AI Access Security
Discover Risks Posed by GenAI Apps
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
AI Access Security Docs
Discover Risks Posed by GenAI Apps
Discover risks posed by generative AI (GenAI) apps based on the use case, allowed
traffic, data in motion or at rest, risky app, or app users.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
One of the following:
|
Use the AI Access Security Insights dashboard to filter the generative AI
(GenAI) app usage on your network. The AI Access Security Insights
dashboard provides in-depth details to help you understand which GenAI apps are
being used and by who.
AI Access Security detects Allowed
Users data, Blocked Users data, or both based
on the following filters.
- 1 Hour and 3 HoursUsers can count as Allowed, Blocked, or both.For example, UserA gets blocked from accessing GenAI-App1 to due Policy Rule1. An hour later, UserA travels to a branch office where Policy Rule2 allows access to GenAI-App1. In this case, UserA displays in both Allowed Users and Blocked Users counts.Conversely, Policy Rule1 blocks UserA from accessing a GenAI-App1. A few minutes after later, your security administrator modifies Policy Rule1 to allow UserA access. In this case, UserA displays in the Blocked Users counts. AI Access Security displays users in the Blocked Users count regardless of how many times regardless of how many times you allowed access in the past 1 Hour or 3 Hours if they matched the same Security policy rule and were blocked from accessing at least once.
- 24 Hour, 7 Day, and 30 DayUsers can count as Allowed, Blocked, or both.For example, you initially blocked UserA from accessing GenAI-App1. Six hours later UserA travels to a branch office where Policy Rule2 allows access to GenAI-App1. In this case, UserA displays in both Allowed Users and Blocked Users counts.
Discover Risks Posed by GenAI Apps by Use Case
Discover risks posed by generative AI (GenAI) apps based on the GenAI app use
case.
Review the Supported Use Cases for full descriptions of all use
case categories that a GenAI app falls into.
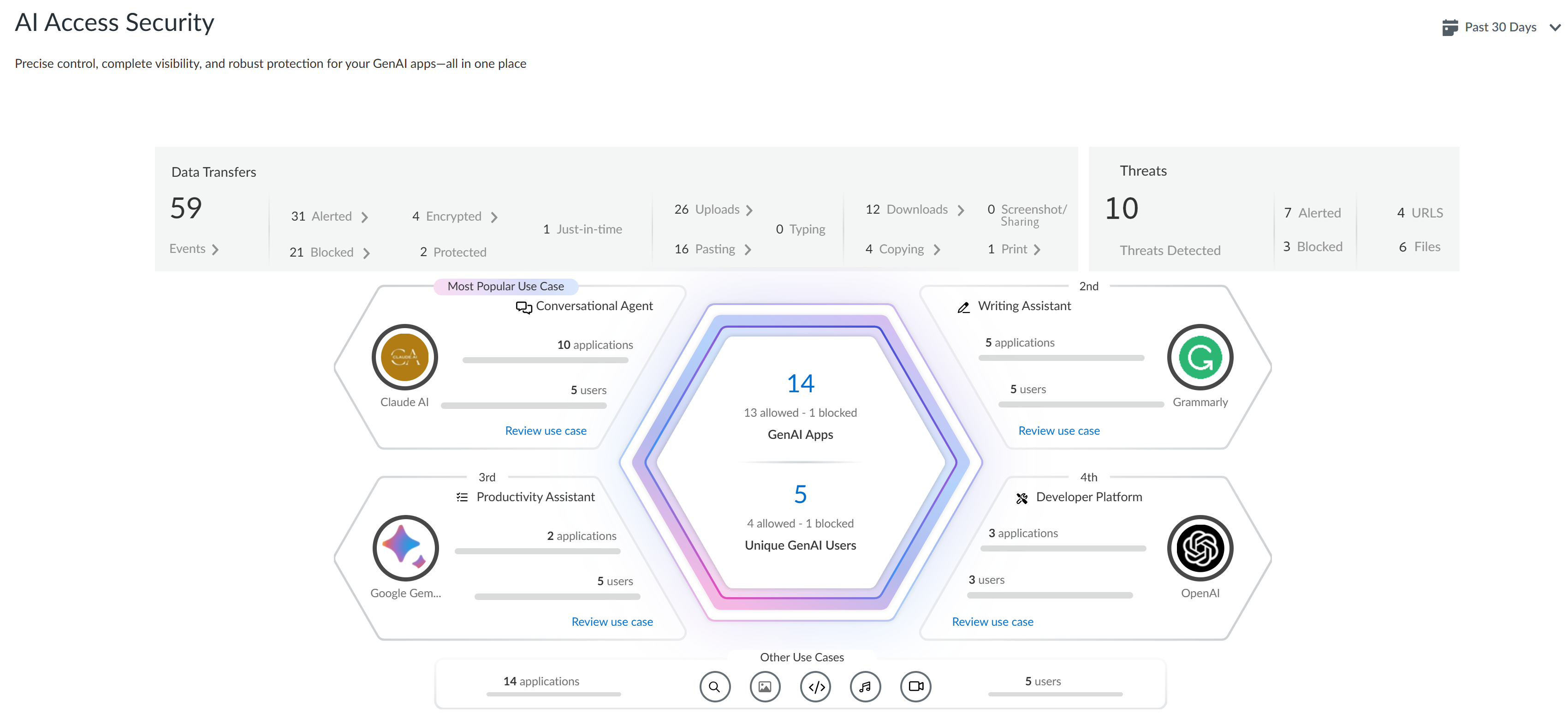
- Log in to Strata Cloud Manager.Select InsightsAI Access to view the AI Access Security Insights dashboard.The AI Access Security Insights dashboard displays GenAI app usage on your network by use case by default as well as the following high-level information about your top GenAI use cases:
- Time FilterFilter your GenAI use case breakdown for the time period you want to investigate. You can select Past 1 Hour, Past 3 Hours, Past 24 Hours, Past 7 Days, or Past 30 Days.
