Mobile Network Security Support on New Mid-Range Hardware Platforms
Table of Contents
10.2
Expand all | Collapse all
-
- CN-Series Firewall as a Kubernetes CNF
- High Availability Support for CN-Series Firewall as a Kubernetes CNF
- High Availability Support for CN-Series Firewall on AWS EKS
- DPDK Support for CN-Series Firewall
- Daemonset(vWire) IPv6 Support
- Panorama Plugin for Kubernetes 3.0.0
- L3 IPV4 Support for CN-Series
- 47 Dataplane Cores Support for VM-Series and CN-Series Firewalls
- Memory Scaling of the VM-Series Firewall
Mobile Network Security Support on New Mid-Range Hardware Platforms
Private 5G networks and multi-access edge computing
(MEC) can present security concerns for enterprises and can increase
the attack surface for malicious actors. As a wider range of enterprises,
including manufacturing, energy, utilities, logistics, real estate,
and healthcare, transition to private 5G technologies, the need
for enterprise-grade security that can deploy zero-trust architecture
in 5G increases.
You can now protect your MEC and private 5G environments with
the industry’s only 5G-native security using the Palo Alto Networks
next-generation firewall. On the latest mid-size next-generation
firewalls, Palo Alto Networks now supports mobility protocols with
mobile identifiers like subscriber ID (the International Mobile Subscriber
Identifier or IMSI) and equipment ID (the International Mobile Equipment
Identifier or IMEI) for enhanced visibility and security policy
enforcement. This allows enterprise IT security teams to extend
their enterprise-grade security to their 5G or 4G/LTE mobile networks.
The new firewalls support the following mobility security features
for MEC and private 5G network deployments:
The following diagrams depict a selection of supported scenarios
that highlight some of the potential applications for this new capability.
In the following deployment scenario of a private 4G/LTE network,
the 4G core is located on-premises. To enforce security policy for
user and control traffic, the firewall must be positioned on the
4G/LTE interfaces, including the User Plane (S1-U) and the Control
Plane (S11).
The
second firewall in this diagram is positioned on the perimeter (the
SGI interface connected to the internet and the enterprise IT datacenter).
For complete subscriber-level
and equipment-level visibility and security policy control for network
traffic threats, enable GTP Security.

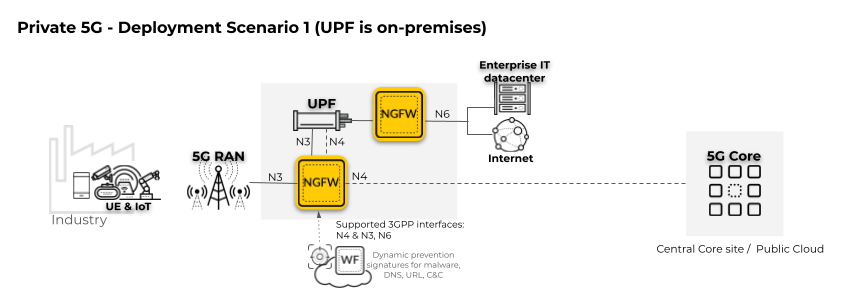
In the following private 5G network deployment scenario, only
the User Plane Function (UPF) is located on-premises. The 5G Core
is located remotely in a central core site or public cloud. To enforce
security policy for user and control traffic, the firewall must
be positioned on the 5G interfaces, including the User Plane (N3) and
Control Plane (N4).
The
second firewall in the diagram is positioned on the perimeter (the
N6 interface connected to the internet and the enterprise IT datacenter).
For complete subscriber-level
and equipment-level visibility and security policy control for network
traffic threats, enable GTP Security.
In the following private 5G network deployment scenario, the
5G Core, including the User Plane Function (UPF), is located on-premises.
The 5G Core includes network functions (NFs) such as Session Management (SMF)
and Access and Mobility Management Function (AMF), as well as others.
To enforce security policy for user and control traffic, the firewall
must be positioned on the 5G interfaces, including the User Plane
(N3) and the Control Plane (N4).
The
second firewall in the diagram is positioned on the perimeter (the
N6 interface connected to the internet and the enterprise IT datacenter).
For complete
subscriber-level and equipment-level visibility and security policy control
for network traffic threats, enable GTP Security. Apply security
policy to the Control Plane (N2) between the 5G RAN and the 5G Core
for signaling protection by enabling SCTP Security.

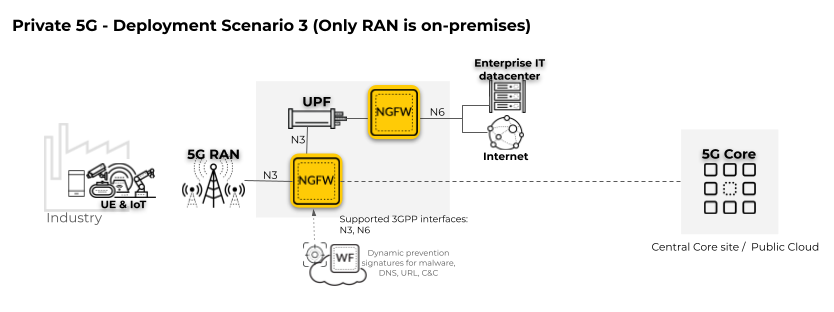
In the following private 5G network deployment scenario, only
the Radio Access Network (RAN) is located on-premises.
The
firewall must be positioned on the 5G interface for the User Plane
(N3).
To apply security policy to user traffic,
enable Tunnel Content Inspection.
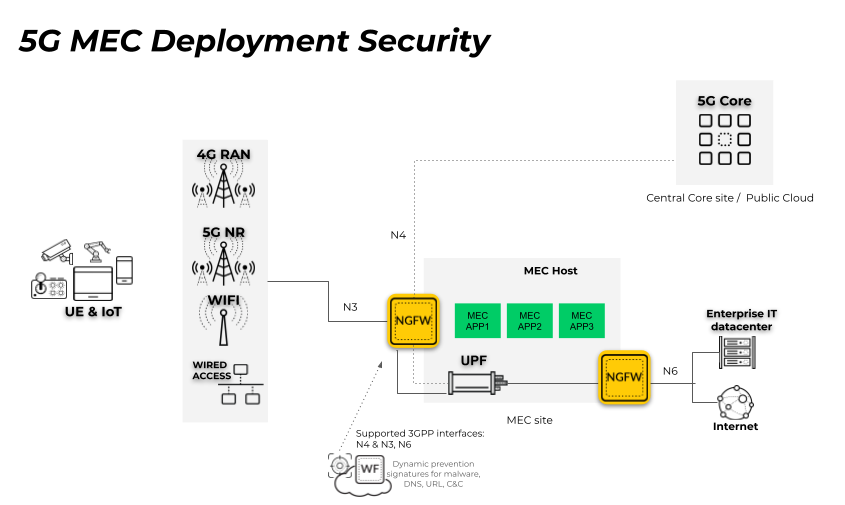
In the following 5G MEC deployment scenario, the User Plane Function
(UPF) is located on the MEC in the service provider’s edge location
or on the public cloud edge and the 5G Core is located remotely
in a central core site or the public cloud. To enforce security
policy for user and control traffic, the firewall must be positioned
on the 5G interfaces, including the User Plane (N3) and the Control
Plane (N4).
The
second firewall in the diagram is positioned on the perimeter (the
N6 interface connected to the internet and the enterprise IT datacenter).
For complete subscriber-level
and equipment-level visibility and security policy control for network
traffic threats, enable GTP Security.