Download PDF
GlobalProtect
Deploy GlobalProtect Credential Provider Settings in the Windows Registry
Table of Contents
Deploy GlobalProtect Credential Provider Settings in the Windows Registry
You can deploy GlobalProtect credential provider settings in the Windows Registry to
delay or enforce its sign-in request.
You can deploy the GlobalProtect credential
provider settings to delay the GlobalProtect credential provider
Windows sign-in request or to enforce the GlobalProtect credential
provider as the default sign-in option for Windows 10 by using the
Windows Registry.
- Delay the GlobalProtect credential provider Windows sign-in request.Establishing the GlobalProtect tunnel before Windows login can be useful in certain situations. For example, you may want to enforce the Windows device to synchronize data with the Active Directory or want to delay the GlobalProtect credential provider Windows sign-in request.You can configure the amount of time (in seconds) that the GlobalProtect credential provider waits for the tunnel to be established before submitting a Windows sign-in request when single sign on (SSO) is enabled. By default, the GlobalProtect Credential Provider Support to Delay Windows Login Before Establishing the Tunnel Connection feature is disabled and the GlobalProtect credential provider submits the sign-in requests without any delay.
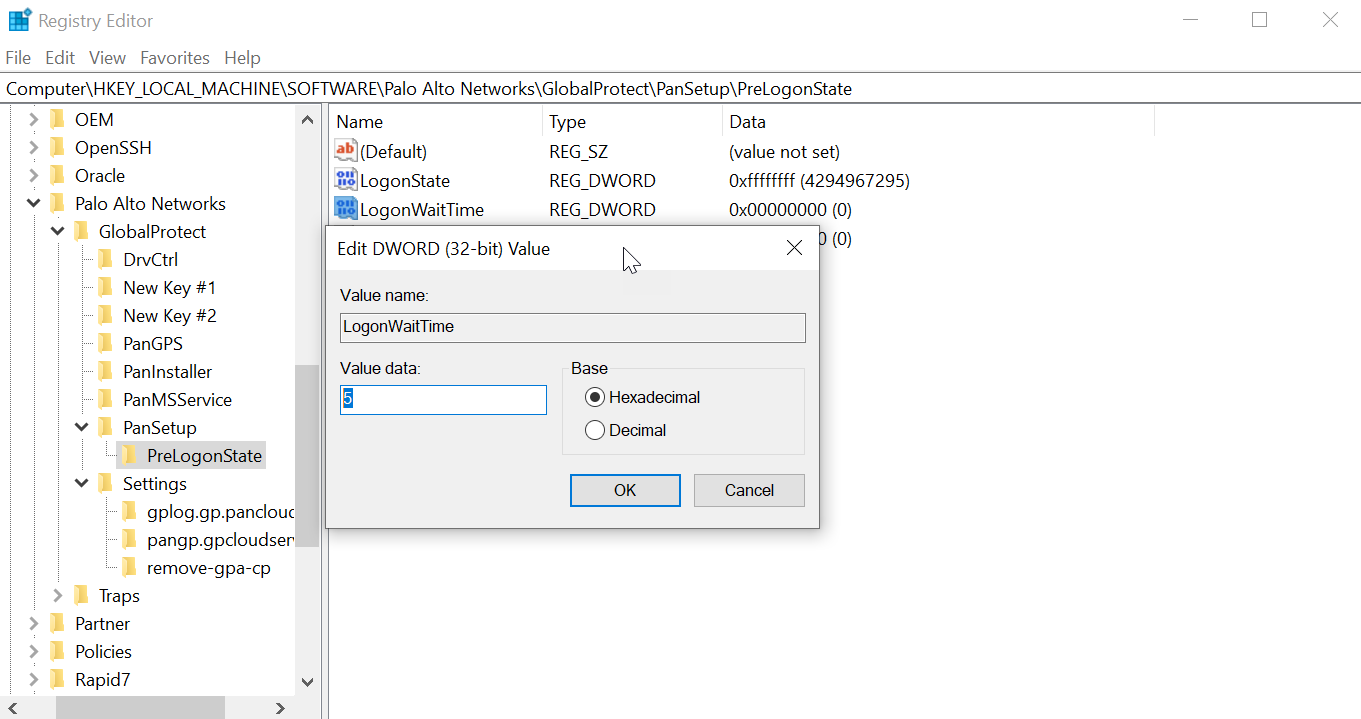
- From the command prompt, enter the regedit command to open the Windows Registry Editor.In the Windows Registry, go to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Palo Alto Networks\GlobalProtect\PanSetupRight-click PreLogonState and then select NewDWORD (32-bit) Value.Right-click New Value #1 and then select Rename.Enter LogonWaitTime. Right-click LogonWaitTime and then select Modify. In the Value Data field, set the number of seconds (range is 5-30) for end users to wait to log in to Windows before establishing a tunnel connection. Click OK.
