Changes to Default Behavior
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Next-Generation Firewall Docs
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- PAN-OS 12.1
- PAN-OS 11.2
- PAN-OS 11.1
- PAN-OS 11.0 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 10.2
- PAN-OS 10.1
- PAN-OS 10.0 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 9.1 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 9.0 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 8.1 (EoL)
-
- PAN-OS 12.1
- PAN-OS 11.2
- PAN-OS 11.1
- PAN-OS 10.2
- PAN-OS 10.1
End-of-Life (EoL)
Changes to Default Behavior
Changes to the default behavior in PAN-OS® 9.0
The following table details the changes in default behavior
upon upgrade to PAN-OS® 9.0. You may also want to review
the CLI Changes in PAN-OS 9.0 and
the Upgrade/Downgrade Considerations before
upgrading to this release.
| Feature | Change |
|---|---|
API Key Lifetime | When you generate a new API key, the key
metadata includes a timestamp of the creation date which makes the
key size larger than those generated with PAN-OS version earlier
than 9.0. |
Default Administrator Password Requirements (PAN-OS
9.0.4 and later 9.0 releases) | Starting with PAN-OS 9.0.4, the firewall
enforces password complexity for the default admin account on the
first log in. If the current password doesn't meet the complexity
requirements, the device prompts you to change it. The new
password must have a minimum of eight characters and include a minimum
of one lowercase and one uppercase character, as well as one number or
special character. On a new installation, password complexity is
enabled with a minimum password length of eight characters. This
change does not affect other administrative users. |
HTTP/2 Inspection | The firewall now processes and inspects
HTTP/2 traffic by default. If you want to disable HTTP/2 inspection,
you can specify for the firewall to remove any value contained in
the Application-Layer Protocol Negotiation (ALPN) TLS extension:
select ObjectsDecryptionDecryption ProfileSSL DecryptionSSL Forward Proxy and then
select Strip ALPN. ALPN is used to secure
HTTP/2 connections—when there is no value specified for this TLS
extension, the firewall either downgrades HTTP/2 traffic to HTTP/1.1
or classifies it as unknown TCP traffic. |
Strict Default Ports for Decrypted Applications,
Including Web-Browsing | Application default—which enables you to
allow applications only on their most commonly-used ports—now enforces
standard port usage for certain applications that use a different
default port when encrypted: web-browsing, SMTP, FTP, LDAP, IMAP
and POP3. This means that, if you’re decrypting SSL traffic,
a security policy that allows web-browsing on the application default
ports now strictly enforces web-browsing on port 80 and SSL-tunneled web-browsing
on port 443. To enhance security, if you currently have a
security policy rule configured to allow web-browsing on service-HTTP and service-HTTPS,
you might consider updating the rule to instead allow web-browsing
on the application-default ports: 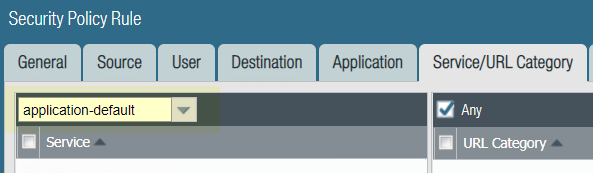
|
Network Processing Card Session Capacity
Change (PA-7000-20G-NPC and PA-7000-20GQ-NPC) | The session capacity for these two 20Gbps
Network Processing Cards changed from 4 million sessions per NPC
to 3.2 million sessions per NPC on firewalls running a PAN-OS 9.0
or later release. |
PA-7000 Series Firewall Memory Limit
for the Management Server | As of PAN-OS 9.0.10, the PA-7000 Series
firewalls have new CLI commands to enable or disable resource control
groups and new CLI commands to set an upper memory limit of 8G on
a process (mgmtsrvr). To enable resource-control
groups, use: debug software resource-control enableTo
disable resource-control groups, use: debug software resource-control disableTo
set the memory limit, use: debug management-server limit-memory enableTo
remove the memory limit, use: debug management-server limit-memory disableReboot
the firewall to ensure the memory limit change takes effect. |
Refresh of Default Trusted CAs | The certificate authorities (CAs) that the
firewall trusts by default are updated; new trusted root CAs are
added and expired CAs are removed. To view and manage the lists
of CAs that the firewall trusts by default, select DeviceCertificate ManagementCertificatesDefault Trusted Certificate Authorities. |
VM-50 and VM-50 Lite Firewalls | The minimum memory requirement has changed from
4GB to 4.5GB for the VM-50 Lite and from 4.5GB to 5.5GB for the
VM-50 in PAN-OS 9.0. You cannot upgrade the
VM-50 Lite without allocating additional memory. If you upgrade
the VM-50 with less than 5.5GB memory, it will default to the system capacities
(number of sessions, rules, security zones, address objects, etc)
associated with the VM-50 Lite. See Upgrade/Downgrade Considerations for
more information. |
VM-Series Plugin | Beginning with PAN-OS 9.0, the built-in
VM-Series plugin manages interactions between the VM-Series firewalls
and the supported public and private cloud platforms. Also, the bootstrap package now
has an optional /plugins folder for upgrading
a plugin. To configure plugin integrations, select DeviceVM-Series. In
Panorama™ 9.0 the VM-Series plugin is available in PanoramaPlugins but
must be manually installed. |
VXLAN Tunnel Content Inspection | In PAN-OS 8.1 and earlier releases, the
firewall used the UDP Session key to create UDP sessions for all tunnel content inspection protocols.