![]()
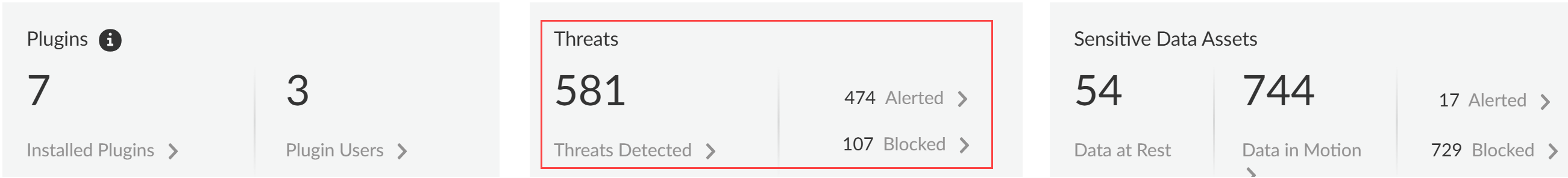
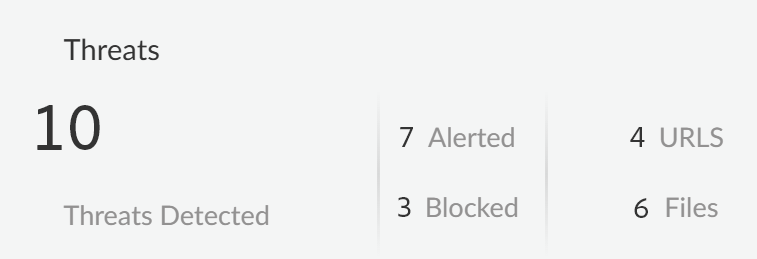
- Threats DetectedThreats are detected by the Vulnerability Protection profile attached to the Web Security policy rule. This profile detects threats such as malicious and phishing URLs, malicious files, or malware. The Threats Detected summarizes all threats across all GenAI apps and enforcement points.
- Alerted—Total number of threats detected that generated an alert.
- Blocked—Total number of threats detected that were blocked by your NGFW or Prisma Access tenants.
![]()
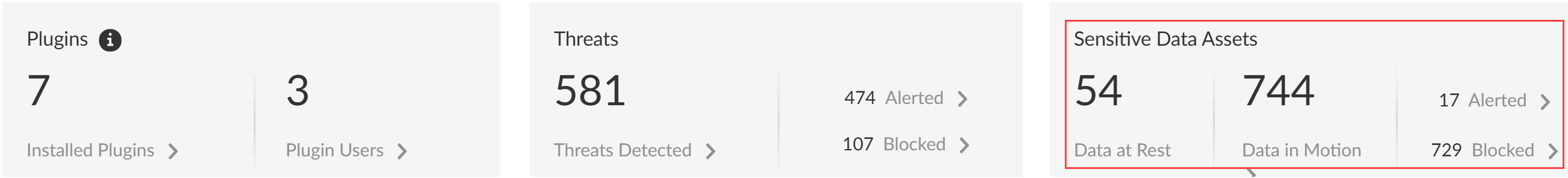
- Sensitive Data AssetsSensitive data assets displays the number of incidents of sensitive data detected when traffic matches the match criteria in your Enterprise Data Loss Prevention (E-DLP) data profile for data at rest (Data Security) and data in motion (SaaS Security Inline).
- Data at Rest—Total number of DLP Incidents that either generated an alert or were blocked through the SaaS API (Data Security) enforcement channel.
- Data in Motion—Total number of DLP Incidents that either generated an alert or were blocked through the SaaS Security Inline enforcement channel.
- Alerted—Total number of DLP Incidents that generated an alert for both data at rest and data in motion.
- Blocked—Total number of DLP incidents blocked by your NGFWs or Prisma Access tenants for both data at rest and data in motion.
![]()
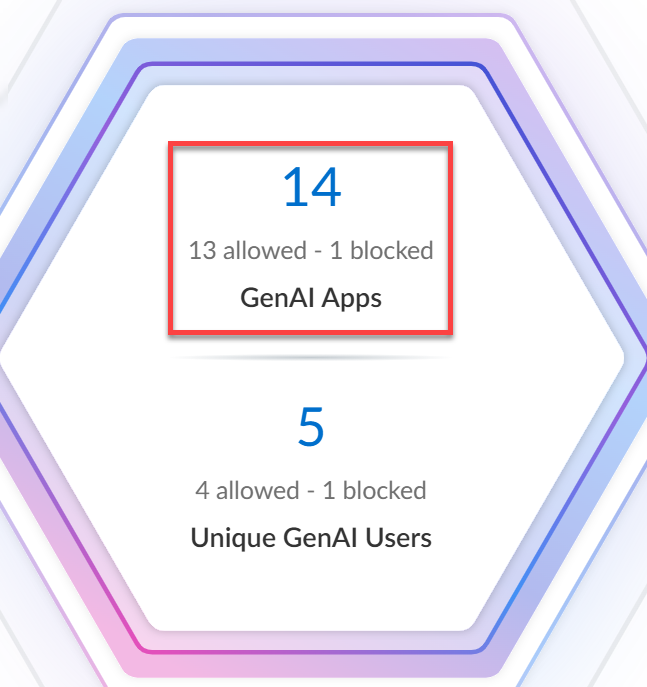
- Top Use CasesThe AI Access Security Insights dashboard dynamically displays the top four GenAI app use cases based on activity on your network, along with the total number of GenAI apps and users who accessed any GenAI in the selected time period. This allows you to quickly investigate security incidents related to your most widely used GenAI apps and implement access control policy rules.
- GenAI Apps—Total number of GenAI apps that fall into the particular use case. A line graph provides an at-a-glance breakdown of Sanctioned, Tolerated, and Unsanctioned GenAI apps.
- Unique GenAI Users—Total number of users who accessed any GenAI app that falls into the particular use case. Click the Unique GenAI Users count to view a list of each unique user who was blocked from accessing the GenAI appAI Access Security automatically aggregates the total Unique GenAI Users count on a set interval and generates the user list immediately when you click on the Unique GenAI Users count. This might cause the Unique GenAI Users count to slightly differ from the list count.