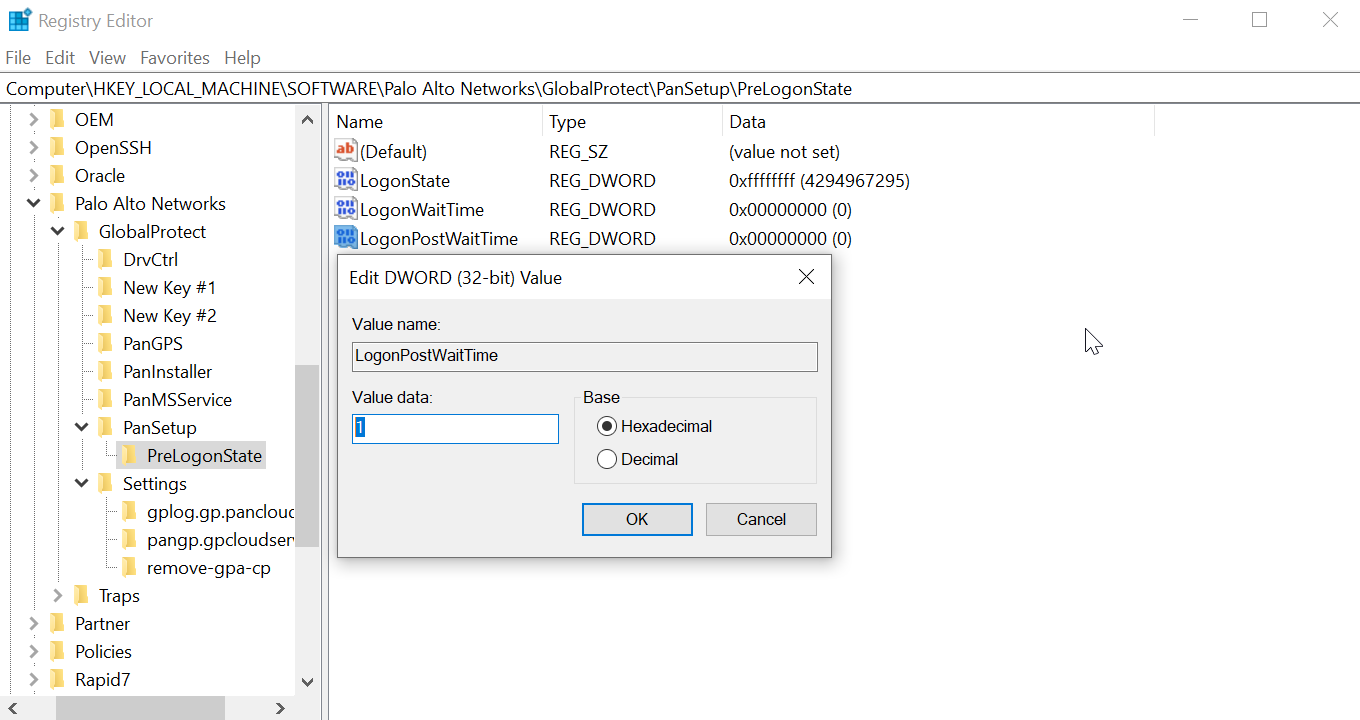
![]() Repeat substeps 1, 2, and 3 to delay the GlobalProtect credential provider from submitting the Windows sign-in request after the tunnel is established.Enter LogonPostWaitTime. Right-click LogonPostWaitTime and then select Modify. In the Value Data field, set the number of seconds (range is 3-10) for end users to wait to log in to Windows. Click OK.You are required to first enter the amount of time (in seconds) for LogonWaitTime, and then enter the amount of time (in seconds) for LogonPostWaitTime.
