IoT Security
Create IoT Security Users
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
IoT Security Docs
-
-
- Firewall Deployment Options for IoT Security
- Use a Tap Interface for DHCP Visibility
- Use a Virtual Wire Interface for DHCP Visibility
- Use SNMP Network Discovery to Learn about Devices from Switches
- Use Network Discovery Polling to Discover Devices
- Use ERSPAN to Send Mirrored Traffic through GRE Tunnels
- Use DHCP Server Logs to Increase Device Visibility
- Control Allowed Traffic for Onboarding Devices
- Support Isolated Network Segments
-
Create IoT Security Users
Create IoT Security users, assign user roles, and view users in the IoT Security
portal.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
When users log in to the IoT Security portal using single sign-on (SSO), they go
through a two-step process. In step 1, an SSO identity provider (IdP) authenticates
users by verifying their credentials. In step 2, users are authorized and provided
with a role to access IoT Security.
When users log in to the IoT Security portal using Palo Alto Networks SSO, their
credentials are verified against user accounts in the Customer Service Portal (CSP).
Then their user role is assigned according to the Identity & Access section of
the hub. User roles determine what they can see and do in the portal. These user
roles are referred to as “externally managed user roles” in contrast to “internally
managed user roles”, which are assigned in the IoT Security portal and are described
in a later section.
In addition, IoT Security also provides an option to verify users against an Active
Directory (AD) authentication system through SSO. In this case, user accounts are in
Active Directory, which verifies user credentials on behalf of IoT Security. You can
manage the role of a given user in two different ways, similar to the Palo Alto
Networks SSO: (1) managed internally by IoT Security or (2) managed externally by
Active Directory.
External roles are managed in the AD instead of the hub as done in the Palo Alto
Networks SSO option.
Because the user role can be managed in two different places, when users log in
through an SSO, IoT Security might find their external roles are different from
their internal roles. In such cases, whichever role is higher takes precedence.
Authenticate Users with the Palo Alto Networks SSO and Manage User Roles in the Hub
IoT Security supports role-based access control (RBAC) through App
Administrator, Instance Administrator, Owner, Administrator, and Read-only
roles. Creating users for the IoT Security application involves three steps:
- Create a user account in the Customer Support Portal
- Assign a user role in the hub
- (For Administrator and Read-only users) Allow access to all sites or a subset of sites
- Log in to the Customer Support Portal with superuser permissions, which allow you to create new user accounts.
- Click MembersCreate New User, enter the required information, and then Submit.A new user account is created and added to the account as a member. An email notification is sent to the new user with login credentials.
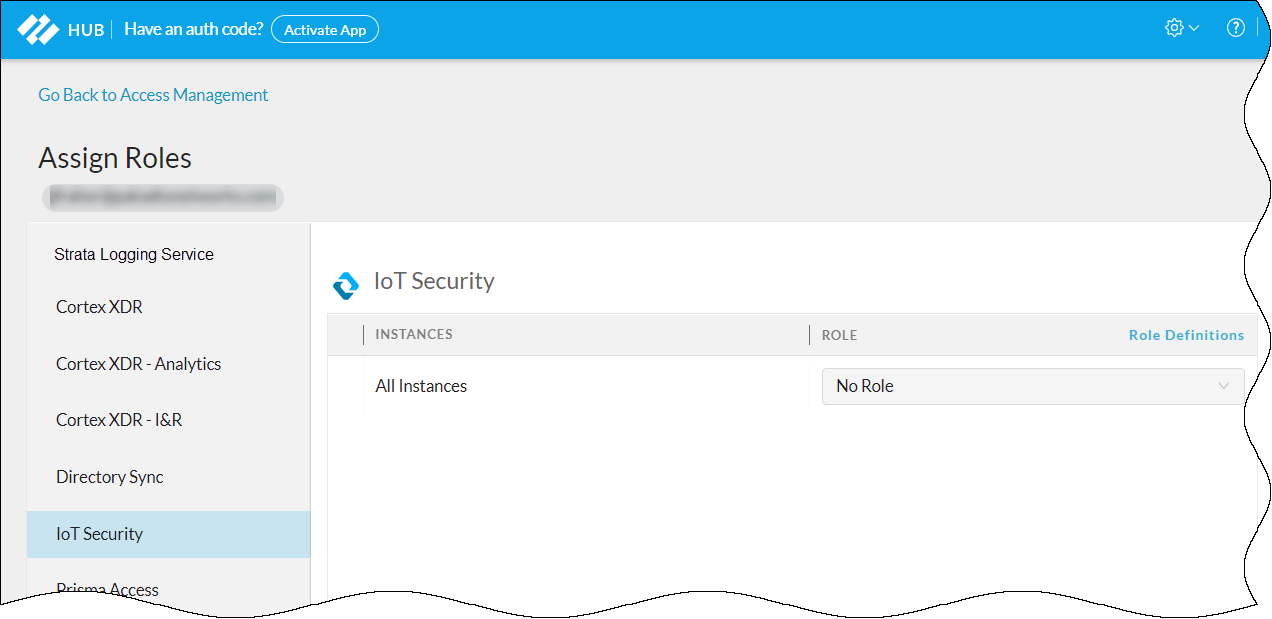
- Log in to the hub.
