- Home
- Prisma Access
- Integrate Third-Party SD-WANs with Prisma Access
- HPE Aruba Networking EdgeConnect SD-WAN Solution Guide
- Integrate Prisma Access with HPE Aruba Networking EdgeConnect SD-WAN (Manual Integration)
- Integrate Prisma Access with HPE Aruba Networking EdgeConnect SD-WAN (Strata Cloud Manager)
Prisma Access
Integrate Prisma Access with HPE Aruba Networking EdgeConnect SD-WAN (Strata Cloud Manager)
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma Access Docs
-
- 6.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 6.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 4.2 Preferred
- 4.1 Preferred
- 4.0 Preferred
- 3.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 2.2 Preferred
-
-
- 4.0 & Later
- Prisma Access China
-
-
Integrate Prisma Access with HPE Aruba Networking EdgeConnect SD-WAN (Strata Cloud Manager)
Integrate Prisma Access with Silver Peak SD-WAN in Strata Cloud Manager.
Use this workflow to configure HPE Aruba Networking EdgeConnect SD-WAN with Prisma
Access.
HPE Aruba Networking EdgeConnect SD-WAN recommends that you configure two tunnels in
an active-backup configuration between HPE Aruba Networking EdgeConnect SD-WAN and
Prisma Access, because there are some restrictions for accessing resources at other
network locations when you configure the tunnels in an active/active configuration
because of the overlapping subnets.
Before you start this workflow, determine your remote tunnel capacity. HPE Aruba
Networking EdgeConnect SD-WAN bases the tunnel capacity on licensing and the
capacity of the device model. For example, the base HPE Aruba Networking
EdgeConnect SD-WAN license supports up to 200 Mbps WAN uplink, and the EC-XS
supports 200 Mbps. Prisma Access bases a location’s bandwidth on the bandwidth
you specify for its compute location.
- Follow the steps to Connect a remote network to Prisma Access.
- Choose a Prisma Access Location that is close to the remote network location that you want to onboard.
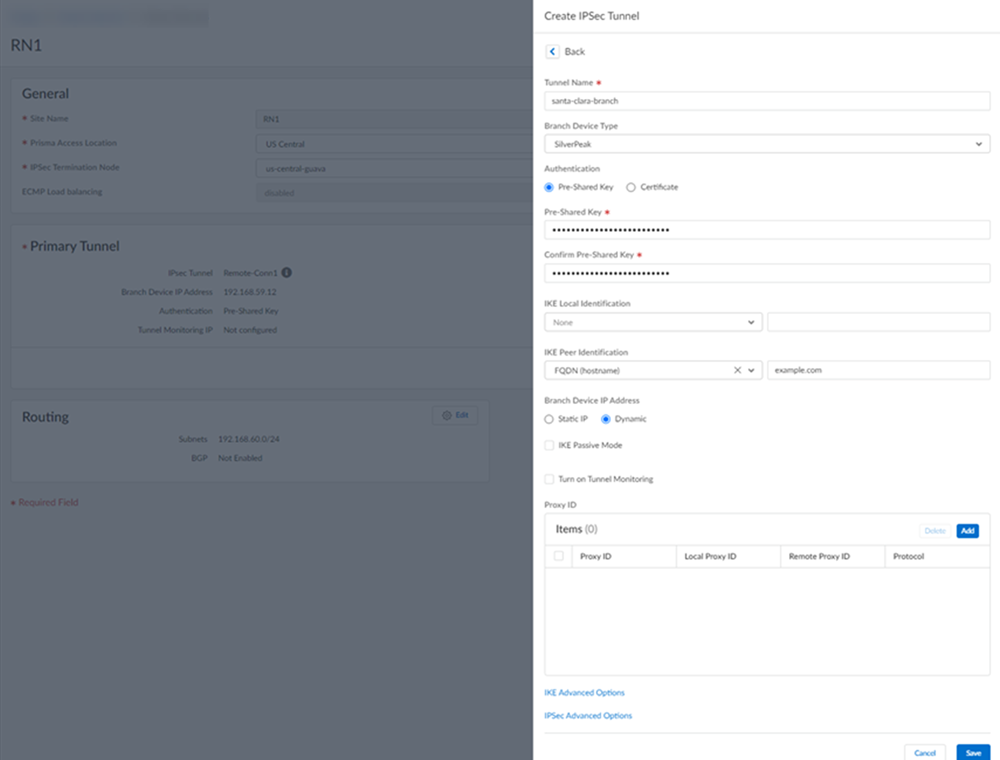
- When creating the IPSec tunnel, use a Branch Device Type of HPE Aruba Networking EdgeConnect SD-WAN.