Repeat substeps 1, 2, and 3 to delay the GlobalProtect credential provider from submitting the Windows sign-in request after the tunnel is established.Enter LogonPostWaitTime. Right-click LogonPostWaitTime and then select Modify. In the Value Data field, set the number of seconds (range is 3-10) for end users to wait to log in to Windows. Click OK.You are required to first enter the amount of time (in seconds) for LogonWaitTime, and then enter the amount of time (in seconds) for LogonPostWaitTime.![]() Enforce GlobalProtect credential provider as the default sign-in option for Windows 10.When GlobalProtect SSO is enabled on Windows devices, users can have more than one sign-in option in addition to using the GlobalProtect credential provider options such as a third-party credential, smart card, Windows Hello PIN, Windows Hello Password, or Windows Hello Fingerprint. Users can use any of these sign-in options to sign in to their Windows device and set it as the default sign-in option at the next Windows login making GlobalProtect SSO unavailable. Users must manually switch to the GlobalProtect credential provider again to enable GlobalProtect SSO. When the GlobalProtect credential provider is enabled as the default sign-in option even when users can login with any other sign-in option, the GlobalProtect credential provider sign-in option is selected at the next Windows login and for subsequent logins.When GlobalProtect is installed on Windows devices, users cannot log in to the device using the User Principal Name (UPN)- for example, username@domain- when the GlobalProtect credential provider is selected and the device is offline.Follow these guidelines when you are enforcing the GlobalProtect credential provider to be the default-sign option on Windows devices:
Enforce GlobalProtect credential provider as the default sign-in option for Windows 10.When GlobalProtect SSO is enabled on Windows devices, users can have more than one sign-in option in addition to using the GlobalProtect credential provider options such as a third-party credential, smart card, Windows Hello PIN, Windows Hello Password, or Windows Hello Fingerprint. Users can use any of these sign-in options to sign in to their Windows device and set it as the default sign-in option at the next Windows login making GlobalProtect SSO unavailable. Users must manually switch to the GlobalProtect credential provider again to enable GlobalProtect SSO. When the GlobalProtect credential provider is enabled as the default sign-in option even when users can login with any other sign-in option, the GlobalProtect credential provider sign-in option is selected at the next Windows login and for subsequent logins.When GlobalProtect is installed on Windows devices, users cannot log in to the device using the User Principal Name (UPN)- for example, username@domain- when the GlobalProtect credential provider is selected and the device is offline.Follow these guidelines when you are enforcing the GlobalProtect credential provider to be the default-sign option on Windows devices:- While the GlobalProtect app is installed or SSO is enabled, the GlobalProtect credential provider is set as the default sign-in option for all users even when the MakeGPCPDefault setting is disabled.
- When SSO is enabled and the MakeGPCPDefault setting is enabled, users can use any sign-in options such as a third-party credential provider, smart card, Windows Hello PIN, Windows Hello password, or Windows Fingerprint to sign in to their Windows device. Regardless of the sign-in option selected, the GlobalProtect credential provider will be used as the default sign-in option at the next Windows login.
- When SSO is enabled and the MakeGPCPDefault setting is disabled or empty, the user selected sign-in option will be used as the default at the next Windows login.
- When SSO is disabled, the GlobalProtect credential provider is unavailable. The Windows default sign-in option will work as expected.