![]()
- All Other Use Cases
- Applications—Total number of GenAI apps that fall into any other GenAI app use case. A line graph provides an at-a-glance breakdown of Sanctioned, Tolerated, and Unsanctioned GenAI apps.
- Users—Total number of users who have accessed any GenAI app that falls into any other GenAI app use case.
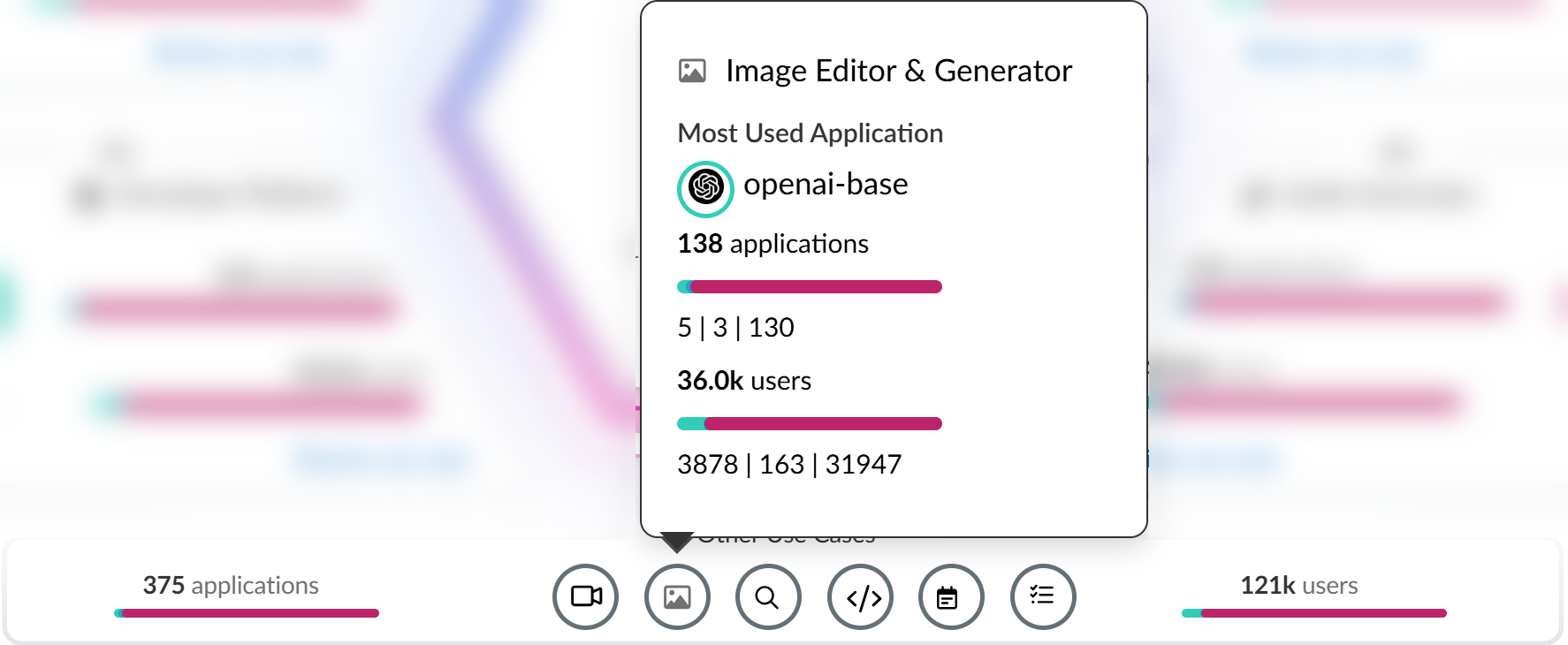
Hover your mouse over each of the use cases to see summary information about GenAI app usage associated with the use case.![]()
Review use case to see a detailed breakdown of all Sanctioned, Tolerated, and Unsanctioned GenAI apps in the use case you're interested in.Review the use case details page to understand GenAI app usage.The use case details page provides granular data about the GenAI app usage. You can use this information to understand GenAI app usage to help inform you of what policy rules your security administrators need to write to strengthen your security posture. This ensures that your organization is safely adopting GenAI apps and to prevent exfiltration of sensitive data.- Use Case SummaryThe use case summary aggregates all important GenAI app usage information for the use case you're investigating.
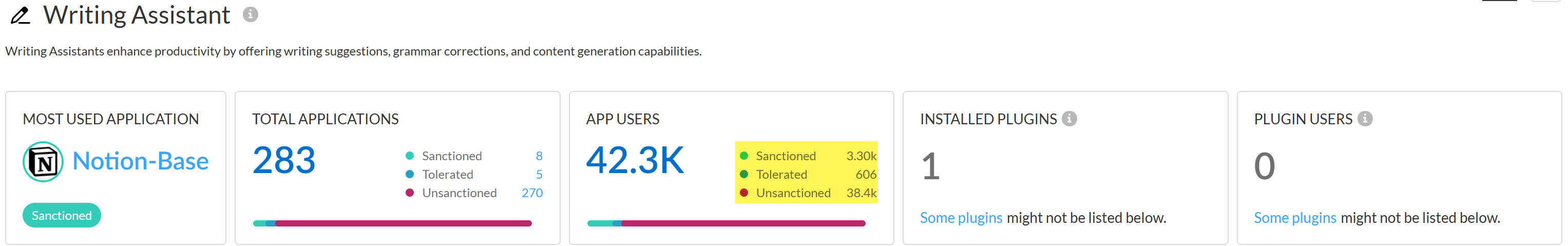
- Most Used Applications—The most used GenAI app for the use case. This also includes the app tag (Sanctioned, Tolerated, or Unsanctioned) currently assigned to the GenAI app.
- Application Breakdown—Summary of the total number of GenAI apps associated with the use case as well as a summary of the app tags across all detected GenAI apps.
- User Breakdown—Summary of the total number of users who accessed any of the GenAI apps associated with the use case. A summary of how many users accessed Sanctioned, Tolerated, or Unsanctioned GenAI apps is also provided.