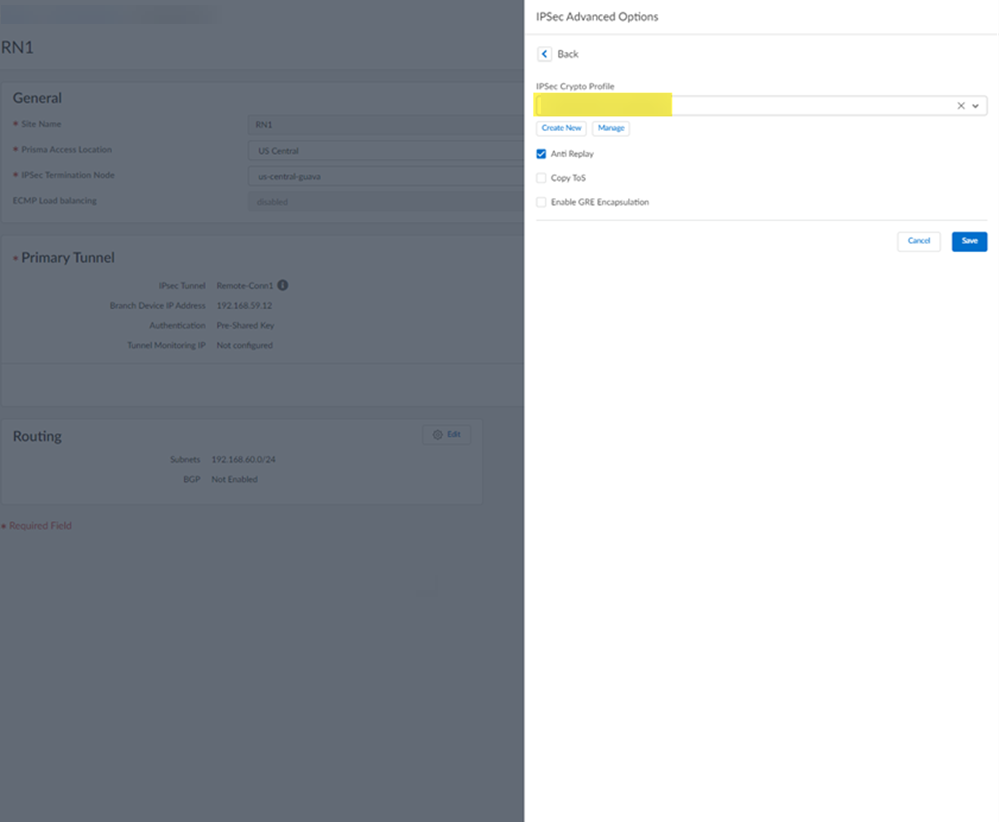
![]() Select IPSec Advanced Options and select an IPSec Crypto profile of HPE Aruba Networking EdgeConnect SD-WAN-IPSec-Crypto-Default.
