Prisma Access
Configure a Service Connection in Prisma Access (Strata Cloud Manager)
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma Access Docs
-
- 6.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 6.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 4.2 Preferred
- 4.1 Preferred
- 4.0 Preferred
- 3.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 2.2 Preferred
-
-
- 4.0 & Later
- Prisma Access China
-
-
Configure a Service Connection in Prisma Access (Strata Cloud Manager)
Configure service connections for Prisma Access (Managed by Strata Cloud Manager).
To configure a service connection for Prisma Access (Managed by Strata Cloud Manager) to allow access
to private apps or internal corporate resources, complete the following steps.
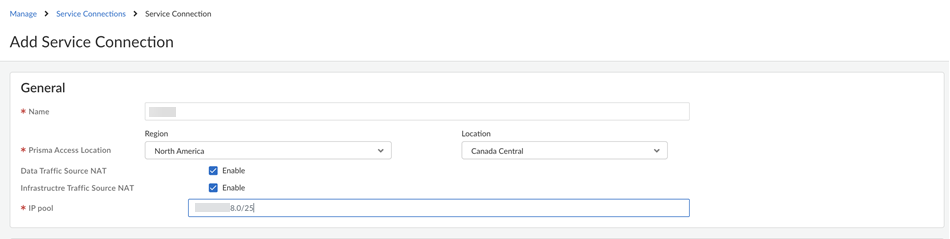
- Select ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessConfiguration ScopePrisma AccessService Connections and Add Service Connection.Give the service connection a descriptive Name.Select the Prisma Access Location where your HQ or data center is located.(Optional) Enable source NAT for Mobile Users—GlobalProtect IP pool addresses, IP addresses in the Infrastructure subnet, or both.You can specify a subnet at one or more service connections that are used to NAT traffic between Prisma Access GlobalProtect mobile users and private applications and resources at a data center.
- Data Traffic source NAT—Performs NAT on Mobile User IP address pool addresses so that they are not advertised to the data center, and only the subnets you specify at the service connections are advertised and routed in the data center.
- Infrastructure Traffic source NAT—Performs NAT on addresses from the Infrastructure subnet so that they are not advertised to the data center, and only those subnets you specify at the service connections are advertised and routed in the data center.
- User-ID—When selected, Prisma Access uses this service connection for identity redistribution.User-ID Redistribution Management—Sometimes, granular controls are needed for user-ID redistribution in particularly large scale Prisma Access deployments. User-ID Redistribution Management lets you manually disable the default identity redistribution behavior for certain service connections by removing the check mark in the User ID column, and then select specific service connections to be used for identity redistribution. It's not necessary to do this for most configurations. Contact Palo Alto Networks support to activate this functionality.
- Source NAT Pool—Specify the IP address pool used to perform NAT on the mobile user IP address pool, Infrastructure subnet, or both.
- Use a private IP (RFC 1918) subnet or a suitable subnet that is routable in your routing domain.
- Make sure that the subnet does not overlap with the Mobile Users—GlobalProtect IP address pool, the Infrastructure subnet, or any other source NAT addresses used for this tenant.
- Enter a subnet between /25 and /32.
![]() Select an IPSec Tunnel. If you have not yet set up a primary or secondary IPSec Tunnel, Set Up and follow the steps below.
Select an IPSec Tunnel. If you have not yet set up a primary or secondary IPSec Tunnel, Set Up and follow the steps below.- Give the tunnel a descriptive Name.Select the Branch Device Type for the IPSec device and the HQ or data center that you’re using to establish the tunnel with Prisma Access.For the Branch Device IP Address, choose to use either a Static IP address that identifies the tunnel endpoint or a Dynamic IP address.If you set the Branch Device IP Address to Dynamic, you must also add the IKE ID for the HQ or data center (IKE Local Identification) or for Prisma Access (IKE Peer Identification) to enable the IPSec peers to authenticate.Because you don't have the values to use for the Prisma Access IKE ID (IKE Peer Identification) until the service connection is fully deployed, you would typically want to set the IKE ID for the HQ or data center (IKE Local Identification) rather than the Prisma Access IKE ID.Turn on Tunnel Monitoring.Enter a Tunnel Monitoring Destination IP address on the HQ or data center network for Prisma Access to determine whether the tunnel is up and, if your branch IPSec device uses a policy-based VPN, enter the associated Proxy ID.The tunnel monitoring IP address you enter is automatically added to the list of branch subnetworks.Save the tunnel settings.To add or adjust routing and Quality of Service settings, go to ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessConfiguration ScopePrisma AccessService Connections and Add Service Connection. Set Up or Edit the Routing or QoS settings.Configure static routes.
