Device > IoT Security > DHCP Server Log Ingestion
Table of Contents
11.2
Expand all | Collapse all
-
- Firewall Overview
- Features and Benefits
- Last Login Time and Failed Login Attempts
- Message of the Day
- Task Manager
- Language
- Alarms
- Commit Changes
- Save Candidate Configurations
- Revert Changes
- Lock Configurations
- Global Find
- Threat Details
- AutoFocus Intelligence Summary
- Configuration Table Export
- Change Boot Mode
-
- Objects > Addresses
- Objects > Address Groups
- Objects > Regions
- Objects > Dynamic User Groups
- Objects > Application Groups
- Objects > Application Filters
- Objects > Services
- Objects > Service Groups
- Objects > Devices
- Objects > External Dynamic Lists
- Objects > Custom Objects > Spyware/Vulnerability
- Objects > Custom Objects > SaaS Tenant List
- Objects > Custom Objects > SaaS User List
- Objects > Custom Objects > URL Category
- Objects > Security Profiles > Antivirus
- Objects > Security Profiles > Anti-Spyware Profile
- Objects > Security Profiles > Vulnerability Protection
- Objects > Security Profiles > File Blocking
- Objects > Security Profiles > WildFire Analysis
- Objects > Security Profiles > Data Filtering
- Objects > Security Profiles > DoS Protection
- Objects > Security Profiles > AI Security
- Objects > Security Profiles > Mobile Network Protection
- Objects > Security Profiles > SCTP Protection
- Objects > Security Profile Groups
- Objects > Log Forwarding
- Objects > Authentication
- Objects > Packet Broker Profile
- Objects > Schedules
-
-
- Firewall Interfaces Overview
- Common Building Blocks for Firewall Interfaces
- Common Building Blocks for PA-7000 Series Firewall Interfaces
- Tap Interface
- HA Interface
- Virtual Wire Interface
- Virtual Wire Subinterface
- PA-7000 Series Layer 2 Interface
- PA-7000 Series Layer 2 Subinterface
- PA-7000 Series Layer 3 Interface
- Layer 3 Interface
- Layer 3 Subinterface
- Log Card Interface
- Log Card Subinterface
- Decrypt Mirror Interface
- Aggregate Ethernet (AE) Interface Group
- Aggregate Ethernet (AE) Interface
- Network > Traffic Objects
- Network > Interfaces > VLAN
- Network > Interfaces > Loopback
- Network > Interfaces > Tunnel
- Network > Interfaces > SD-WAN
- Network > Interfaces > PoE
- Network > Interfaces > Cellular
- Network > Interfaces > Fail Open
- Network > VLANs
- Network > Virtual Wires
-
- Network > Routing > Logical Routers > General
- Network > Routing > Logical Routers > Static
- Network > Routing > Logical Routers > OSPF
- Network > Routing > Logical Routers > OSPFv3
- Network > Routing > Logical Routers > RIPv2
- Network > Routing > Logical Routers > BGP
- Network > Routing > Logical Routers > Multicast
-
- Network > Routing > Routing Profiles > BGP
- Network > Routing > Routing Profiles > BFD
- Network > Routing > Routing Profiles > OSPF
- Network > Routing > Routing Profiles > OSPFv3
- Network > Routing > Routing Profiles > RIPv2
- Network > Routing > Routing Profiles > Filters
- Network > Routing > Routing Profiles > Multicast
- Network > Proxy
-
- Network > Network Profiles > GlobalProtect IPSec Crypto
- Network > Network Profiles > IPSec Crypto
- Network > Network Profiles > IKE Crypto
- Network > Network Profiles > Monitor
- Network > Network Profiles > Interface Mgmt
- Network > Network Profiles > QoS
- Network > Network Profiles > LLDP Profile
- Network > Network Profiles > SD-WAN Interface Profile
- Network > Network Profiles > MACsec Profile
-
-
- Device > Setup
- Device > Setup > Management
- Device > Setup > Interfaces
- Device > Setup > Telemetry
- Device > Setup > Content-ID
- Device > Setup > WildFire
