Prisma Access
Configure Routing Preferences
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma Access Docs
-
- 6.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 6.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 4.2 Preferred
- 4.1 Preferred
- 4.0 Preferred
- 3.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 2.2 Preferred
-
-
- 4.0 & Later
- Prisma Access China
-
-
Configure Routing Preferences
Learn how to configure routing preferences for Prisma
Access service connections.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
To enable routing preferences, complete the
following steps.
To configure these routing preferences, you must use BGP
routing and not static routing for your service connections.
- Configure your service connection.(Optional) Select the routing to use for your service connections.
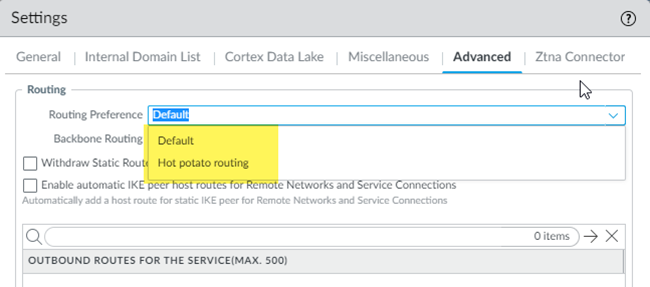
- From the Panorama that manages Prisma Access, go to PanoramaCloud ServicesConfigurationService Setup and click the gear to edit the Settings.In the Advanced settings, select your Routing Preference (either Default or Hot Potato).
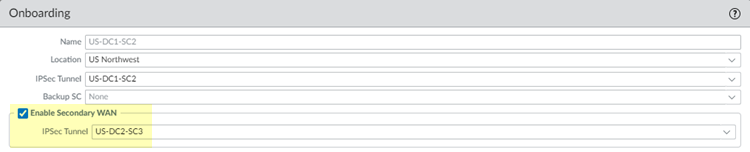
![]() (Optional, Hot Potato Routing Deployments Only) To specify a preferred service connection to use if a link fails, configure a Backup SC when you configure a service connection.You can select any service connection that you have already added. Prisma Access uses the Backup SC you select as the preferred service connection in the event of a link failure. Selecting a backup service connection can prevent asymmetric routing issues if you have onboarded more than two service connections. This choice is available in Hot potato routing mode only.
(Optional, Hot Potato Routing Deployments Only) To specify a preferred service connection to use if a link fails, configure a Backup SC when you configure a service connection.You can select any service connection that you have already added. Prisma Access uses the Backup SC you select as the preferred service connection in the event of a link failure. Selecting a backup service connection can prevent asymmetric routing issues if you have onboarded more than two service connections. This choice is available in Hot potato routing mode only.- Go to PanoramaCloud ServiceConfigurationService ConnectionSelect the service connection to configure, or Add a new one.Select a service connection to use as the preferred backup (Backup SC).
![]() Commit your changes to Panorama and push the configuration changes to Prisma Access.
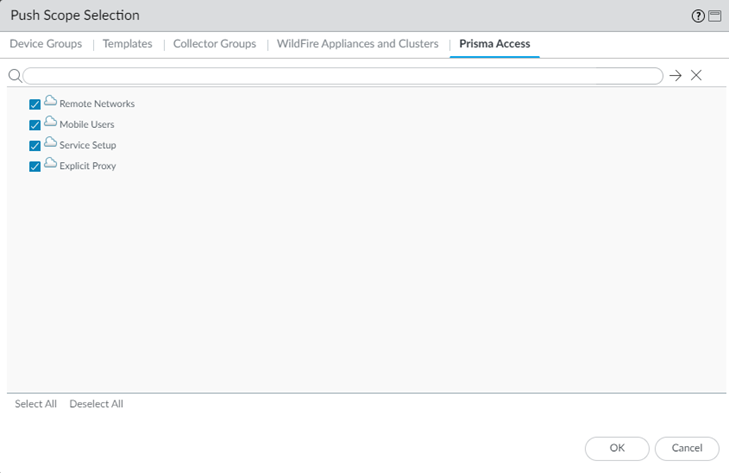
Commit your changes to Panorama and push the configuration changes to Prisma Access.- Click CommitCommit and Push.Edit Selections and, in the Prisma Access tab, make sure that Service Setup is selected in the Push Scope, then click OK.
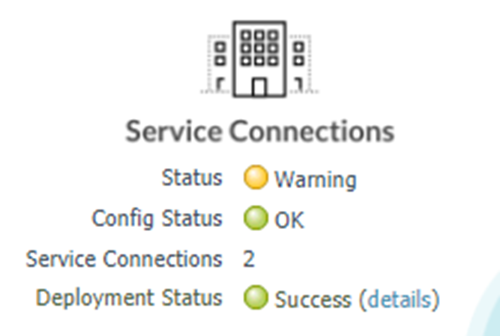
![]() Click Commit and Push.Verify that your service connection is up by selectin Panorama > Cloud Services > Status > Status and checking that its Status is OK.The Deployment Status area allows you to view the progress of onboarding and deployment jobs before they complete, as well as see more information about the status of completed jobs.