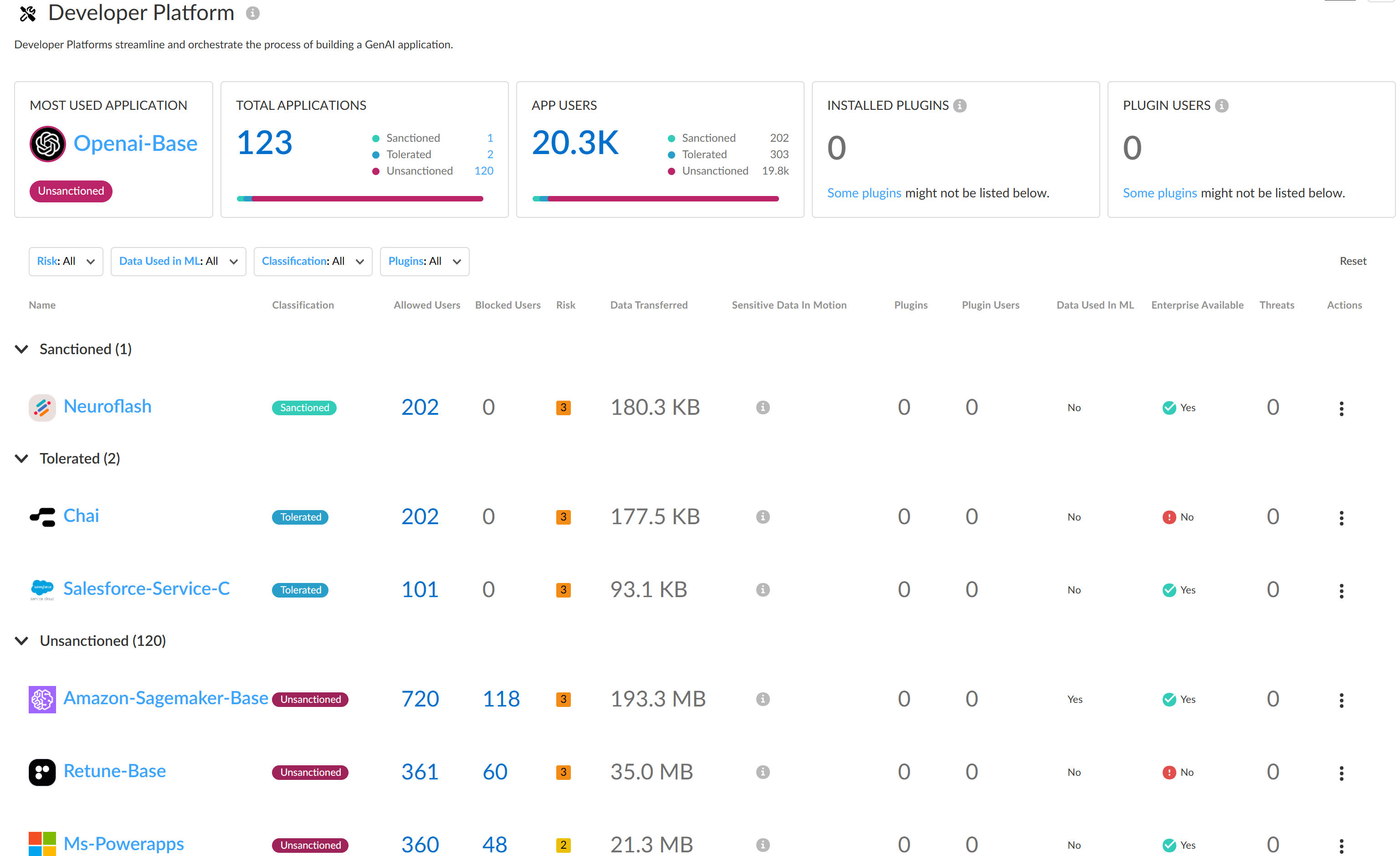
- ApplicationsA list of all GenAI apps associated with the use case accessed by your users. You can apply a Sort By filter to the use case GenAI apps to sort them by User Count, Threats Count, Transferred Count. AI Access Security sorts GenAI apps from highest to lowest count.The apps list displays the following information about each GenAI app detected.
- Application Name—Name of the detected GenAI app. Click the app name to view detailed usage information. You're redirected to the Activity Insights Applications
- Tag—Current GenAI app tag. You can apply a new tag by clicking the tag you want to apply.Palo Alto Networks groups the child App-IDs for app functionality in a container App-ID. However, tagging an App-ID container isn’t supported. You must individually tag the specific child App-ID that are sanctioned, unsanctioned, or tolerated within your organization.
