Download PDF
GlobalProtect
Mixed Internal and External Gateway Configuration
Table of Contents
Mixed Internal and External Gateway Configuration
In a GlobalProtect mixed internal and external
gateway configuration, you can configure separate gateways for VPN
access and for access to your sensitive internal resources. With
this configuration, the GlobalProtect app performs internal host
detection to determine if it is on the internal or external network.
If the app determines that it is on the external network, it attempts
to connect to the external gateways listed in its client configuration,
and then it establishes a connection to the gateway with the highest
priority and shortest response time.
If you configure
all external gateways as manual-only gateways but the GlobalProtect
connect method as User-Logon (Always On) or Pre-Logon
(Always On), the GlobalProtect app does not automatically
connect to any external gateways. GlobalProtect remains in the Not
Connected state until the external user establishes a gateway connection
manually. This behavior enables you to deploy GlobalProtect to derive User-ID
for internal users while supporting On-Demand VPN behavior
for external users.
Because security policies are defined
separately on each gateway, you have granular control over the resources
to which your external and internal users have access. In addition,
you also have granular control over the gateways to which users have
access by configuring the portal to deploy different client configurations
based on user/group membership or HIP profile matching.
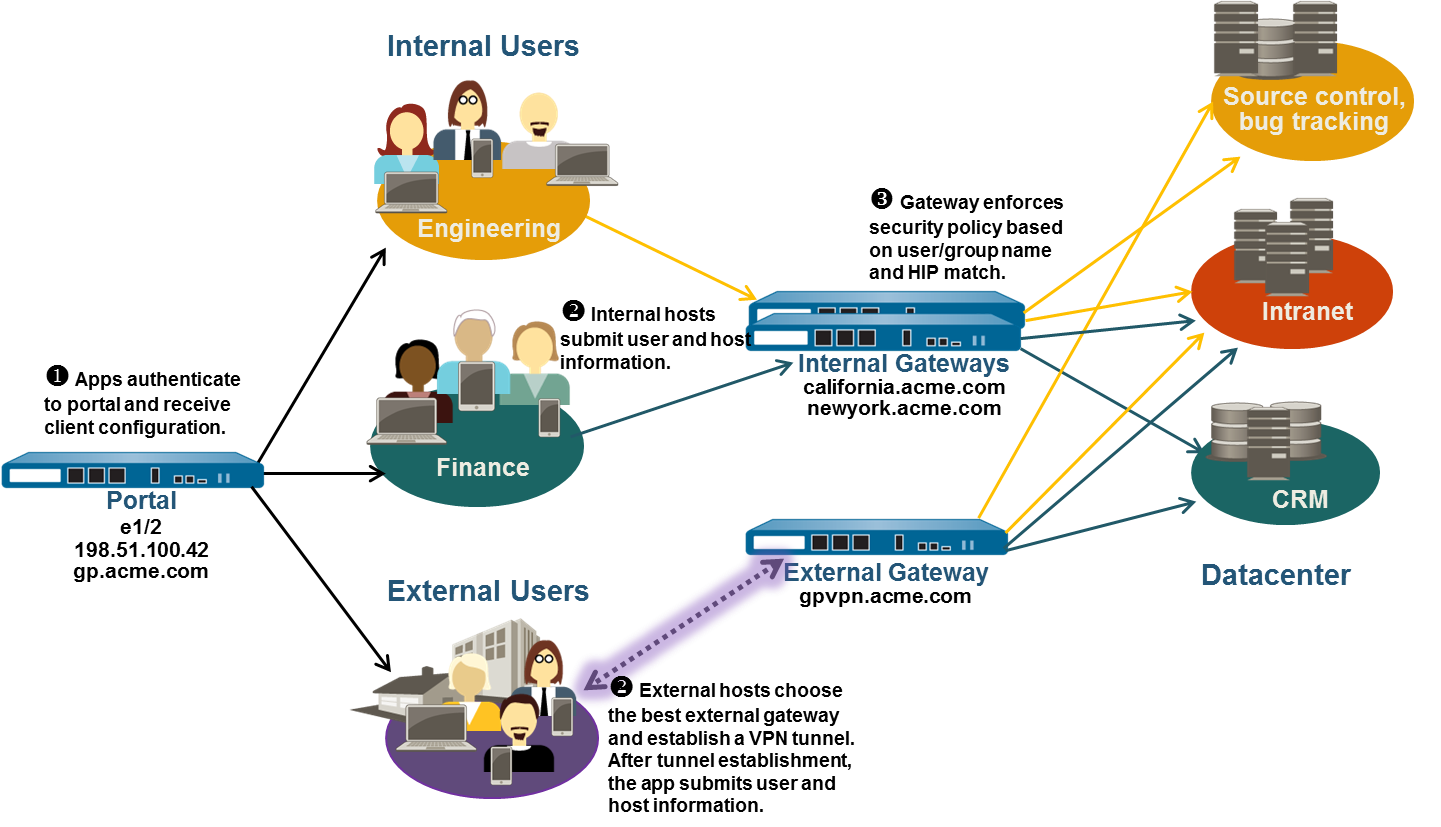
In
this example, the portals and all three gateways (one external and
two internal) are deployed on separate firewalls. The external gateway
at gpvpn.acme.com provides remote VPN access to the corporate network,
while the internal gateways provide granular access to sensitive
datacenter resources based on group membership. In addition, HIP
checks are used to ensure that hosts accessing the datacenter are
up-to-date on security patches.