Click Commit and Push.Verify that your service connection is up by selectin Panorama > Cloud Services > Status > Status and checking that its Status is OK.The Deployment Status area allows you to view the progress of onboarding and deployment jobs before they complete, as well as see more information about the status of completed jobs.![]() If the status is not OK, hover over the Status icon to view any errors.To see a graphical representation of the service connection along with status details, select Service Connection on the Monitor tab.
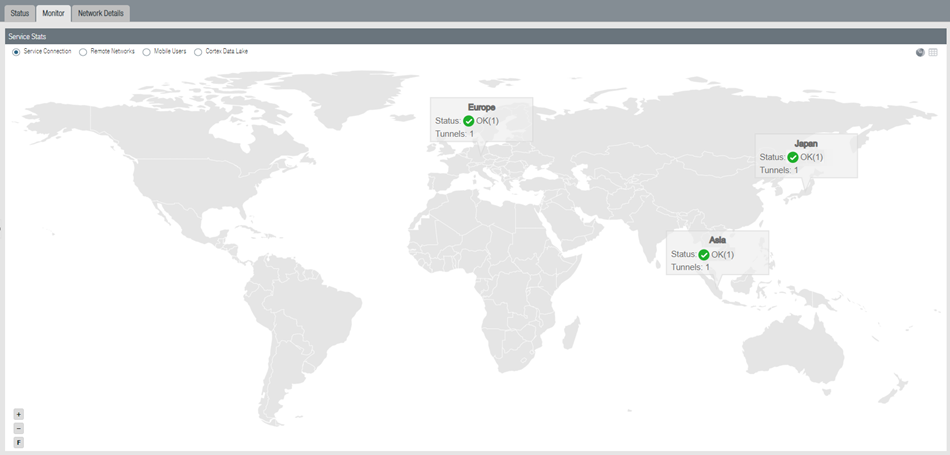
If the status is not OK, hover over the Status icon to view any errors.To see a graphical representation of the service connection along with status details, select Service Connection on the Monitor tab.![]() Select a region to get more detail about that region.
Select a region to get more detail about that region.![]() Click the tabs below the map to see additional information about the service connections.Status tab:
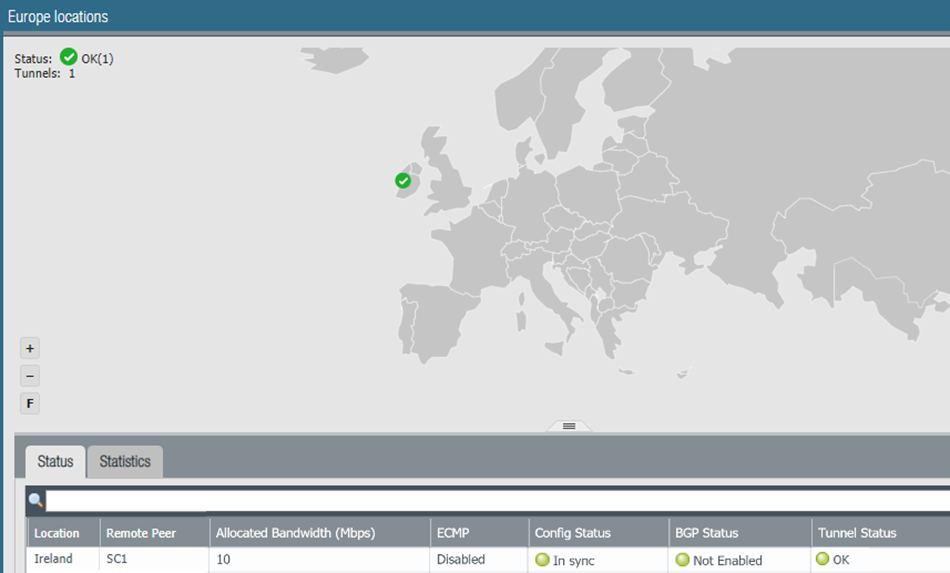
Click the tabs below the map to see additional information about the service connections.Status tab:- Location—The location where your service connection is deployed.
- Remote Peer—The corporate location to which this s service infrastructure is setting up an IPSec tunnel.
- Allocated Bandwidth—The number of service connections you have allocated multiplied by 300 Mbps.This number does not reflect the available service connection bandwidth.While each service connection provides approximately 1 Gbps of throughput, the actual throughput is dependent on several factors, including:
- Traffic mix (for example, frame size)
- Latency and packet loss between the service connection and the headquarters location or data center
- Service provider performance limits
- Customer termination device performance limits
- Other customer data center traffic
- ECMP—If you have equal cost multipath (ECMP) configured for this service connection. Since ECMP is not used for service connections, this status is Disabled.