- The Enforce GlobalProtect Credential Provider as the Default Sign-In for Windows 10 feature does not support the Other user login option. You can configure the Other user login option by using the Group Policy Object (GPO) on the Windows device.
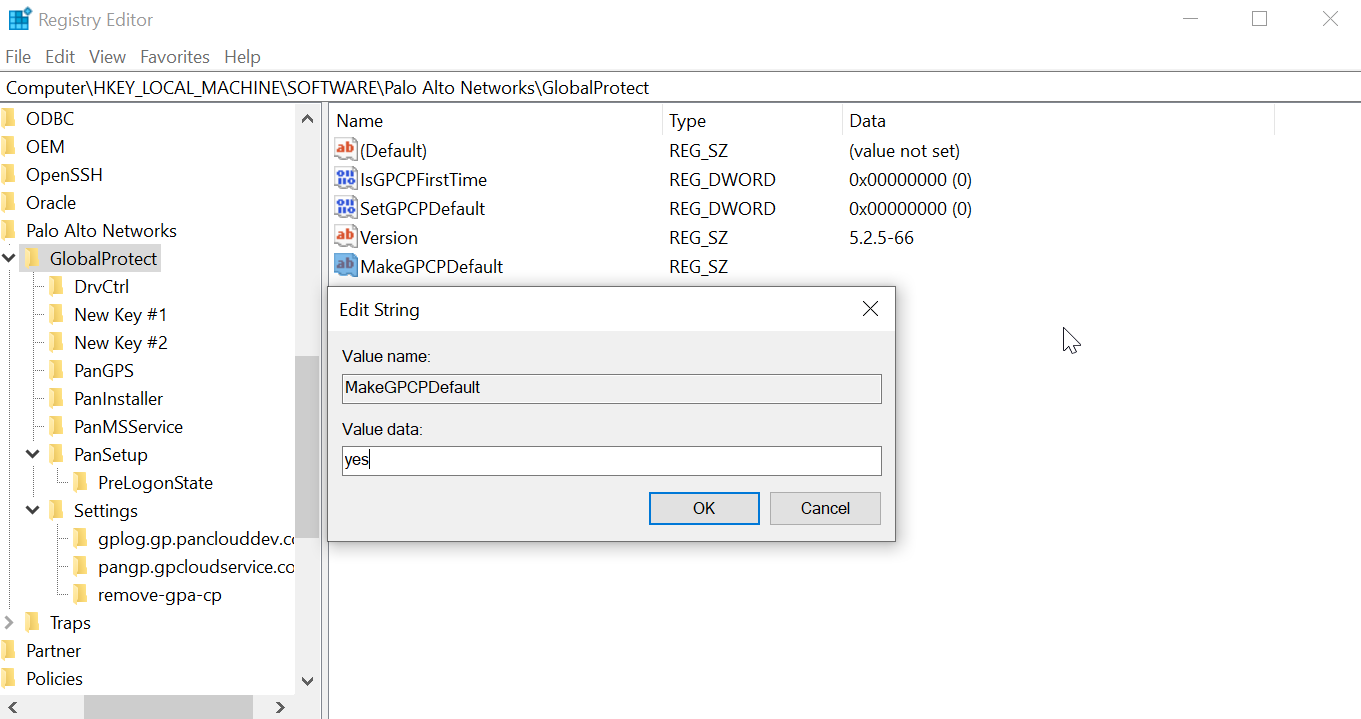
- From the command prompt, enter the regedit command to open the Windows Registry Editor.In the Window Registry, go to:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Palo Alto Networks\GlobalProtectRight-click the GlobalProtect folder, then select NewString Value to add a new string value.Enter the MakeGPCPDefault string value. Right-click MakeGPCPDefault and then select Modify.In the Value data field, enter yes to enable the GlobalProtect credential provider to be the default sign-in option at the next Windows login. If you set the Value data to no, the MakeGPCPDefault setting is disabled and the user selected sign-in option will be used as the default at the next Windows login. Click OK.
![]()