- Device > Setup > ACE
- Device > Setup > DLP
- Device > Log Forwarding Card
- Device > Config Audit
- Device > Administrators
- Device > Admin Roles
- Device > Access Domain
- Device > Authentication Sequence
- Device > IoT Security > DHCP Server Log Ingestion
- Device > Device Quarantine
-
- Security Policy Match
- QoS Policy Match
- Authentication Policy Match
- Decryption/SSL Policy Match
- NAT Policy Match
- Policy Based Forwarding Policy Match
- DoS Policy Match
- Routing
- Test Wildfire
- Threat Vault
- Ping
- Trace Route
- Log Collector Connectivity
- External Dynamic List
- Update Server
- Test Cloud Logging Service Status
- Test Cloud GP Service Status
- Device > Virtual Systems
- Device > Shared Gateways
- Device > Certificate Management
- Device > Certificate Management > Certificate Profile
- Device > Certificate Management > OCSP Responder
- Device > Certificate Management > SSL/TLS Service Profile
- Device > Certificate Management > SCEP
- Device > Certificate Management > SSL Decryption Exclusion
- Device > Certificate Management > SSH Service Profile
- Device > Response Pages
- Device > Server Profiles
- Device > Server Profiles > SNMP Trap
- Device > Server Profiles > Syslog
- Device > Server Profiles > Email
- Device > Server Profiles > HTTP
- Device > Server Profiles > NetFlow
- Device > Server Profiles > RADIUS
- Device > Server Profiles > SCP
- Device > Server Profiles > TACACS+
- Device > Server Profiles > LDAP
- Device > Server Profiles > Kerberos
- Device > Server Profiles > SAML Identity Provider
- Device > Server Profiles > DNS
- Device > Server Profiles > Multi Factor Authentication
- Device > Local User Database > Users
- Device > Local User Database > User Groups
- Device > Scheduled Log Export
- Device > Software
- Device > Dynamic Updates
- Device > Licenses
- Device > Support
- Device > Policy Recommendation > IoT
- Device > Policy > Recommendation SaaS
- Device > Policy Recommendation > IoT or SaaS > Import Policy Rule
-
- Device > User Identification > Connection Security
- Device > User Identification > Terminal Server Agents
- Device > User Identification > Group Mapping Settings
- Device > User Identification> Trusted Source Address
- Device > User Identification > Authentication Portal Settings
- Device > User Identification > Cloud Identity Engine
-
- Network > GlobalProtect > MDM
- Network > GlobalProtect > Clientless Apps
- Network > GlobalProtect > Clientless App Groups
- Objects > GlobalProtect > HIP Profiles
-
- Use the Panorama Web Interface
- Context Switch
- Panorama Commit Operations
- Defining Policies on Panorama
- Log Storage Partitions for a Panorama Virtual Appliance in Legacy Mode
- Panorama > Setup > Interfaces
- Panorama > High Availability
- Panorama > Firewall Clusters
- Panorama > Administrators
- Panorama > Admin Roles
- Panorama > Access Domains
- Panorama > Device Groups
- Panorama > Plugins
- Panorama > Log Ingestion Profile
- Panorama > Log Settings
- Panorama > Server Profiles > SCP
- Panorama > Scheduled Config Export
- Panorama > Device Registration Auth Key
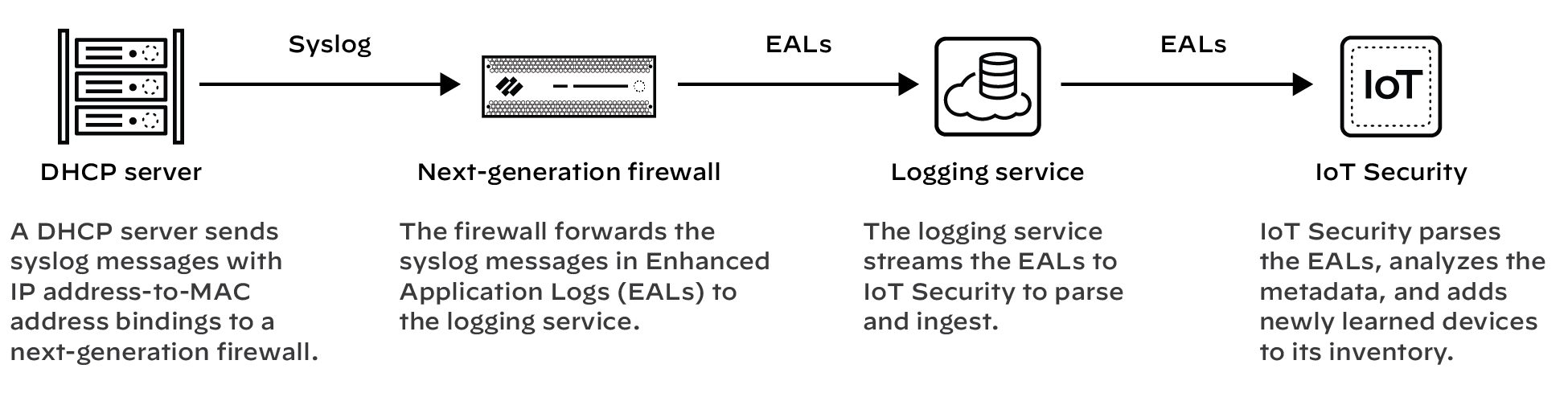
Device > IoT Security > DHCP Server Log Ingestion
IoT Security relies on IP address-to-MAC address bindings
to ascribe observed network behaviors to IoT devices and uniquely
track them. IoT Security typically uses DHCP traffic collected by
next-generation firewalls to learn IP address-to-MAC address bindings
and track IP address changes. However, when it’s not possible to
position a firewall in the DHCP data path, you can use this method
to ingest DHCP server logs and expand DHCP traffic visibility.
