Advanced Threat Prevention Powered by Precision AI®
View Threat Logs (Cloud Management)
Table of Contents
View Threat Logs (Cloud Management)
- Use the credentials associated with your Palo Alto Networks support account and log in to the Strata Cloud Manager on the hub.For more information on using Activity dashboards, refer to the Log Viewer.Filter threat logs based on the Threat Category or Subtype in Prisma Access.
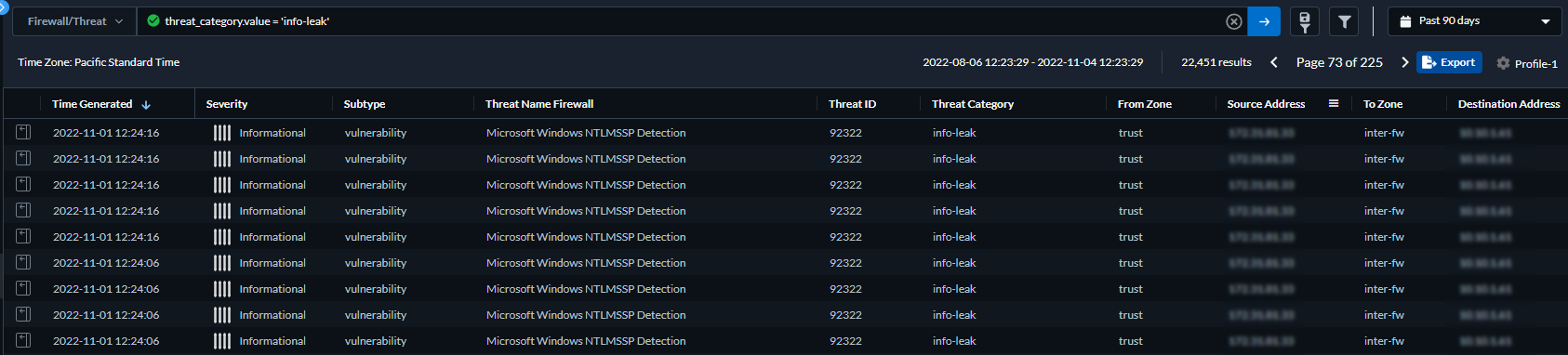
- Select Log Viewer.Change the log type to be searched to Threat.Create a search filter using one the threat signature subtypes used by the Antivirus, Anti-spyware, or Vulnerability Protection profiles (antivirus, spyware, and vulnerability, respectively) or based on the threat category using the query builder. For example, you can use sub_type.value = 'spyware' to view logs for threats that have been determined to be spyware. To search for other subtypes, replace spyware in the above example with another supported subtype (vulnerability or spyware). You can also search based on a specific Threat Category, such as an info-leak vulnerability by using the following query threat_category.value = 'info-leak'. For a list of valid categories you can use, refer to Threat Signature Categories. Adjust the search criteria as necessary for your search, including additional query parameters (such as the severity level and action) along with a date range.
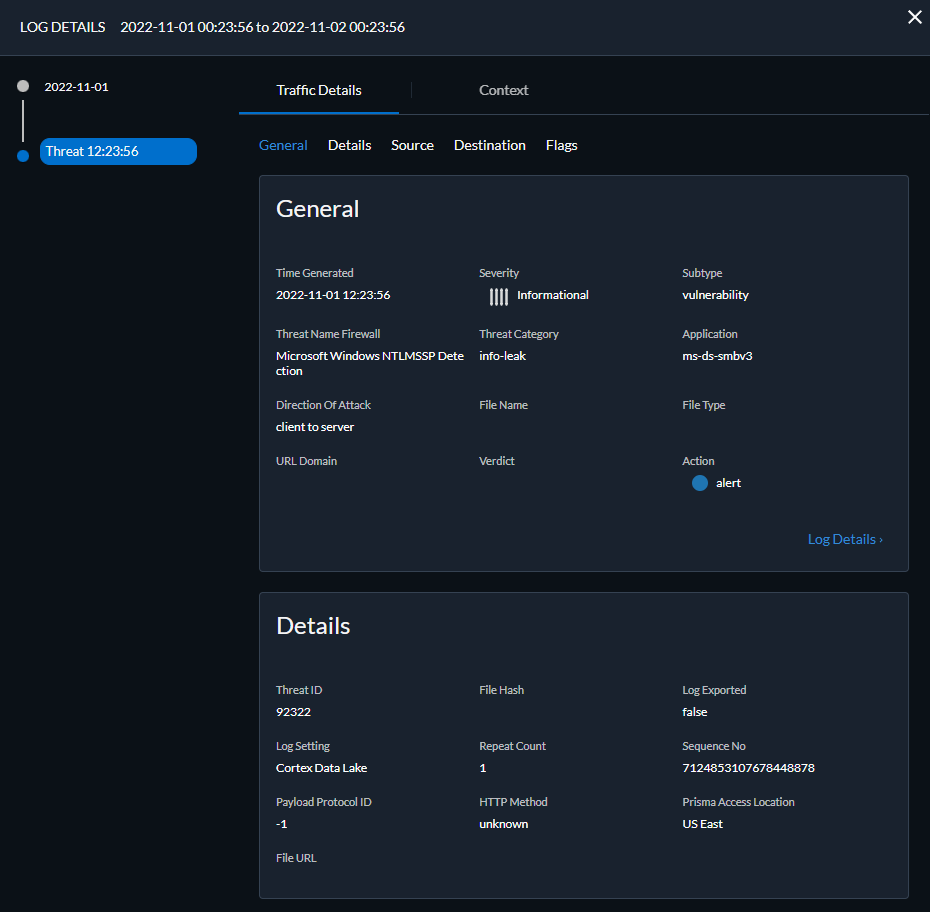
![]() Run the query after you have finished assembling your filters.Select a log entry from the results to view the log details.
Run the query after you have finished assembling your filters.Select a log entry from the results to view the log details.![]() The threat Category is displayed in the Details pane of the detailed log view. Other relevant details about the threat are displayed in their corresponding windows.Filter Threat logs by threat [categories] that have been detected using inline cloud analysis (spyware).HTTP-based C2 traffic that was originally categorized with the threat name Inline Cloud Analyzed HTTP Command and Control Traffic Detection and is associated with multiple Threat IDs, is now separated into three unique threat names to correspond to the unique Threat IDs and more accurately describe the detections made by Advanced Threat Prevention: Evasive HTTP C2 Traffic Detection (Threat ID: 89950), Evasive Cobalt Strike C2 Traffic Detection (Threat ID: 89955, 89956, and 89957), and Evasive Empire C2 Traffic Detection (Threat ID: 89958).HTTP-based C2 traffic logs generated prior to December 11, 2023 will continue to be categorized with the threat name Inline Cloud Analyzed HTTP Command and Control Traffic Detection.
