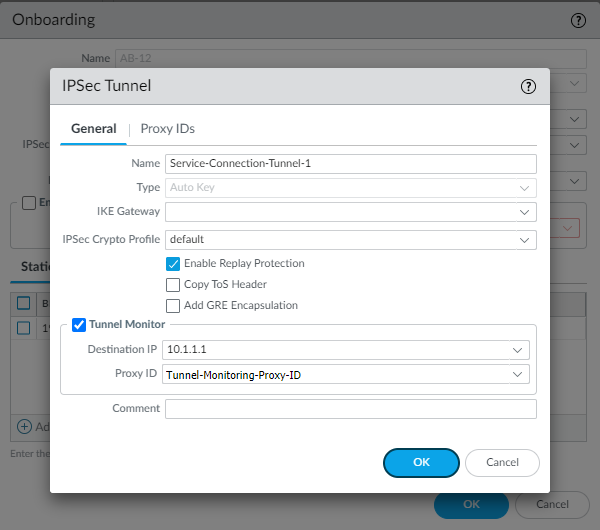
- To enable tunnel monitoring for the service connection, select Tunnel Monitor.
- Enter a Destination IP address.Specify an IP address at your HQ or data center site to which Prisma Access can send ICMP ping requests for IPSec tunnel monitoring. Make sure that this address is reachable by ICMP from the entire Prisma Access infrastructure subnet.
- If you use tunnel monitoring with a peer device that uses multiple proxy IDs, specify a Proxy ID or add a New Proxy ID that allows access from the infrastructure subnet to your HQ or data center site.The following figure shows a proxy ID with the service infrastructure subnet (172.16.55.0/24 in this example) as the Local IP subnet and the HQ or data center’s subnet (10.1.1.0/24 in this example) as the Remote subnet.
![]() The following figure shows the Proxy ID you created being applied to the tunnel monitor configuration by specifying it in the Proxy ID field.
The following figure shows the Proxy ID you created being applied to the tunnel monitor configuration by specifying it in the Proxy ID field.
![]() You must configure a static route on your CPE to the Tunnel Monitor IP Address for tunnel monitoring to function. To find the destination IP address to use for tunnel monitoring from your data center or HQ network to Prisma Access, select PanoramaCloud ServicesStatusNetwork Details, click the Service Infrastructure radio button, and find the Tunnel Monitor IP Address.
You must configure a static route on your CPE to the Tunnel Monitor IP Address for tunnel monitoring to function. To find the destination IP address to use for tunnel monitoring from your data center or HQ network to Prisma Access, select PanoramaCloud ServicesStatusNetwork Details, click the Service Infrastructure radio button, and find the Tunnel Monitor IP Address.
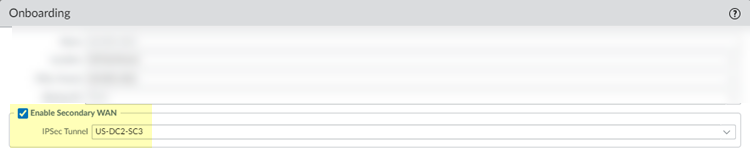
BGP and hot potato routing deployments only—Select a service connection to use as the preferred backup (Backup SC).You can select any service connection that you have already added. Prisma Access uses the Backup SC you select as the preferred service connection in the event of a link failure. Selecting a backup service connection can prevent asymmetric routing issues if you have onboarded more than two service connections. This choice is available in Hot potato routing mode only.If you have a secondary WAN link at this location, select Enable Secondary WAN and then select or configure an IPSec Tunnel the same way you did to set up the primary IPSec tunnel.If the primary WAN link goes down, Prisma Access detects the outage and establishes a tunnel to the headquarters or data center location over the secondary WAN link. If the primary WAN link becomes active, the link switches back to the primary link.Configuring a Secondary WAN is not supported in the following deployments:- If your secondary WAN is set up in active-active mode with the Primary IPSec tunnel.
- If your customer premises equipment (CPE) is set up in an Equal Cost Multipath (ECMP) configuration with the Primary and Secondary IPSec tunnel.
![]() If you use static routes, tunnel failover time is less than 15 seconds from the time of detection, depending on your WAN provider.If you configure BGP routing and have enabled tunnel monitoring, the shortest default hold time to determine that a security parameter index (SPI) is failing is the tunnel monitor, which removes all routes to a peer when it detects a tunnel failure for 15 consecutive seconds. In this way, the tunnel monitor determines the behavior of the BGP routes. If you do not configure tunnel monitoring, the hold timer determines the amount of time that the tunnel is down before removing the route. Prisma Access uses the default BGP HoldTime value of 90 seconds as defined by RFC 4271, which is the maximum wait time before Prisma Access removes a route for an inactive SPI. If the peer BGP device has a shorter configured hold time, the BGP hold timer uses the lower value.When the secondary tunnel is successfully installed, the secondary route takes precedence until the primary tunnel comes back up. If the primary and secondary are both up, the primary route takes priority.If you use a different BGP peer for the secondary (backup) connection, Prisma Access does not honor the Multi-Exit Discriminator (MED) attributes advertised by the CPE. This caveat applies if you use multiple BGP peers on either remote network connections or service connections.