In areas of the network where it’s difficult to route DHCP traffic
to or through a firewall, configure DHCP servers to send their server
logs as syslog messages to the firewall. The firewall then forwards
the messages as Enhanced Application Logs (EALs) with a subtype
of dhcp-syslog through the logging service to IoT Security. IoT
Security parses them to learn the IP address-to-MAC address bindings
and then adds newly learned devices to its inventory.
Prerequisites
- A DHCP server with syslog capabilities configured to send messages to a syslog server running on a next-generation firewall
- A next-generation firewall running PAN-OS 11.1 or later with an active IoT Security subscription
Set up the Next-generation Firewall
Set up your next-generation firewall to receive syslog messages
from one or more DHCP servers. The firewall will automatically forward
the syslog messages it receives as EALs to the logging service,
which streams them to IoT Security to parse and analyze.
- Add a DHCP server to the next-generation firewall.Log in to your next-generation firewall, select DeviceIoT+ Add, configure the following, and then click OK:FieldDescriptionNameEnter a name for the DHCP server. It can be up to 32 characters, including spaces.DescriptionEnter a note about the DHCP server for future reference. It can be up to 256 characters, including spaces.EnabledSelect to enable the firewall to listen for connections from the DHCP server and process them when they come.IP AddressEnter the IP address from which the DHCP server will connect to the firewall. The address can be in IPv4 or IPv6 format. An FQDN is not allowed.ProtocolSelect TCP, UDP, or SSL. When making your choice, consider what’s important for the connection between the DHCP server and firewall. TCP provides transmission reliability but not security. UDP provides low processing overhead and faster speeds but lacks reliability and security. SSL provides reliability and security but incurs more overhead.The firewall listens for DHCP server connections using TCP and UDP on port 10514 and connections using SSL on port 16514.
- Repeat the previous step to add more DHCP servers.Add more DHCP servers to expand visibility of DHCP traffic throughout your network as needed. All next-generation firewalls support a maximum of 100 DHCP servers per firewall.
Set up DHCP Servers for Syslog
Configure your DHCP servers to send syslog messages of their
server logs to the management interface on the next-generation firewall.
Make sure to configure the DHCP servers to use the same protocol
configured for them on the firewall: TCP, UDP, or SSL. See the documentation
for your DHCP servers for configuration instructions.
Check the DHCP Server Connection Status
To see all the configured DHCP servers, select DeviceIoT.
A green circle next to a DHCP server name means it was configured
in Panorama and is read-only when viewed in the web interface of
the local next-generation firewall.
When a DHCP server using TCP or SSL is currently connected to
the firewall, “Connected” appears in the Status column. “Connected”
also appears in this column if a DHCP server using UDP has been
connected within the past two hours. At all other times, the Status
column is empty, indicating that the server isn’t currently connected
to the firewall.
The following CLI commands are also useful for checking DHCP
server settings, the status of their connections, and the data they’re
providing to IoT Security:
| show iot dhcp-server status { all | server <server-name> } | Entering all shows
a table with all DHCP servers configured on the firewall, the port
numbers on which they connect, and their current connection status. Entering server <server-name> shows
detailed information about a specific DHCP server and its recent
activity. |
| show iot eal dhcp-syslog-eal | This command shows information related to
EALs carrying DHCP server syslog messages. |