The threat Category is displayed in the Details pane of the detailed log view. Other relevant details about the threat are displayed in their corresponding windows.Filter Threat logs by threat [categories] that have been detected using inline cloud analysis (spyware).HTTP-based C2 traffic that was originally categorized with the threat name Inline Cloud Analyzed HTTP Command and Control Traffic Detection and is associated with multiple Threat IDs, is now separated into three unique threat names to correspond to the unique Threat IDs and more accurately describe the detections made by Advanced Threat Prevention: Evasive HTTP C2 Traffic Detection (Threat ID: 89950), Evasive Cobalt Strike C2 Traffic Detection (Threat ID: 89955, 89956, and 89957), and Evasive Empire C2 Traffic Detection (Threat ID: 89958).HTTP-based C2 traffic logs generated prior to December 11, 2023 will continue to be categorized with the threat name Inline Cloud Analyzed HTTP Command and Control Traffic Detection.- Select Log Viewer.Change the log type to be searched to Threat.Create a search filter using a threat category used exclusively by Inline Cloud Analysis (spyware): threat_category.value = 'inline-cloud-c2'. You can further constrain the search by cross-referencing a Threat-ID value that corresponds to a specific C2 type. For example, threat_category.value = 'inline-cloud-c2' AND Threat ID = 89958, whereby 89958 indicates the Threat ID of evasive empire C2 traffic.Select a log entry to view the details of a detected C2 threat.The threat Category is displayed under the General pane of the log details. C2 threats that have been detected using inline cloud analysis have a threat category of inline-cloud-c2. You can cross-reference the Threat ID value in the Details pane to determine the specific type of C2 that has been detected.Filter Threat logs by threat [categories] that have been detected using inline cloud analysis (vulnerability).
- Select Log Viewer.Change the log type to be searched to Threat.Create a search filter using a threat category used exclusively by Inline Cloud Analysis (vulnerability): threat_category.value = 'inline-cloud-exploit'.Select a log entry to view the details of the detected command injection and SQL injection vulnerabilities. Inline exploit (SQL injection) threats have an ID of 99950 while inline exploit (command injection) threats have an ID of 99951.