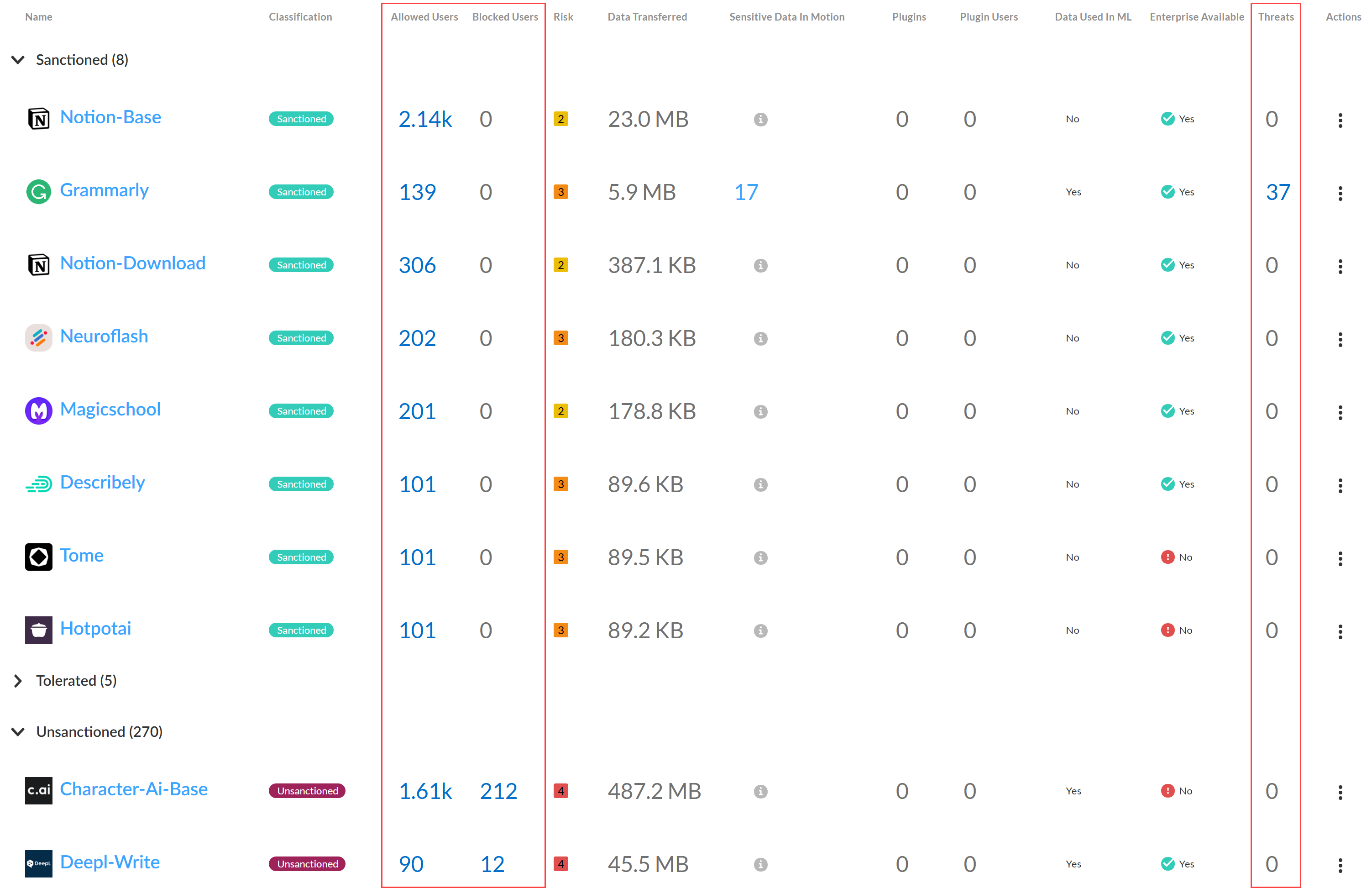
- Allowed Users—Total number of unique users who accessed the GenAI app based on the access privileges configured in your Security policy rules. Click the Allowed Users count to view a list of each unique user who successfully accessed the GenAI app.
- Blocked Users—Total number of unique users blocked from accessing the GenAI app based on the access privileges configured in your Security policy rules. Click the Blockers Users count to view a list of each unique user blocked from accessing the GenAI app.
- Threats—Total number of detected threat activity.
- Transferred—Total amount of data in gigabyte (GB) uploaded to or downloaded from the GenAI app.
- Sensitive Asset—Number of DLP incidents generated due to sensitive data detected and blocked by Enterprise DLP.
- Enterprise Available—Indicates whether the GenAI app offers an enterprise plan or license schema.
- Data Used in ML—Indicates whether the GenAI app uses user-uploaded data for training purposes.
- Risk Score—Risk score of the GenAI app.
- Use Case Highlights
- Applications—Total number of GenAI apps that fall into any other GenAI app use case. A line graph provides an at-a-glance breakdown of Sanctioned, Tolerated, and Unsanctioned GenAI apps.
- Users—Total number of users who have accessed any GenAI app that falls into any other GenAI app use case.
- Rules
- Recommended Actions
- Alerted—Total number of DLP Incidents that generated an Alert across all GenAI apps associated with the use case.
- Blocked—Total number of DLP incidents that were Blocked across all GenAI apps associated with the use case.
![]() Create a custom Security policy rule to control access to a GenAI app.In the example above, Openai-Base is the most used GenAI app in the Code Assistant & Generator use case. Additionally, this is an Unsanctioned app and indicates this an app not approved for use on your corporate network.In this case, you can modify the default GenAI app access policy rule to explicitly block all access to OpenAI if this is an app your organization should not access.