It is a six-tuple key (zone, source IP, destination IP, protocol,
source port, and destination port), and it remains in use. PAN-OS
9.0 introduces the VNI Session key specifically for VXLAN tunnel content inspection.
The VNI Session key is a five-tuple key incorporating the zone,
source IP, destination IP, protocol, and the VXLAN Network Identifier
(VNI). By default, VXLAN tunnels now automatically use the VNI
Session key to create a VNI Session, which is visible in logs. If
you prefer to use the UDP Session key for VXLAN (as you did in previous
releases), you can define a custom application for
VXLAN and use an application override policy to
invoke your custom application. |
Panorama Commit and push operations |
|
Security Group Tag (SGT) Ethertype Support | If you're using Security Group Tags (SGTs)
to control user and device access in a Cisco Trustsec network, inline
firewalls in Layer 2 or Virtual Wire mode now inspect and provide
threat prevention for the tagged traffic by default. Before PAN-OS
9.0, a firewall in Layer 2 or virtual wire mode could allow SGT
traffic but did not process and inspect it. The firewall
does not enforce security policy based on SGTs. |
Authentication Policy | In PAN-OS 8.1 and earlier, administrators
needed to add a rule to decrypt TLS sessions to apply authentication
policy. In PAN-OS 9.0, the firewall applies the authentication policy
without needing to decrypt the session. |
IP Address Registration and Dynamic Address
Groups | In PAN-OS 8.1 and earlier, it could take
up to 60 seconds to register an IP address, and the associated tags,
and update the membership information for a dynamic address group
(DAG). In PAN-OS 9.0, IP address registration occurs in real time.
Any policy matches for updates on a registered IP address (IP-tag
mapping) are reflected only in new sessions. Any existing sessions
are reevaluated for a policy match when you perform a commit or
the App-ID™ on the session changes. |
URL Filtering Overrides | In earlier release versions, URL category
overrides received priority enforcement over custom URL categories.
However, override priority goes away in PAN-OS 9.0 with the conversion
of URL category overrides to custom URL categories. After you upgrade,
the firewall enforces the new custom URL category using the Security
policy rule with the strictest URL Filtering profile action. From
most to least strict, possible URL Filtering profile actions are: block,
override, continue, alert, and allow. As a result, overrides with
the allow action might be blocked after being converted to custom
URL categories. For more details on this, review PAN-OS 9.0 Upgrade and Downgrade
Considerations. Workaround:
The Overrides tab
objects are removed and Custom URL Category objects
are created for firewalls running PAN-OS 8.1 or earlier releases
when managed by a Panorama management server that is upgraded to
PAN-OS 9.0. |
CLI Commands for the Option to Hold Web
Requests During URL Category Lookup (PAN-OS 9.0.4
or later 9.0 releases) | The CLI commands for this feature are now the following:
|
URL Filtering CLI Change | You no longer need to download a predefined
set of URLs after activating a URL Filtering license, so the following
commands associated with that operation have been removed:
|
SAML Authentication (PAN-OS
9.0.9 and later 9.0 releases) | To ensure your users can continue to authenticate successfully
with SAML Authentication, you must:
|
SIP TCP Cleartext | The cleartext proxy is enabled by default for
SIP TCP sessions when a segmented SIP header is detected. This helps
with the correct reassembly and ordering of TCP segments for proper
ALG operation. You can disable this option if
SIP message sizes are generally smaller than the MSS and when the
SIP messages fit within a single segment, or if you need to ensure
TCP proxy resources are reserved for SSL forward proxy or HTTP/2. |
Resolution of FQDN Address Objects | Firewalls started using DNSProxy daemon
instead of Linux network stack to resolve FQDNs, and therefore there
is a difference in the ability of Panorama and firewalls to resolve
FQDNs. Both Panorama and firewalls require that when you create
an address object using an FQDN, you enter an FQDN and not just
a hostname. |
URL Filtering PAN-DB Updates | In PAN-OS 9.0 and later, firewalls no longer
download a PAN-DB seed database or incremental database updates;
instead, firewalls populate the cache as URL queries are made. In
an active/passive HA environment, as database updates are no longer applicable,
only the active firewall connects to PAN-DB to perform URL lookups.
Should a failure occur, the passive firewall transitions to an active state,
and will establish a connection to PAN-DB. |
Forwarded Emails for System Events | After a successful upgrade to PAN-OS 9.0,
the subject line for system events forwarded to an email address have
a maximum of 99 characters. This means that email subject lines
that exceed 95 characters are truncated with an ellipsis (...)
to indicate there is additional text to review. |
View Rulebase as Groups | On upgrade to PAN-OS 9.0, View
Rulebase as Groups replaces the Tag Browser in the Policies tab. In
this view, select the group tag to view the policy rules grouped
by the selected tag. |