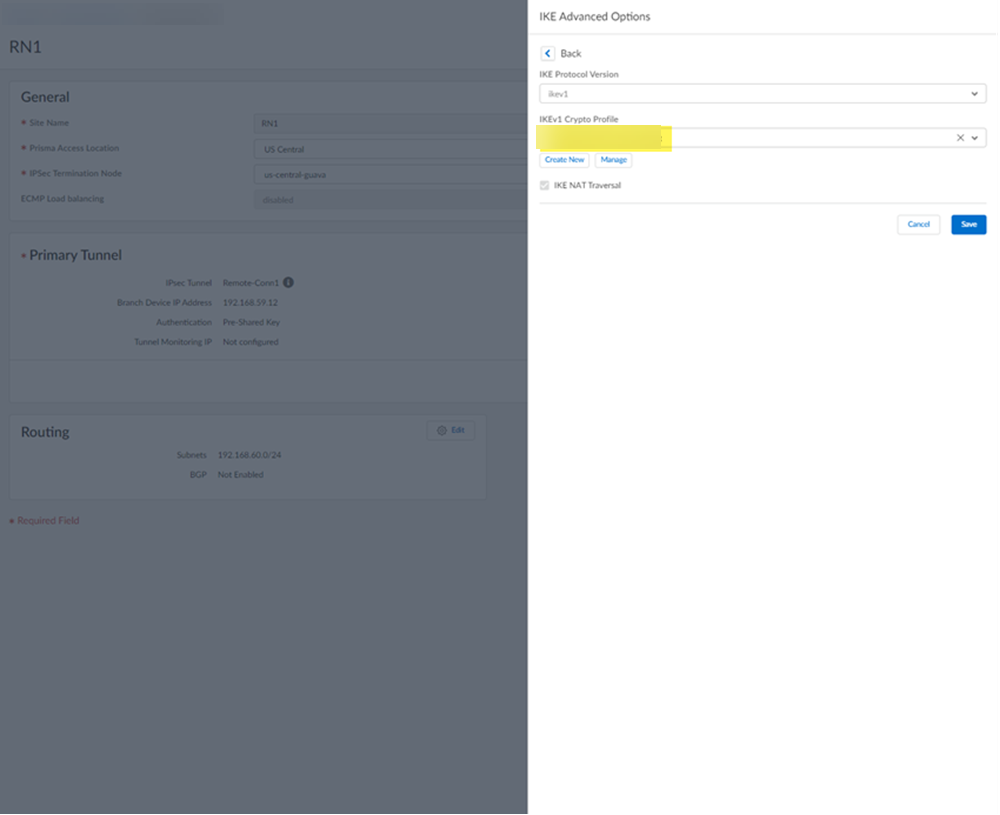
Select IPSec Advanced Options and select an IPSec Crypto profile of HPE Aruba Networking EdgeConnect SD-WAN-IPSec-Crypto-Default.![]() Select IKE Advanced Options and select an IKEv1 crypto profile of HPE Aruba Networking EdgeConnect SD-WAN-IKE-Crypto-Default.
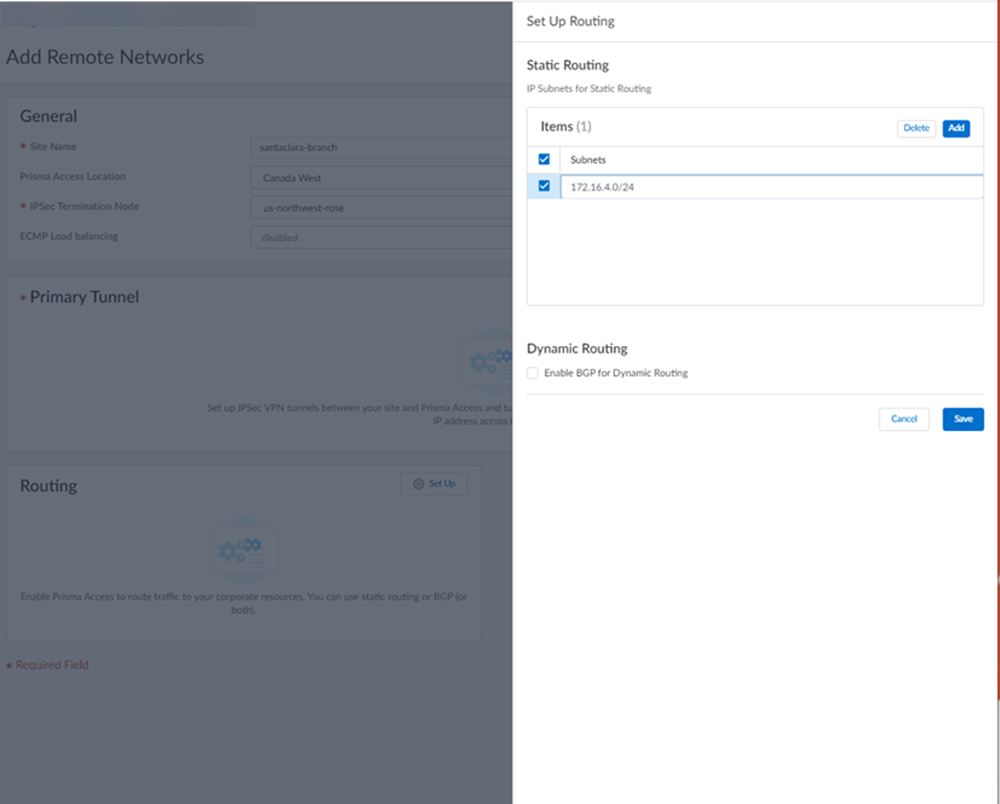
Select IKE Advanced Options and select an IKEv1 crypto profile of HPE Aruba Networking EdgeConnect SD-WAN-IKE-Crypto-Default.![]() Set up routing for the remote network.Set Up Routing and Add the IP subnets for Static Routing.
Set up routing for the remote network.Set Up Routing and Add the IP subnets for Static Routing.![]() Push your configuration changes.
Push your configuration changes.- Return to ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessConfiguration ScopePrisma AccessRemote Networks and select Push ConfigPush.
![]() Select Remote Networks.
Select Remote Networks.![]() Push your changes.Make a note of the Service IP address of the Prisma Access side of the tunnel. To find this address in Prisma Access (Managed by Strata Cloud Manager), select ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessConfiguration ScopePrisma AccessRemote Networks, click the Remote Networks, and look for the Service IP field corresponding to the remote network configuration you created.From the HPE Aruba Networking EdgeConnect SD-WAN orchestrator, create a tunnel configuration.
Push your changes.Make a note of the Service IP address of the Prisma Access side of the tunnel. To find this address in Prisma Access (Managed by Strata Cloud Manager), select ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessConfiguration ScopePrisma AccessRemote Networks, click the Remote Networks, and look for the Service IP field corresponding to the remote network configuration you created.From the HPE Aruba Networking EdgeConnect SD-WAN orchestrator, create a tunnel configuration.- Select Configuration.Select TunnelsPassthroughSelect Add Tunnel.Select a Name, Local IP, Remote IP, and Mode.In the Advanced Options area, enter the IKE and IPSec parameters.The parameters must be the same as the parameters that you specified on Prisma Access. HPE Aruba Networking EdgeConnect SD-WAN recommends the following IKE and IPSec encryption settings:
- IKE encryption settings:
- Encryption—AES-256-CBC
- Authentication—SHA512
- IKE Lifetime—8 hours
- Dead Peer Detection—Delay time: 300 seconds Retry: 3
- IKE Identifier —IP address (leave blank - public IP is auto-detected)
- DH—Group 14
- Mode—Aggressive
- IPSec encryption settings:
- Encryption—AES-25-CBC
- Authentication—SHA512
- Lifetime—60 minutes
- PFS—DH - Group 14
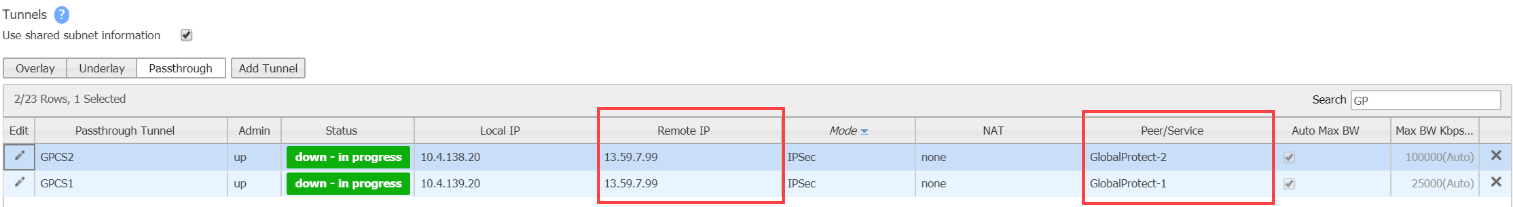
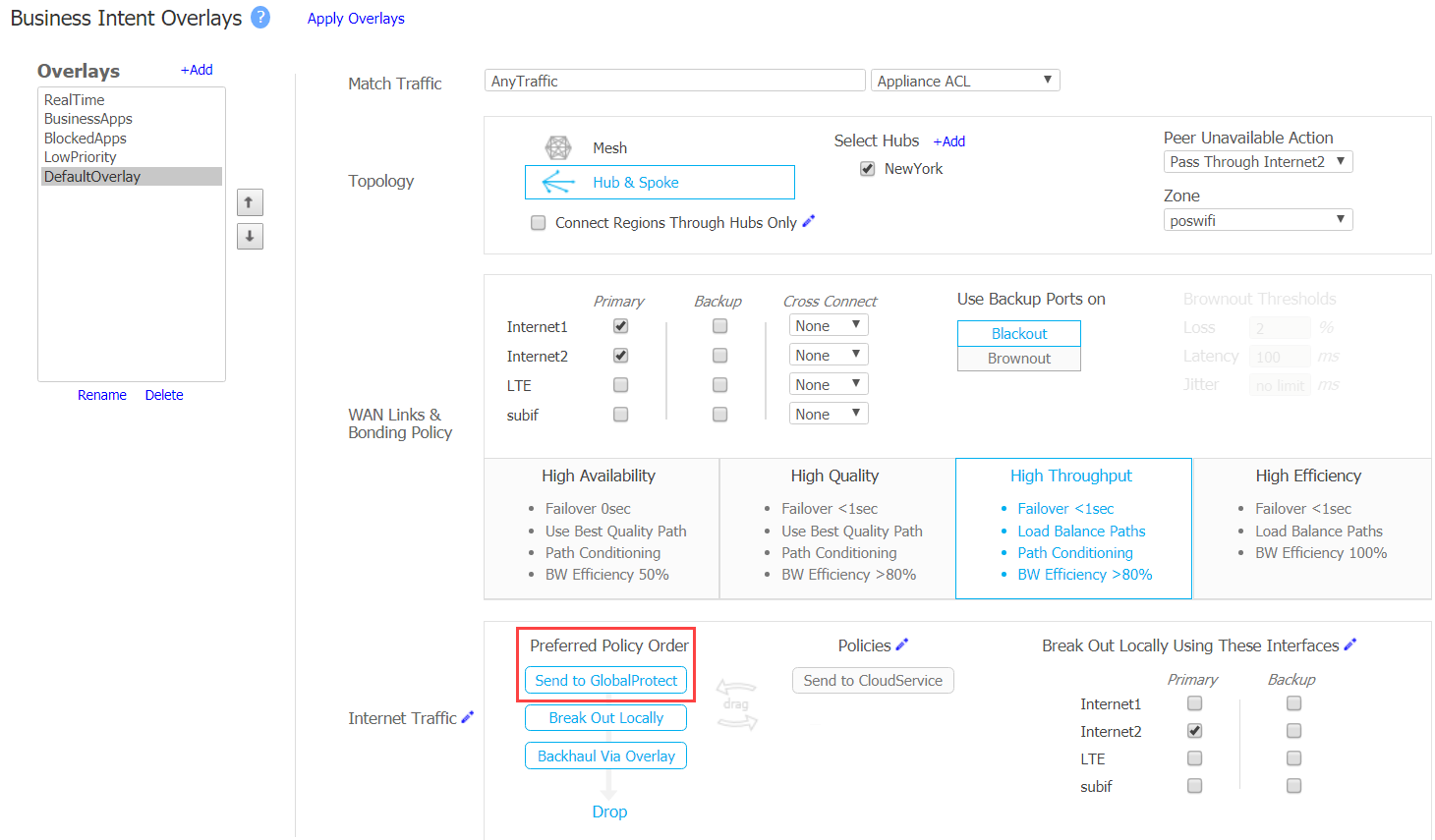
Create two tunnels to Prisma Access: one Active and the other Backup.The following example creates two tunnels named GlobalProtect-1 and GlobalProtect-2.Specify the Prisma Access Service IP address in the Remote IP field.Select the Local IP address from the list of WAN interface IP addresses.![]() Use the 3rd party IPSec tunnels in a Business Intent overlay policy by selecting Business Intent Overlay and configuring the Peer/Service in the Policies area.Order the GlobalProtect-1 GlobalProtect-2 service to the Preferred Policy Order field in the internet Traffic area.