- Config Status—The status of your last configuration push to the service. If the local configuration and the configuration in the cloud match, the Config Status is In sync. If you have made a change locally, and not yet pushed the configuration to the cloud, this may display the status Out of sync. Hover over the status indicator for more detailed information. After committing and pushing the configuration to Prisma Access, the Config Status changes to In sync.
- BGP Status—Displays information about the BGP state between the firewall or router at your corporate/headquarters location and Prisma Access where the service connection is established. Although you might temporarily see the status pass through the various BGP states (Idle, Active, Open send, Open pend, Open confirm, most commonly, the BGP status shows:
- Connect—The router at your data center/headquarters is trying to establish the BGP peer relationship with Prisma Access.
- Established—The BGP peer relationship has been established.
This field will also show if the BGP connection is in an error state:- Warning—There has not been a BGP status update in more than eight minutes. This may indicate an outage on the firewall.
- Error—The BGP status is unknown.
- Tunnel Status—The operational status of the connection between Prisma Access and your service connection.
Statistics tab:- Location—The location where your service connection is deployed.
- Remote Peer—The corporate location to which the service connection is setting up an IPSec tunnel.
- Ingress Bandwidth (Mbps)—The bandwidth from the HQ/data center location to Prisma Access.
- Ingress Peak Bandwidth (Mbps)—The peak load from the HQ/data center location into the cloud service.
- Egress Bandwidth (Mbps)—The bandwidth from Prisma Access into the HQ/data center location.
- Egress Peak Bandwidth (Mbps)—The peak load from Prisma Access into the HQ/data center location.
- QoS—Select this button to display a graphic chart that shows a real-time and historical QoS statistics, including the number of dropped packets per class. This chart displays only for service connections or remote network connections that have QoS enabled.
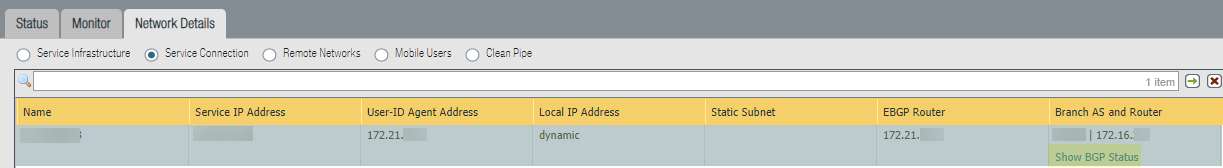
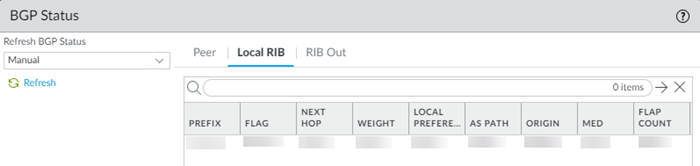
If you configured BGP, you can check its status by selecting PanoramaCloud ServicesStatusNetwork DetailsService ConnectionShow BGP Status.![]() The BGP Status dialog displays. This table provides you with the following information:
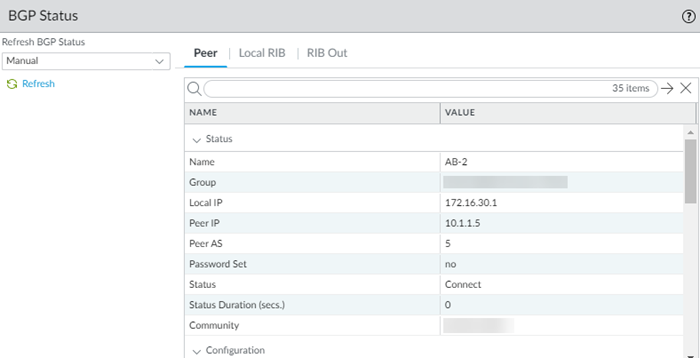
The BGP Status dialog displays. This table provides you with the following information:- Peer—Routing information for the BGP peer, including status, total number of routes, configuration, and runtime statistics and counters. The total number of routes display in the bgpAfiIpv4-unicast Counters area, in the Incoming Total and Outgoing Total fields.
![]()
- Local RIB—BGP routes that Prisma Access uses locally. Prisma Access selects this information from the BGP RIB-In table, which stores the information sent by neighboring networking devices, applies local BGP import policies and routing decisions, and stores the Local RIB information in the Routing Information Base (RIB).Note that only the first 256 entries are shown. To view additional entries, enter a subnet or IP address in the Filter field and click Apply Filter to view a subset of the routing entries up to a maximum of 256.
![]()
- RIB Out—Routing information that Prisma Access advertises to its peers through BGP update messages.