Create a custom Security policy rule to control access to a GenAI app.In the example above, Openai-Base is the most used GenAI app in the Code Assistant & Generator use case. Additionally, this is an Unsanctioned app and indicates this an app not approved for use on your corporate network.In this case, you can modify the default GenAI app access policy rule to explicitly block all access to OpenAI if this is an app your organization should not access.Discover Risks Posed by GenAI Apps by Risky Apps
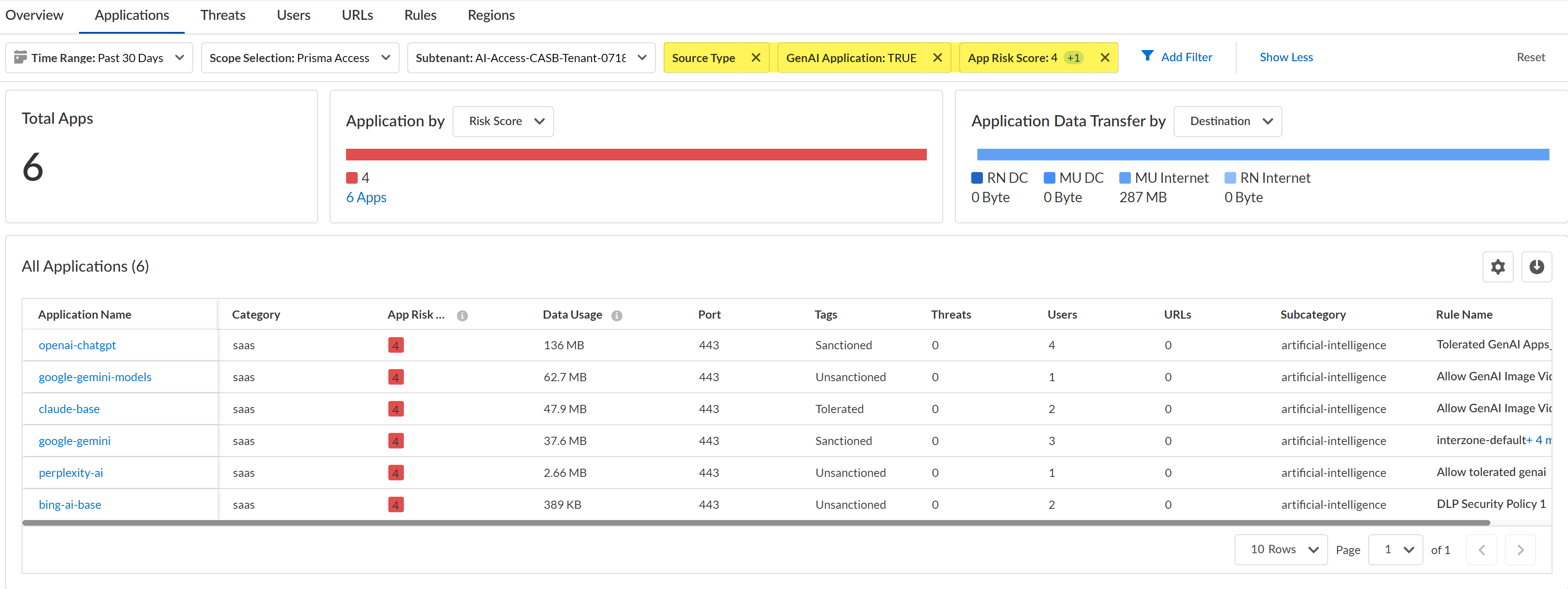
Discover risky generative AI (GenAI) apps accessed on your network.- Log in to Strata Cloud Manager.Select InsightsActivity InsightsApplications.Configure the filters for the app list to narrow down the GenAI apps you want to investigate.
- Configure the Time Range and Scope Selection to filter for the specific time range and enforcement point you want to investigate.Add Filter and add the following filters.
- Source Type - Users—Filters the list of apps to only display GenAI apps accessed by users in your organization. This is a required filter.
- GenAI Application - TRUE—Filters the list of app to only display GenAI apps. This is a required filter.
- App Risk Score—For the App Risk Score filter, select the specific risk score you want to investigate. All GenAI apps are displays if you don't select at least one risk score.In this example, we are investigating apps with a risk score of 4 and 5 because these are the risk scores attributed to the riskiest apps.
Review the list filtered GenAI apps.Some important information to review is:- Application Name—App-ID of the GenAI app.
- Data Usage—Amount of data uploaded to or downloaded from the GenAI app. This can help you understand the GenAI app usage; a GenAI app with a large volume of data usage could mean that this app is widely used and might need strict controls to prevent exfiltration of sensitive data and malicious actors.
- Tags—Current app tag for the GenAI app. If some of the listed GenAI apps are approved for use, you can modify the tag to Tolerated or Sanctioned.Palo Alto Networks groups the child App-IDs for app functionality in a container App-ID. However, tagging an App-ID container is not supported. You must individually tag the specific child App-ID that are sanctioned, unsanctioned, or tolerated within your organization.
![]() Create a custom Security policy rule to control access to a GenAI app for specific users.For example, based on your investigation you discover that there are multiple unsanctioned GenAI apps with a large volume of data usage. This poses a security risk because there are users accessing an unapproved app on the network and you don't know what data is being downloaded or uploaded. Until you can perform proper due diligence to understand the GenAI app purpose and who is permitted to use the GenAI app, you can Block the GenAI app for all users.Conversely, you notice there are some Unsanctioned GenAI apps listed that but they are GenAI apps approved for use on your network by specific users with a large volume of data usage. In this case, you can change the tag to Sanctioned and write a policy rule to Allow usage of the app but only for users in specific roles or departments. In the policy rule you can associate an Enterprise Data Loss Prevention (E-DLP) data profile to prevent exfiltration of sensitive data and a Vulnerability profile to stop attempts to exploit system flaws or gain unauthorized access to systems.
Create a custom Security policy rule to control access to a GenAI app for specific users.For example, based on your investigation you discover that there are multiple unsanctioned GenAI apps with a large volume of data usage. This poses a security risk because there are users accessing an unapproved app on the network and you don't know what data is being downloaded or uploaded. Until you can perform proper due diligence to understand the GenAI app purpose and who is permitted to use the GenAI app, you can Block the GenAI app for all users.Conversely, you notice there are some Unsanctioned GenAI apps listed that but they are GenAI apps approved for use on your network by specific users with a large volume of data usage. In this case, you can change the tag to Sanctioned and write a policy rule to Allow usage of the app but only for users in specific roles or departments. In the policy rule you can associate an Enterprise Data Loss Prevention (E-DLP) data profile to prevent exfiltration of sensitive data and a Vulnerability profile to stop attempts to exploit system flaws or gain unauthorized access to systems.Discover Risks Posed by GenAI Apps by App Users
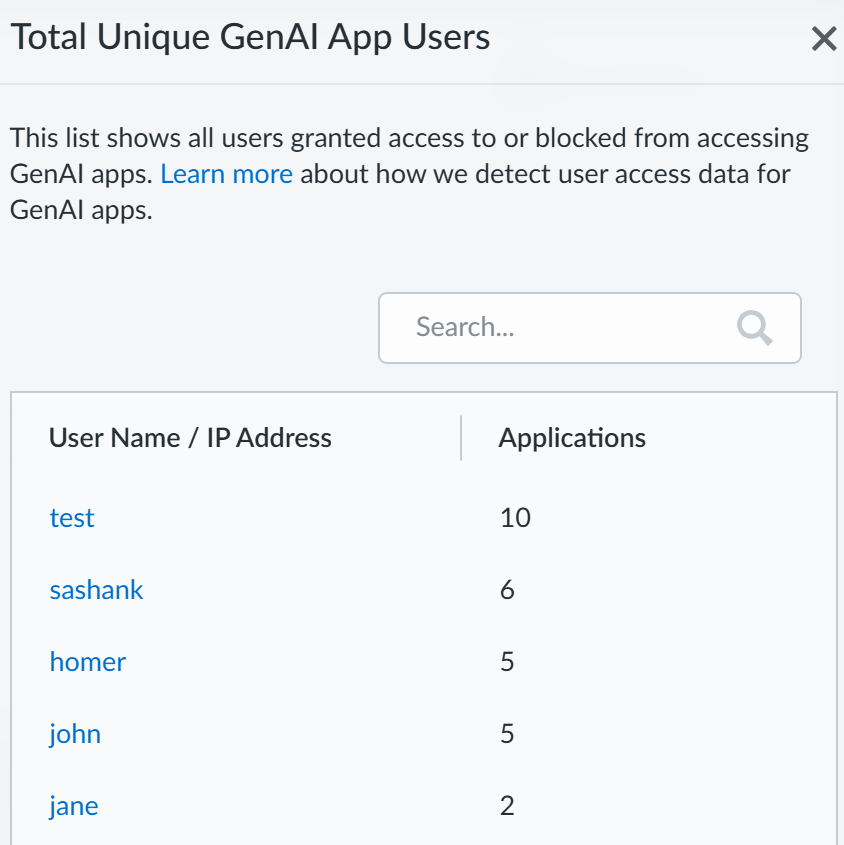
Discover the risks posed by risky users accessing generative AI (GenAI) apps.- Log in to Strata Cloud Manager.Select InsightsAI Access to view the AI Access Security Insights dashboard.This displays the top GenAI apps that risky users accessed to help narrow your focus.Click Review use case for the GenAI app Use Case associated with the GenAI app your risky users are accessing.The AI Access Security Insights dashboard displays the GenAI app accessed on your network by use case by default and displays the following high-level information about your top GenAI app users. Click on the user count o view the User Name or IP Address and the number of GenAI Applications that user accessed.
- User BreakdownThis provides a summary of the total number of users accessing any GenAI app associated with the selected GenAI use case. AI Access Security includes a breakdown of how many users accessed Sanctioned, Tolerated, and Unsanctioned apps.Click total App Users count to view a list of all users who accessed or were blocked from accessing a GenAI app associated with the selected use case.
![]()
- Users by GenAI Use CaseThis provides a summary of the total number of users accessing each individual GenAI app associated with the selected GenAI use case. The Sanctioned, Tolerated, and Unsanctioned GenAI apps are listed with the total user count for each individual app.Review the Allowed Users and Blocked Users counts to measure the effectiveness of your GenAI app security and access policy rules.