- Click the gear icon in the upper right of the hub landing page and then Access Management.
- Expand the IoT Security section in the left panel, select the IoT Security instance to which you want to assign the user, select the check box for the user account you just created, and then Assign Roles.

- Select IoT Security in the left panel to display the IoT Security role assignment window in the main panel.

- Choose one of the following roles from the Role drop-down list:App AdministratorInstance AdministratorOwnerAdministratorRead only
- For information about these user roles, click Role Definitions.To learn more about the App Administrator and Instance Administrator roles, which are common roles for all Palo Alto Networks apps and provide the same privileges in IoT Security as Owner, see Available Roles. To learn more about the Owner, Administrator, and Read only roles, which are specific to IoT Security, see Manage IoT Security Users.
Authenticate Users with an Active Directory SSO and Manage User Roles in Active Directory
- Prepare the authentication system.Before you configure IoT Security, prepare your Active Directory to communicate with it and export the identity provider (IdP) metadata file that IoT Security will need to communicate with the IdP.
- Configure your IdP with the following URLs, replacing the tenant-id variable with your own tenant ID, which is the first part of your IoT Security portal URL:https://tenant-id.iot.paloaltonetworks.com/loginDepending on how you configure your IdP, either point it to the IoT Security metadata URL to retrieve all the necessary data or enter the information separately.
- Assertion Consumer Service (ACS) – This is the destination to which the IdP sends authentication assertions in response to user authentication requests.https://tenant-id.iot.paloaltonetworks.com/v0.3/zauth/saml2_sso/acs
- Entity ID – This is the URL that uniquely identifies the Zingbox SP.https://tenant-id.iot.paloaltonetworks.com/v0.3/zauth/saml2_sso/metadata
- Palo Alto Networks Metadata – This file includes the ACS URL and entity ID plus other parameters such as its public Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) 2.0 encryption key.https://tenant-id.iot.paloaltonetworks.com/v0.3/zauth/saml2_sso/metadata
To see the URLs with your specific tenant ID, follow steps 1-2 in the next section and then copy the URLs in the Service Provider (SP) Configuration Details section. - Either copy and save the URL where IoT Security can import the IdP metadata file from your SSO authentication system or download the file and save it in XML format. You will later import it to the IoT Security portal.
- Prepare IoT Security to use an externally managed SSO.