If you use static routes, tunnel failover time is less than 15 seconds from the time of detection, depending on your WAN provider.If you configure BGP routing and have enabled tunnel monitoring, the shortest default hold time to determine that a security parameter index (SPI) is failing is the tunnel monitor, which removes all routes to a peer when it detects a tunnel failure for 15 consecutive seconds. In this way, the tunnel monitor determines the behavior of the BGP routes. If you do not configure tunnel monitoring, the hold timer determines the amount of time that the tunnel is down before removing the route. Prisma Access uses the default BGP HoldTime value of 90 seconds as defined by RFC 4271, which is the maximum wait time before Prisma Access removes a route for an inactive SPI. If the peer BGP device has a shorter configured hold time, the BGP hold timer uses the lower value.When the secondary tunnel is successfully installed, the secondary route takes precedence until the primary tunnel comes back up. If the primary and secondary are both up, the primary route takes priority.If you use a different BGP peer for the secondary (backup) connection, Prisma Access does not honor the Multi-Exit Discriminator (MED) attributes advertised by the CPE. This caveat applies if you use multiple BGP peers on either remote network connections or service connections.Set up an IPSec Tunnel (Remote Network)
- (Static routing or single-tunnel deployments only) Select or add a new IPSec Tunnel configuration to access the firewall, router, or SD-WAN device at the corporate location:
- Select one of the predefined IPSec templates in the Remote_Network_Template, or, if you have added a template to the Remote_Network_Template_Stack (or modified the predefined Remote_Network_Template) that includes an IPSec Tunnel configuration, select that IPSec Tunnel from the drop-down. Note that the tunnel you are creating for each remote network connection connects Prisma Access to the IPSec-capable device at each branch location.Use the following guidelines when configuring an IPSec tunnel:
- The peer addresses in the IKE Gateway configuration must be unique for each tunnel. You can, however, re-use some of the other common configuration elements, such as crypto profiles.
- The IPSec Tunnel you select from a template must use Auto Key exchange and IPv4 only.
- The IPSec tunnel, IKE gateway, and crypto profile names cannot be longer than 31 characters.
- If you onboard multiple remote networks to the same location with dynamic IKE peers, you must use the same IKE crypto profile for all remote network configurations.
- To
create a new IPSec
Tunnel
configuration, click New IPSec Tunnel, give
it a Name and configure the
IKE
Gateway,
IPSec Crypto
Profile,
and
Tunnel
Monitoring
settings.
- If the IPSec-capable device at your branch location uses policy-based VPN, on the Proxy IDs tab, Add a proxy ID that matches the settings configured on your local IPSec device to ensure that Prisma Access can successfully establish an IPSec tunnel with your local device.
- Leave Enable Replay Protection selected to detect and neutralize against replay attacks.
- Select Copy TOS Header to copy the Type of Service (TOS) header from the inner IP header to the outer IP header of the encapsulated packets in order to preserve the original TOS information.
- To enable tunnel monitoring for the service connection, select Tunnel Monitor.
- Enter a Destination IP address.Specify an IP address at your branch location to which Prisma Access can send ICMP ping requests for IPSec tunnel monitoring. Make sure that this address is reachable by ICMP from the entire Prisma Access infrastructure subnet.
- If you use tunnel monitoring with a peer device that uses multiple proxy IDs, specify a Proxy ID or add a New Proxy ID that allows access from the infrastructure subnet to your branch location.The following figure shows a proxy ID with the service infrastructure subnet (172.16.55.0/24 in this example) as the Local IP subnet and the branch location’s subnet (10.1.1.0/24 in this example) as the Remote subnet.
![]() The following figure shows the Proxy ID you created being applied to the tunnel monitor configuration by specifying it in the Proxy ID field.
The following figure shows the Proxy ID you created being applied to the tunnel monitor configuration by specifying it in the Proxy ID field.
![]() You must configure a static route on your CPE to the Tunnel Monitor IP Address for tunnel monitoring to function. To find the destination IP address to use for tunnel monitoring from your branch location to Prisma Access, select PanoramaCloud ServicesStatusNetwork Details, click the Service Infrastructure radio button, and find the Tunnel Monitor IP Address.
You must configure a static route on your CPE to the Tunnel Monitor IP Address for tunnel monitoring to function. To find the destination IP address to use for tunnel monitoring from your branch location to Prisma Access, select PanoramaCloud ServicesStatusNetwork Details, click the Service Infrastructure radio button, and find the Tunnel Monitor IP Address.
If you have a secondary WAN link at this location, select Enable Secondary WAN.Be sure to create a unique IPSec tunnel for each remote network’s secondary WAN; Prisma Access does not support reusing the same IPSec tunnel for secondary WANs in multiple remote networks.Configuring a Secondary WAN is not supported in the following deployments:- If your secondary WAN is set up in active-active mode with the Primary IPSec tunnel.
- If your customer premises equipment (CPE) is set up in an Equal Cost Multipath (ECMP) configuration with the Primary and Secondary IPSec tunnel.
If you use static routes, tunnel failover time is less than 15 seconds from the time of detection, depending on your WAN provider.If you configure BGP routing and have enabled tunnel monitoring, the shortest default hold time to determine that a security parameter index (SPI) is failing is the tunnel monitor, which removes all routes to a peer when it detects a tunnel failure for 15 consecutive seconds. In this way, the tunnel monitor determines the behavior of the BGP routes. If you do not configure tunnel monitoring, the hold timer determines the amount of time that the tunnel is down before removing the route. Prisma Access uses the default BGP HoldTime value of 90 seconds as defined by RFC 4271, which is the maximum wait time before Prisma Access removes a route for an inactive SPI. If the peer BGP device has a shorter configured hold time, the BGP hold timer uses the lower value.When the secondary tunnel is successfully installed, the secondary route takes precedence until the primary tunnel comes back up. If the primary and secondary are both up, the primary route takes priority.If you use a different BGP peer for the secondary (backup) connection, Prisma Access does not honor the Multi-Exit Discriminator (MED) attributes advertised by the CPE. This caveat applies if you use multiple BGP peers on either remote network connections or service connections.