Use
the following steps to configure a mix of internal and external
GlobalProtect gateways.
- Create Interfaces and Zones for GlobalProtect.In this configuration, you must set up interfaces on the firewall hosting a portal and each firewall hosting a gateway.Do not attach an interface management profile that allows HTTP, HTTPS, Telnet, or SSH on the interface where you have configured a GlobalProtect portal or gateway because this enables access to your management interface from the internet. Follow the Adminstrative Access Best Practices to ensure that you are securing administrative access to your firewalls in a way that will prevent successful attacks.Use the default virtual router for all interface configurations to avoid having to create inter-zone routing.On the firewall hosting the portal gateway (gp.acme.com):
- Select NetworkInterfacesEthernet and configure ethernet1/2 as a Layer 3 Ethernet interface with IP address 198.51.100.42. Assign it to the l3-untrust Security Zone and the default Virtual Router.
- Create a DNS “A” record that maps IP address 198.51.100.42 to gp.acme.com.
- Select NetworkInterfacesTunnel and Add the tunnel.2 interface. Assign it to a new Security Zone called corp-vpn and the default Virtual Router.
- Enable User Identification on the corp-vpn zone.
On the firewall hosting the external gateway (gpvpn.acme.com):- Select NetworkInterfacesEthernet and configure ethernet1/5 as a Layer 3 Ethernet interface with IP address 192.0.2.4. Assign it to the l3-untrust Security Zone and the default Virtual Router.
- Create a DNS “A” record that maps IP address 192.0.2.4 to gpvpn.acme.com.
- Select NetworkInterfacesTunnel and Add the tunnel.3 interface. Assign it to a new Security Zone called corp-vpn and the default Virtual Router.
- Enable User Identification on the corp-vpn zone.
On the firewall hosting the internal gateways (california.acme.com and newyork.acme.com):- Select NetworkInterfacesEthernet and configure a Layer 3 Ethernet interface with IP addresses on the internal network. Assign them to the l3-trust Security Zone and the default Virtual Router.
- Create a DNS “A” record that maps the internal IP addresses california.acme.com and newyork.acme.com.
- Enable User Identification on the l3-trust zone.
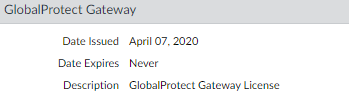
Purchase and install a GlobalProtect subscription for each firewall hosting a gateway (internal and external) if your end users will be using the GlobalProtect app on their mobile endpoints or if you plan on using HIP-enabled security policy.![]() After you purchase the GlobalProtect subscriptions and receive your activation code, install the GlobalProtect subscriptions on the firewalls hosting your gateways:
After you purchase the GlobalProtect subscriptions and receive your activation code, install the GlobalProtect subscriptions on the firewalls hosting your gateways:- Select DeviceLicenses.Select Activate feature using authorization code.When prompted, enter the Authorization Code and then click OK.Verify that the license and subscriptions were successfully activated.Contact your Palo Alto Networks Sales Engineer or Reseller if you do not have the required licenses. For more information on licensing, see About GlobalProtect Licenses.Obtain server certificates for the GlobalProtect portal and each GlobalProtect gateway.In order to connect to the portal for the first time, the endpoints must trust the root CA certificate used to issue the portal server certificate.You can use self-signed certificates on the gateways and deploy the root CA certificate to the apps in the client configuration. The best practice is to generate all of the certificates on firewall hosting the portal and deploy them to the gateways.The recommended workflow is as follows:
- On the firewall hosting the portal:
- Use the root CA on the portal to generate a self-signed server certificate. Repeat this step for each gateway.