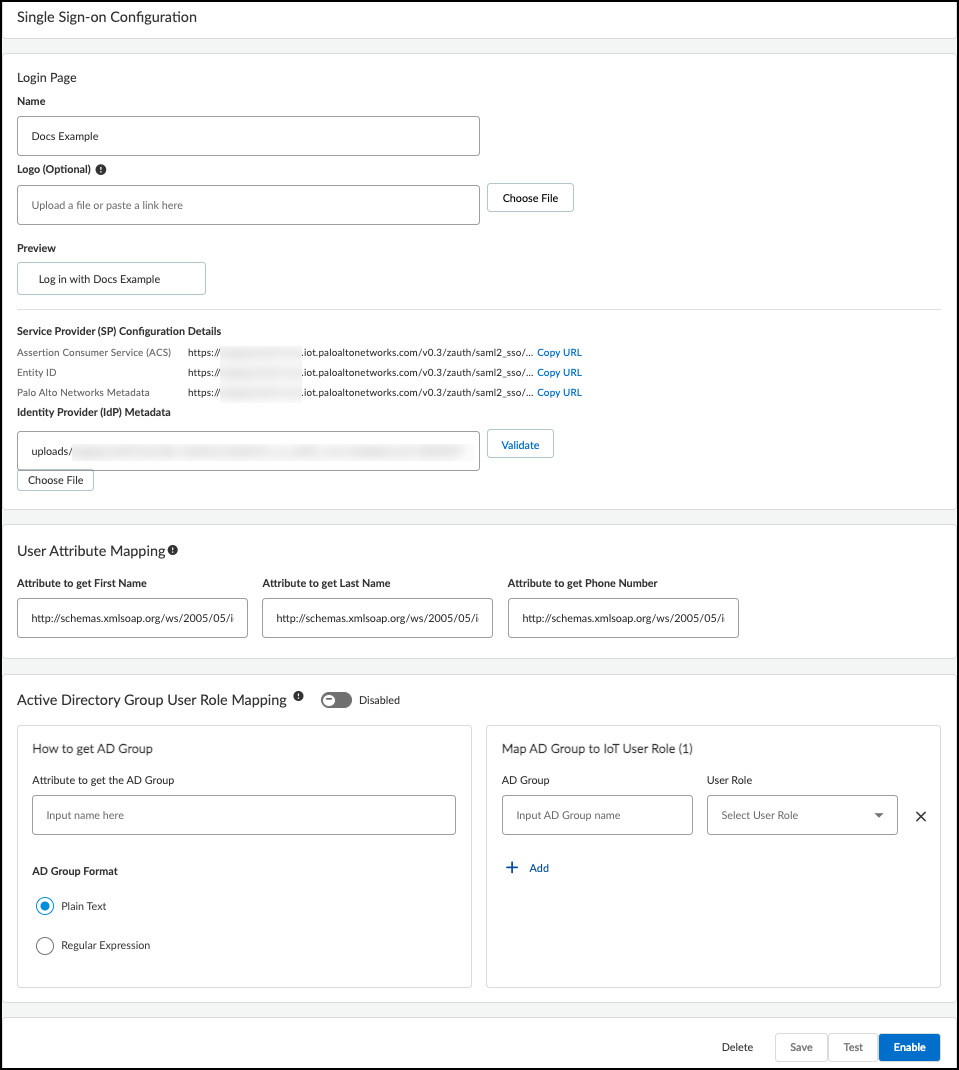
- Log in to the IoT Security portal as an owner, navigate to AdministrationUser Accounts, and then Manage SSO.Palo Alto Networks is the default SSO identity provider (IdP) that authenticates users accessing the IoT Security portal and assigns user roles to them.
- To add a user-configured SSO, Add New SSO, and then enter the following in the Single Sign-on Configuration dialog box that appears:Name: Enter a name for the SSO. It can be up to 16 characters. This name will appear on the login page as shown in the Preview below.Logo (Optional): Upload an image file to display next to the SSO name on the login page as shown in the Preview. The image file can be up to 2 MB and must be in .bmp, .jpg, or .png format.IdP Metadata: Either enter the URL of the IdP metadata file you copied and saved earlier or click Choose file, navigate to the XML file you exported from your authentication system, and select it.
- Validate the IdP metadata URL or uploaded file.Validating the IdP metadata URL activates the Save and Test buttons.