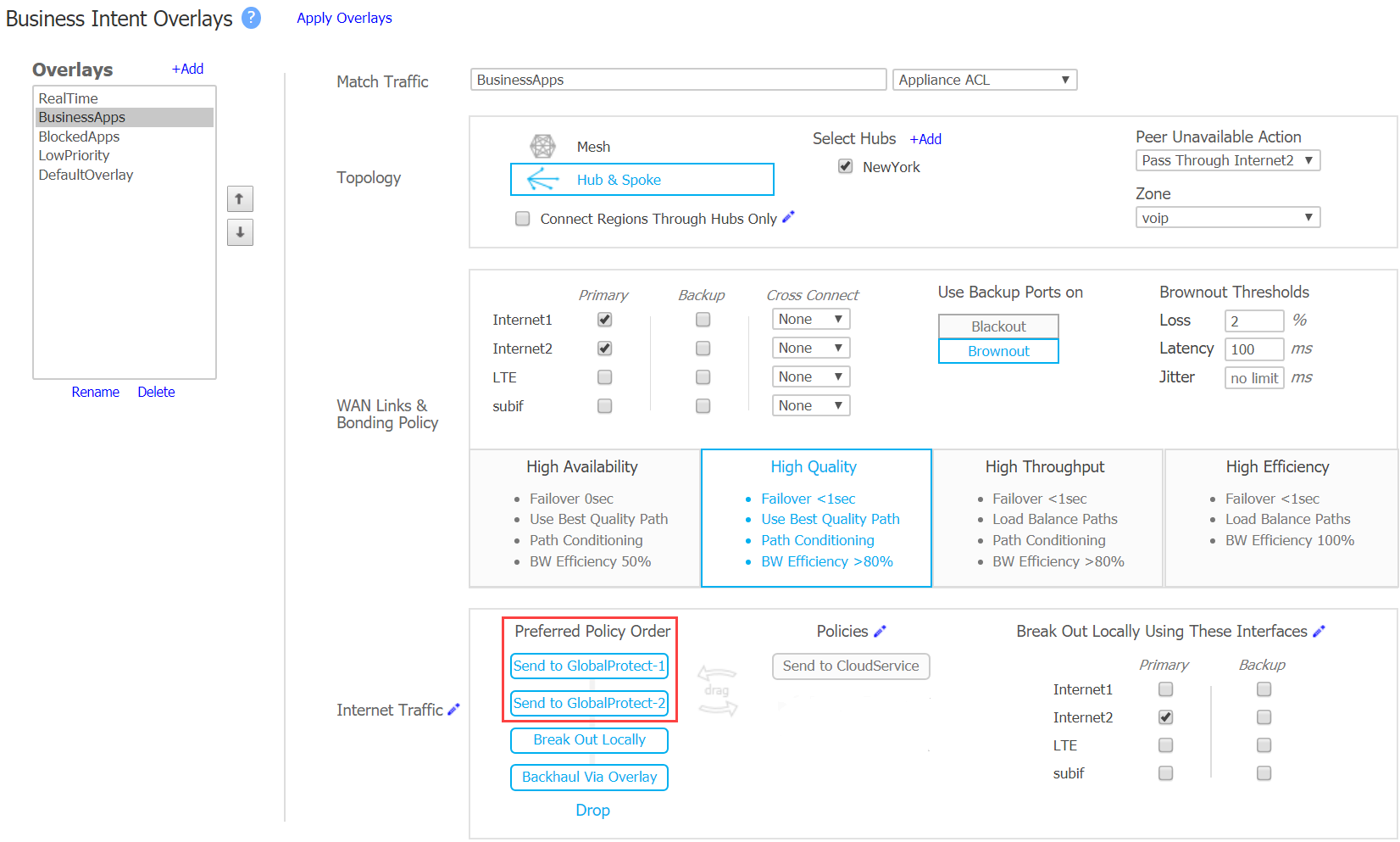
Use the 3rd party IPSec tunnels in a Business Intent overlay policy by selecting Business Intent Overlay and configuring the Peer/Service in the Policies area.Order the GlobalProtect-1 GlobalProtect-2 service to the Preferred Policy Order field in the internet Traffic area.![]() Defining the order in the Preferred Policy Order configures the GlobalProtect-1 tunnel to automatically failover to the GlobalProtect-2 if the GlobalProtect-1 goes down. When both tunnels from the branch to GPCS are down, HPE Aruba Networking EdgeConnect SD-WAN uses any other defined path such as local breakout or backhaul using the Overlay.
Defining the order in the Preferred Policy Order configures the GlobalProtect-1 tunnel to automatically failover to the GlobalProtect-2 if the GlobalProtect-1 goes down. When both tunnels from the branch to GPCS are down, HPE Aruba Networking EdgeConnect SD-WAN uses any other defined path such as local breakout or backhaul using the Overlay.Support for Two Active-Active Connections