- Allowed Users—Total number of users allowed to access the GenAI app. Use this information to measure the effectiveness of your Security policy rule by verifying that the allowed user count matches your expectations, or to gauge the adoption rate of a GenAI app newly allowed for use by your organization.
- Blocked Users—Total number of used blocked from accessing the GenAI app. Use this information to verify whether you configured Security policy rules controlling access for a specific GenAI app correctly, or to understand if users in your organization are accessing unsanctioned GenAI apps.
For example, consider the Grammarly GenAI app below. Your organization classified this GenAI app as Sanctioned for use by specific users within your organization. In this case, your security administrator clicked the Allowed Users count and verified that all users accessing the GenAI app are allowed to do so.Conversely, your security administrator sees that over 1,600 users accessed the Character-Ai-base app. Your security administrators classified this GenAI app as Unsanctioned and intended to restrict all access with your organization. In this case, your security administrator should review your Security policy rulebase and individual Security policy rules controlling access to the Character-Ai-base app to confirm it was positioned correctly within your Security policy rulebase and to confirm it was configured correctly to block all access.
![]() Create a custom Security policy rule to control access to a GenAI app for specific users.For example, based on your investigation you discover that a large number of users are accessing the bing-ai-uploading GenAI app. While this is a Sanctioned GenAI, it's only sanctioned for a specific set of users within your organization. You can decide to write a policy rule to explicitly block access to users who should not have access to this GenAI app to prevent misuse and a Security policy rule to explicitly allow access to users who are approved to access the GenAI app. Alternatively, you can write a policy rule to allow access for all users but implement data loss and threat prevention measures to prevent exfiltration of sensitive data and prevent threats such as malicious and phishing URLs, malicious files, or malware.
Create a custom Security policy rule to control access to a GenAI app for specific users.For example, based on your investigation you discover that a large number of users are accessing the bing-ai-uploading GenAI app. While this is a Sanctioned GenAI, it's only sanctioned for a specific set of users within your organization. You can decide to write a policy rule to explicitly block access to users who should not have access to this GenAI app to prevent misuse and a Security policy rule to explicitly allow access to users who are approved to access the GenAI app. Alternatively, you can write a policy rule to allow access for all users but implement data loss and threat prevention measures to prevent exfiltration of sensitive data and prevent threats such as malicious and phishing URLs, malicious files, or malware.Discover Risks Posed by GenAI Apps Installed as Third-Party Plugins
Discover the risks posed by GenAI apps that users installed as third-party plugins.- Log in to Strata Cloud Manager.Select InsightsAI Access to view the AI Access Security Insights dashboard.The dashboard displays the number of third-party plugins that users installed and the number of users who installed third-party plugins. AI Access Security determines these numbers from all data that AI Access Security has stored. These numbers are not limited to the time period indicated by the time filter.Click Installed Plugins or Plugin Users to navigate to detailed information in SaaS Security Posture Management (SSPM).Clicking Installed Plugins opens the 3rd Party Plugins page showing details about the GenAI third-party plugins. From here, you can review the plugin information to determine if the plugins are a risk.Clicking Plugin Users opens the 3rd Party Plugins page showing details about the users who installed third-party plugins. For each user, you can view how many plugins they have installed, and the marketplace apps in which they have installed plugins. Use this information to identify plugin risks posed by individual users.To view installed plugins by use case, complete the following steps:
- Select InsightsAI Access to view the AI Access Security Insights dashboard.The dashboard prominently displays the top four GenAI app use cases, based on activity on your network. The dashboard also displays icons for the other use cases.Navigate to details about a use case. For a top use case, click Review use case. For other use cases, click the use case icon.The use case details page displays a table of all the GenAI apps for the use case.Summary information on this page includes the number of INSTALLED PLUGINS and the number of PLUGIN USERS. These numbers are determined from all data that AI Access Security has stored and are not limited to the time period indicated by the time filter. For this reason, these totals might not be reflected in the use case details table.In the use case details table, identify GenAI apps that are installed as plugins in one or more marketplace app instances, and the number of plugin users. This information is shown in the Plugins and Plugin Users columns of the table.For a GenAI app that is installed as a plugin, click the number in the Plugins or Plugin Users columns.Clicking the number in the Plugins column opens the 3rd Party Plugins page in SSPM showing the instances of the GenAI app that users installed as third-party plugins. From here, you can review the plugin information to determine if the plugins are a risk.Clicking the number in the Plugin Users column opens the 3rd Party Plugins page showing details about the users who installed the app as a third-party plugin. Use this information to identify plugin risks posed by individual users.