- Configure the following fields to map attributes to IoT Security user roles. Map an SAML fully qualified claim name to the user attribute.Attribute to get First Name: Enter a fully qualified domain for a first name, such as http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/firstnameAttribute to get Last Name: Enter a fully qualified domain for a surname, such as http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/lastnameAttribute to get Phone Number: Enter a fully qualified domain for a phone number, such as http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/mobile
- Configure the following settings to identify AD user groups whose users you want Active Directory to authorize. If you leave them empty, IoT Security authorizes them locally.Attribute to get AD Groups: Enter the attribute in the SAML 2.0 response that identifies user groups from Active Directory.AD Group Format: Select whether the attribute is formatted as Plain Text or Regular Expression. These are how IoT Security maps AD user groups to IoT Security user roles.Plain Text identifies the user group with the exact value specified in Attribute to get AD Groups. For example, if AD Group Format is Plain Text and the AD Group is Hospital Administrator, then IoT Security maps only users in the AD group named Hospital Administrator to the specified IoT Security role.Regular Expression identifies any user group that contains the value specified in Attribute to get AD Groups. For example, if AD Group Format is Regular Expression and the AD Group is OUI=Hospital*, then IoT Security maps users in any AD group whose organizational unit identifier (OUI) includes Hospital—such as OUI=Hospital Administrator and OUI=Hospital NetSec—to one or more specified IoT Security roles.AD Group and User Role: Enter an Active Directory group name and then choose the IoT Security user role to map it to: Owner, Administrator, or Read Only. Click + to add more AD group-to-user role mappings. You can create up to 50 mappings. A single AD group cannot map to multiple IoT Security user roles, but multiple AD groups can map to the same IoT Security user role.For information about the IoT Security user roles, see Manage IoT Security Users.

- Save the SSO configuration.
- Test the SSO configuration.IoT Security opens a small window to log in using the authentication system.
- When done with the test, click Confirm.
- Enable the SSO configuration.
- After enabling the configuration, the Enable button changes to Disable and Edit.
Authenticate Users with any SSO and Manage User Roles in the IoT Security Portal
User roles are set for user accounts in external SSO authentication systems—the
Palo Alto Network SSO and customer-managed SSOs—but you can also log in to the
IoT Security portal with owner privileges and set other roles for administrators
and read-only users. If the externally and internally managed roles are
different, IoT Security assigns the higher of the two. Therefore, only set user
roles internally on IoT Security that are higher than those set externally;
otherwise, an internal role will never be assigned. The ranking of roles from
highest to lowest is owner, administrator, read-only user.
If user accounts in an external SSO don't have any externally managed roles
defined, these users won't be able to log in to IoT Security until a local user
with owner privileges sets internally managed roles for them and invites them to
log in to IoT Security.
- Invite users who have an account on an external SSO but no externally managed role to access IoT Security.Skip this step if users have an externally managed role that maps to a role in IoT Security.
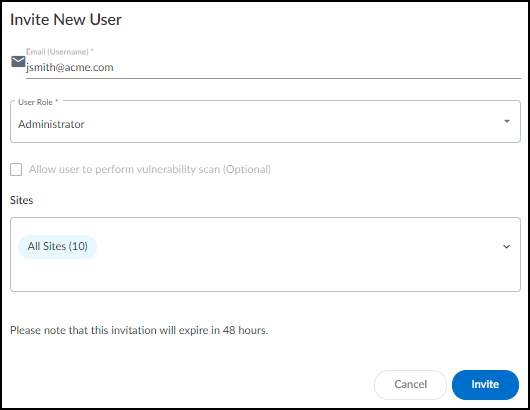
- Log in to IoT Security as a user with owner privileges, select AdministrationUser Accounts and then click the Invite New User icon ( + ) above the User Accounts table.
- Enter an email address, choose a role (Owner, Administrator, or Read only), specify which sites the user can access, and then Invite.
 IoT Security automatically generates an email with a login link and sends it to the user.The invitation is valid for 48 hours after it's sent.When the email recipient clicks a link in the email, he or she is directed to the login page. The user clicks the Log in with <sso-name> button to log in through SSO. After the user logs in, IoT Security grants him or her access with the local role you specified.
IoT Security automatically generates an email with a login link and sends it to the user.The invitation is valid for 48 hours after it's sent.When the email recipient clicks a link in the email, he or she is directed to the login page. The user clicks the Log in with <sso-name> button to log in through SSO. After the user logs in, IoT Security grants him or her access with the local role you specified. - If you want to invite more users, repeat the previous steps for each one.