Two connections from a branch as active-active on Prisma Access are implemented as two separate remote network connections. Onboard the connections in two separate locations using one of the following methods:- Configure two separate remote networks in two different compute locations and specify subnets that overlap (overlapping subnets) for each remote network.
- Onboard both remote networks to the same compute location, making sure that the bandwidth for that compute location is sufficient to support two tunnels.The HPE Aruba Networking EdgeConnect SD-WAN manually injects branch subnets into Prisma Access, but return traffic might not travel through the same tunnel if you use the same branch subnets for both tunnels. To avoid asymmetric traffic paths, configure different branch subnets for each primary tunnel.
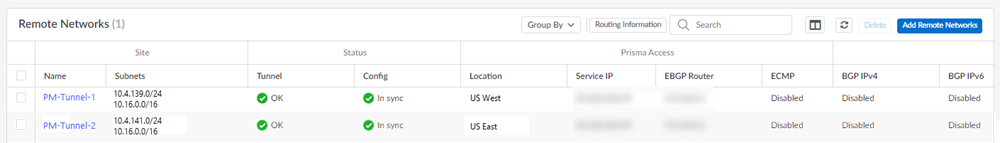
- To load balance between the two tunnels, use identical names under Peer/Service. For example, if you use a Peer/Service name GlobalProtect for the tunnels PrismaAccess-1 and PrismaAccess-2, traffic will load balance between the two tunnels.The following figure shows the different branch subnets configured in Prisma Access for the load-balanced tunnels.