On each firewall hosting an internal gateway:Define how you authenticate users to the portal and gateways.You can use any combination of certificate profiles and/or authentication profiles to ensure the security of your portal and gateways. Portals and individual gateways can also use different authentication schemes. See the following sections for step-by-step instructions:- Set Up External Authentication (authentication profile)
- Set Up Client Certificate Authentication (certificate profile)
- Set Up Two-Factor Authentication (token- or OTP-based)
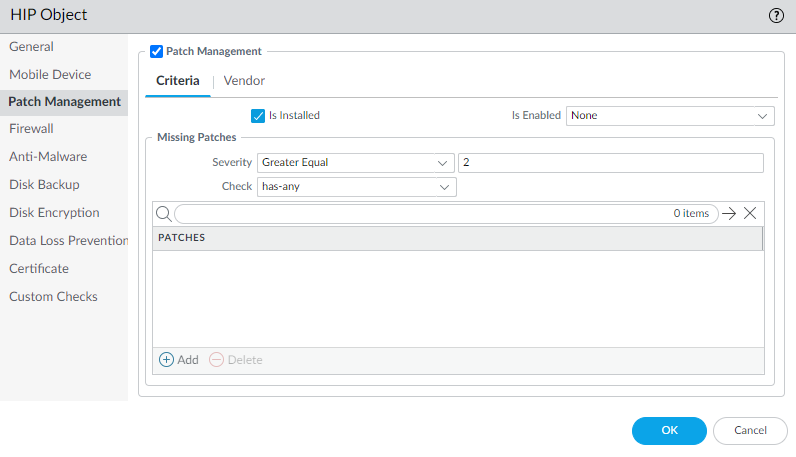
You must then reference the certificate profile and/or authentication profiles that you defined in your portal and gateway configurations.Create the HIP profiles you will need to enforce security policy on gateway access.See Host Information for more information on HIP matching.- Create the HIP objects to filter the raw host data collected by the app. For example, if you are interested in preventing users that are not up to date with required patches, you might create a HIP object to match on whether the patch management software is installed and that all patches with a given severity are up to date.
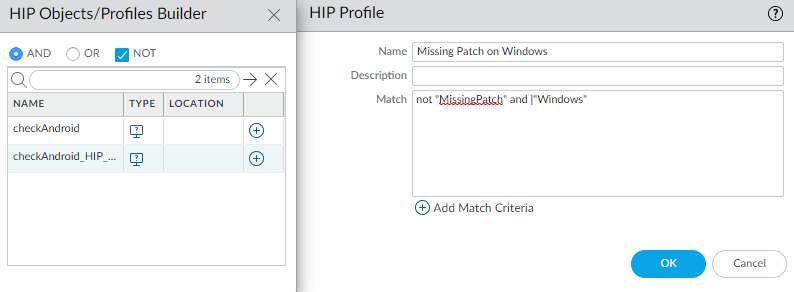
![]() Create the HIP profiles that you plan to use in your policies.For example, if you want to ensure that only Windows endpoints with up-to-date patches can access your internal applications, you might attach the following HIP profile to match hosts that do NOT have a missing patch:
Create the HIP profiles that you plan to use in your policies.For example, if you want to ensure that only Windows endpoints with up-to-date patches can access your internal applications, you might attach the following HIP profile to match hosts that do NOT have a missing patch:![]() Configure the internal gateways.Select NetworkGlobalProtectGateways and Add gateway configurations with the following settings:
Configure the internal gateways.Select NetworkGlobalProtectGateways and Add gateway configurations with the following settings:- Interface
- IP Address
- Server Certificate
- Authentication Profile and/or Configuration Profile
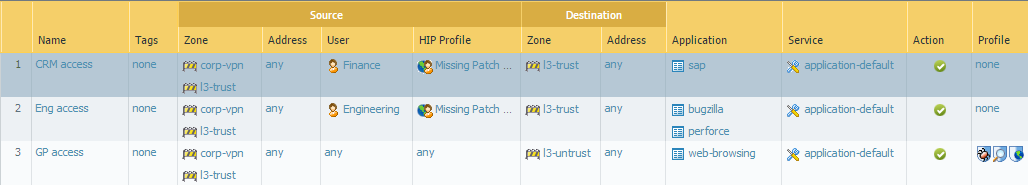
It's not necessary to configure the client authentication settings under the Authentication tab in the gateway (unless you want to set up HIP notifications) because tunnel connections are not required. See Configure a GlobalProtect Gateway for step-by-step instructions on how to configure a gateway.Configure the GlobalProtect Portals.Although this example shows how to create a single client configuration to be deployed to all apps, you could also create separate configurations for different uses and then deploy them based on user/group name and/or the endpoint operating system on which the app is running.Select NetworkGlobalProtectPortals and Add the following portal configuration:- Set Up Access to the GlobalProtect Portal:Interface—ethernet1/2IP Address—198.51.100.42Server Certificate—GP-server-cert.pem issued by GoDaddy with CN=gp.acme.comDefine the GlobalProtect Client Authentication Configurations:Internal Host Detection—enabledUse single sign-on—enabledConnect Method—User-logon (Always On)External Gateway Address—gpvpn.acme.comInternal Gateway Address—california.acme.com, newyork.acme.comUser/User Group—anyCommit the portal configuration.Deploy the GlobalProtect App Software.Select DeviceGlobalProtect Client.In this example, use the procedure to Host App Updates on the Portal.Create security policy rules on each gateway to safely enable access to applications for your VPN users.
- Create security policies (PoliciesSecurity) to enable traffic flow between the corp-vpn zone and the l3-trust zone.
- Create HIP-enabled and user/group-based policy rules to enable granular access to your internal datacenter resources.
- For visibility, create rules that allow all users web-browsing access to the l3-untrust zone using the default security profiles to protect you from known threats.
![]() Save the GlobalProtect configuration.Commit your portal and gateway configurations.
Save the GlobalProtect configuration.Commit your portal and gateway configurations.