- View users, their externally managed roles, role providers, and internally managed roles and which sites they can access.You can see a list of users and their roles on the Access Management page in the hub and, if you’re logged in with owner privileges, on the User Accounts page (AdministrationUser Accounts) in the IoT Security portal.Externally Managed Role and Role Provider: If IoT Security applies the user role that’s set on the external SSO authentication system, the role appears in the Externally Managed Role column and the SSO name appears in the Role Provider column. If IoT Security has an internally managed role for a user that’s the same as or higher than his or her externally managed role, it applies the internally managed role. In this case, these two columns are empty.Internally Managed Role: This column lists user roles defined in IoT Security. It’s only empty if there isn’t a role defined internally.After you create a user account in the Customer Support Portal and hub, the account won't appear on the AdministrationUser Accounts page in the IoT Security portal until the user logs in to the IoT Security portal.
- Assign a user with an internally managed role.
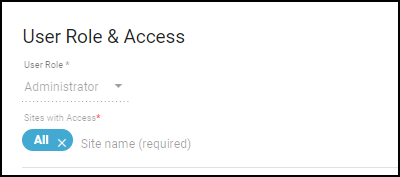
- When logged in to the IoT Security portal with owner privileges, click AdministrationUser Accounts and then click an entry for an administrator or read-only user in the Email (Username) column.The User Role & Access dialog box opens.

- Choose a different role from the User Role drop-down list. When there are different externally and internally managed roles for the same user, IoT Security applies the role with higher privileges. Therefore, when setting an internal role, choose one that is higher than the one assigned by an external SSO authentication system.
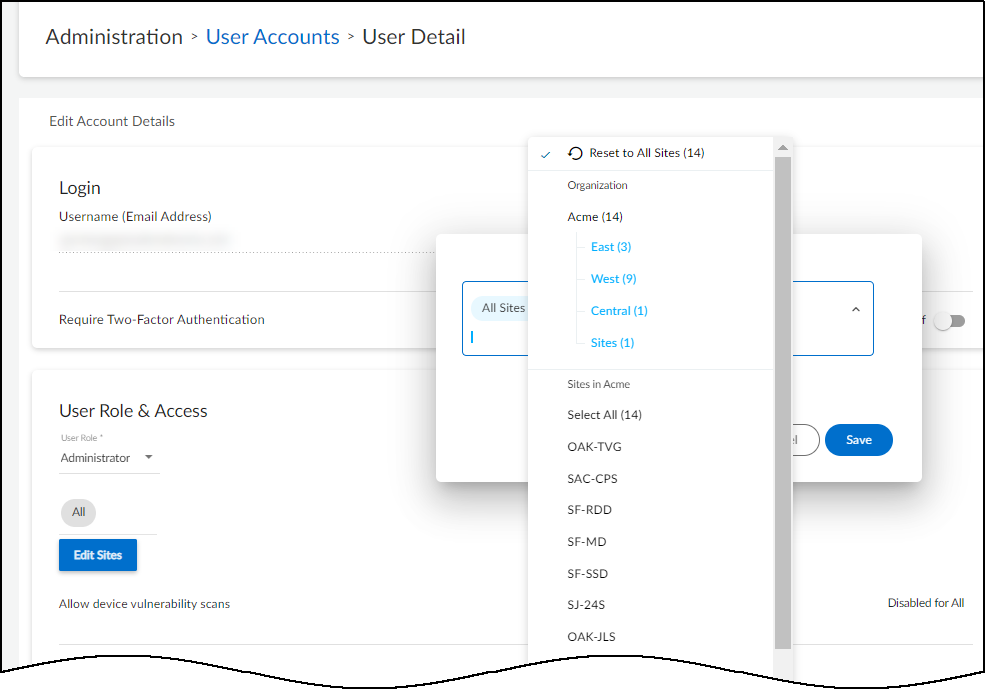
- Determine which sites an administrator or read-only user can access.By default, all users have access to all sites. To give the user access to a subset of sites, click the x in the All label and then select the names of the sites or site groups to which you want to permit access.
 For information about site groups and how to use them to control what data users can access, see Sites and Site Groups.
For information about site groups and how to use them to control what data users can access, see Sites and Site Groups. - When done, Save the configuration change.The next time the user logs in, he or she will only have the privileges of the internally managed role and access to devices and data for the selected sites.