Discover Risks Posed by GenAI Apps on Prisma Browser
Discover the risks posed by GenAI apps on standalone Prisma Browser.Prisma Browser is embedded with AI Access Security to provide comprehensive GenAI app visibility, access control, data, and threat protection to Prisma Browser standalone customers. This integration delivers the most comprehensive catalog of GenAI apps with deep last mile controls such as data classification and real-time threat defense. As a Prisma Browser standalone security administrator, you can access AI Access Security under the Insights menu to monitor third party AI application usage through Prisma Browser with detailed analytics including application metrics, user activity, threats detected, and data transfers.![]()
- Log in to Strata Cloud Manager.Select InsightsAI Access to view the AI Access Security Insights dashboard for standalone Prisma Browser.Click GenAI Apps to view the Application metrics with the Is GenAI:Yes and Category: Access filter applied to view the following metrics:
- Total GenAI Apps
- Allowed GenAI Apps
- Blocked GenAI Apps
![]() Click Unique GenAI Users to view the total GenAI app users granted access to or blocked from accessing GenAI apps. Select the user (from the Total Unique GenAI App Users page) to navigate to the Events page (with the User: <user name> filter applied) to know GenAI apps allowed and blocked for that particular user. Metrics available are:
Click Unique GenAI Users to view the total GenAI app users granted access to or blocked from accessing GenAI apps. Select the user (from the Total Unique GenAI App Users page) to navigate to the Events page (with the User: <user name> filter applied) to know GenAI apps allowed and blocked for that particular user. Metrics available are:- Total GenAI Users
- Allowed GenAI Users
- Blocked GenAI Users
![]()
![]() Click on the Threats Detected widget to view the total threats detected and blocked.This information is available in the Events page (with the Is GenAI:Yes, Category: Malware filter applied). Metrics available are:
Click on the Threats Detected widget to view the total threats detected and blocked.This information is available in the Events page (with the Is GenAI:Yes, Category: Malware filter applied). Metrics available are:- Total GenAI Threats that display the total threats detected and blocked.
- Malicious URLs (Filter applied: Category: Malware and Type: Malicious website)
- Files (Filter applied: Category: Malware and Type: Malicious file identified)
![]() Click on the Data Transfers widget to view the number of incidents of data transfers detected when traffic matches the match criteria in your Enterprise Data Loss Prevention (E-DLP) data profile for your Prisma Browser.This information is available in the Events page (with the Is GenAI:Yes, Category: DLP filter applied).
Click on the Data Transfers widget to view the number of incidents of data transfers detected when traffic matches the match criteria in your Enterprise Data Loss Prevention (E-DLP) data profile for your Prisma Browser.This information is available in the Events page (with the Is GenAI:Yes, Category: DLP filter applied).- Total data transfers detected. Filter applied: Is GenAI:Yes, Category: DLP.
- Data transfers alerted. Filter applied: Is GenAI:Yes, Category: DLP, Action: Allowed.
- Data transfers blocked. Filter applied: Is GenAI:Yes, Category: DLP, Action: Blocked.
- Data transfers protected: Action that is allowed but can only be used by the browser. For example, enabling copy and pasting data between sanctioned apps, and blocking it to other apps in the browser or local desktop apps. Filter applied: Is GenAI:Yes, Category: DLP, Action: Allowed Protected.
- Data transfers encrypted: An encryption action for which only the browser has the decryption key for the specific user and the device it was encrypted by. This allows downloading files and making sure they are allowed to be uploaded (and decrypted) to specific apps, or opened in the browser on offline mode. No other app can open the file, which makes it ideal for files that you don't want to be available on the endpoint, for example, on unmanaged devices. Filter applied: Is GenAI:Yes, Category: DLP, Action: Allowed Encrypted.
- Just-in-time controls on data transfers: Actions that include warning the user before proceeding, asking the user to provide business justification before proceeding, or triggering an admin approval flow. Those trigger temporary access or bypass to rules during emergency situations or justification and logging are required for compliance reasons. Filter applied: Is GenAI:Yes, Category: DLP, Action: Permission Requested.
- Data transfers uploaded. Filter applied: Is GenAI:Yes, Category: DLP, Type: File upload.
- Data transfers in a clipboard activity (Pasting). Filter applied: Is GenAI:Yes, Category: DLP, Type: Clipboard Paste.
- Data transfers typed at the moment. Filter applied: Is GenAI:Yes, Category: DLP, Type: Sanitizing Content.
- Data transfers downloaded. Filter applied: Is GenAI:Yes, Category: DLP, Type: File download.
- Data transfers copied. Filter applied: Is GenAI:Yes, Category: DLP, Type: Clipboard Copy.
- Data transfers shared using a screenshot. Filter applied: Is GenAI:Yes, Category: DLP, Type: Screen share.
- Data transfers printed. Filter applied: Is GenAI:Yes, Category: DLP, Type: Print.
![]()