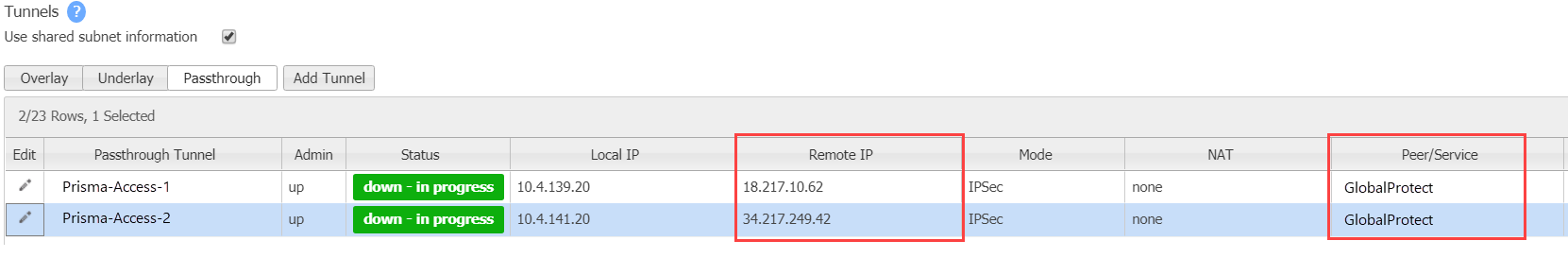
![]() The following figure shows Prisma Access in two locations in the Remote IP area and the peer service configured as GlobalProtect in the Peer/Service area.
The following figure shows Prisma Access in two locations in the Remote IP area and the peer service configured as GlobalProtect in the Peer/Service area.![]() The following figure shows Send to GlobalProtect configured in the Preferred Policy Order field.
The following figure shows Send to GlobalProtect configured in the Preferred Policy Order field.![]()
Troubleshoot the HPE Aruba Networking EdgeConnect SD-WAN
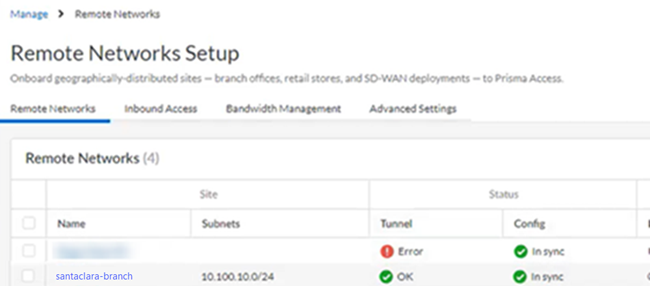
Prisma Access provides logs and widgets that provide you with the status of remote tunnels and the status of each tunnel.- Go to ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessConfiguration ScopePrisma AccessRemote Networks and check the Status of the tunnel.
![]()
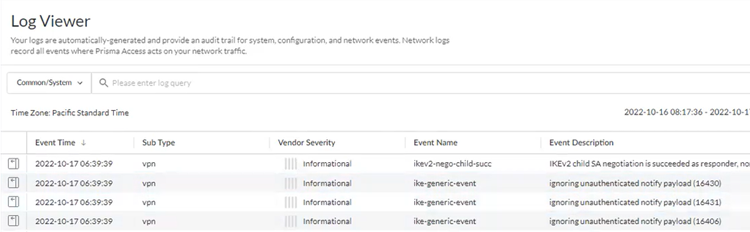
- Go to ActivityLog Viewer and check the Common/System logs for IPSec- and IKE-related messages.To view VPN-relates messages, set the filter to sub_type.value = vpn.The message ignoring unauthenticated notify payload indicates that the route has not been added in the crypto map on the other side of the IPSec tunnel after the IPSec negotiation has already occurred.
![]()
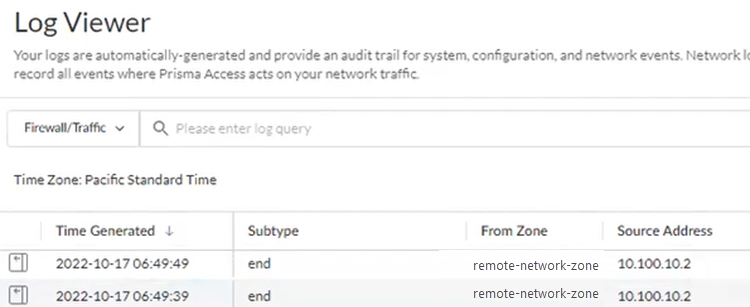
- Check the Firewall/Traffic logs and view the messages that are coming from the zone that has the same name as the remote network.In the logs, the remote network name is used as the source zone.
![]()