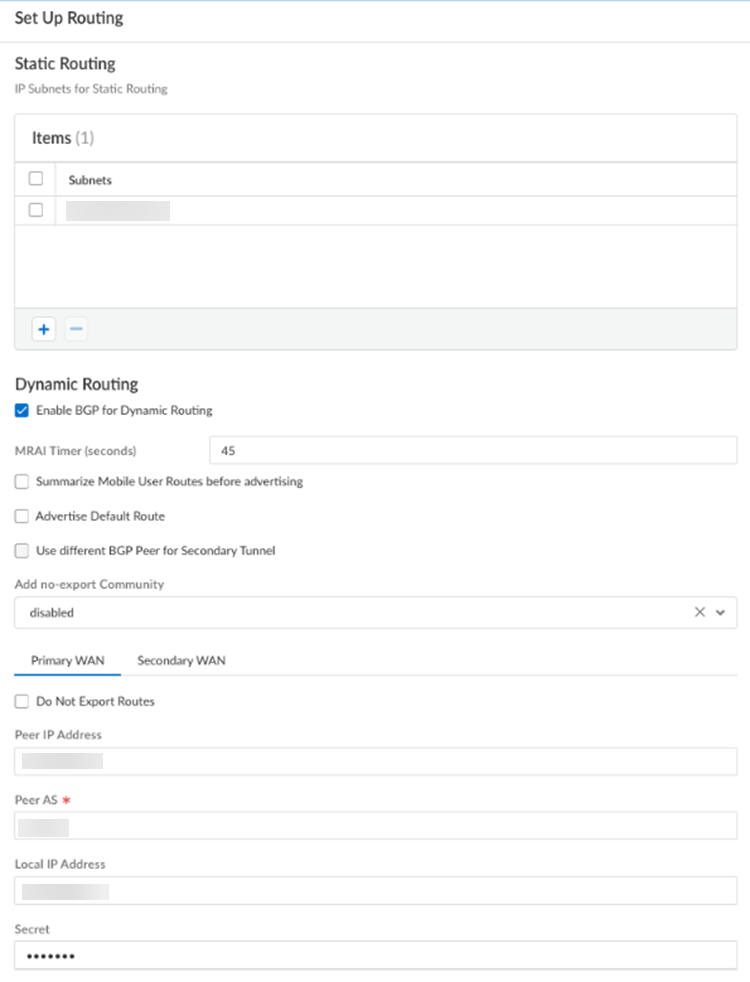
- For static routes to route traffic to and from your HQ or data center, Add the IP subnets or IP addresses that you want to secure at the branch.If you make any changes to the IP subnets on your HQ or data center network, you must manually update the static routes.Configure dynamic routing.
- For dynamic routing to advertise HQ or data center subnets, Enable BGP for Dynamic Routing.(Optional) Select an MRAI Timer value.BGP routing offers a timer you can use to tailor BGP routing convergence in your network called the Minimum Route Advertisement Interval (MRAI). MRAI acts to rate-limit updates on a per-destination basis, and the BGP routers wait for at least the configured MRAI time before sending an advertisement for the same prefix. A smaller number gives you faster convergence time but creates more advertisements in your network. A larger number decreases the number of advertisements that can be sent, but can also make routing convergence slower. You decide the number to put in your network for the best balance between faster routing convergence and fewer advertisements.Configure an MRAI range of between 1 and 600 seconds, with a default value of 30 seconds.Prisma Access does not honor the Multi-Exit Discriminator (MED) attributes advertised by the CPE. This caveat applies if you use multiple BGP peers on either remote network connections or service connections and whether or not you select a secondary (backup) connection.To reduce the number of mobile user IP subnet advertisements over BGP to your customer premises equipment (CPE), specify Prisma Access to summarize the subnets before it advertises them by selecting Summarize Mobile User Routes before advertising.By default, Prisma Access advertises the mobile users IP address pools in blocks of /24 subnets; if you summarize them, Prisma Access advertises the pool based on the subnet you specified. For example, Prisma Access advertises a public user mobile IP pool of 10.8.0.0/20 using the /20 subnet, rather than dividing the pool into subnets of 10.8.1.0/24, 10.8.2.0/24, 10.8.3.0/24, and so on, before advertising them. Summarizing these advertisements can reduce the number of routes stored in CPE routing tables. For example, you can use IP pool summarization with cloud VPN gateways (Virtual Private Gateways (VGWs) or Transit Gateways (TGWs)) that can accept a limited number of routes.(Optional) to have Prisma Access originate a default route advertisement for the remote network using eBGP, select Advertise the Default Route. Be sure that your network does not have another default route being advertised by BGP, or you could introduce routing issues in your network.(Optional) If you configured a secondary WAN and you need to change the peer address for the secondary (backup) BGP peer, select Use different BGP Peer for Secondary Tunnel and enter a unique Peer and, optionally, Local IP address for the secondary WAN.To add a community from service connections to the outbound prefixes from the eBGP peers at the customer premises equipment (CPE), set Add no-export community to Enabled Out. This capability is Disabled by default.Do not select Enabled In or Enabled Both as these choices are not supported.(Optional) Select Do Not Export Routes to prevent Prisma Access from forwarding routes into the HQ or data center.By default, Prisma Access advertises all BGP routing information, including local routes and all prefixes it receives from other service connections, remote networks, and mobile user subnets. Select this check box to prevent Prisma Access from sending any BGP advertisements, but still use the BGP information it receives to learn routes from other BGP neighbors.Because Prisma Access does not send BGP advertisements, if you select this option you must configure static routes on your on-premises equipment to establish routes back to Prisma Access.Enter the Peer IP Address assigned as the Router ID of the eBGP router on the HQ or data center network.Enter the Peer AS, the autonomous system (AS) for your network.Use and RFC 6996-compliant BGP Private AS number.Enter the Local IP Address that Prisma Access uses as its Local IP address for BGP.A local address is only required if your HQ or data center device requires it for BGP peering to be successful. Make sure the address you specify does not conflict or overlap with IP addresses in the infrastructure subnet or subnets in the remote network.Enter a Secret password to authenticate BGP peer communications.Select Confirm Secret.
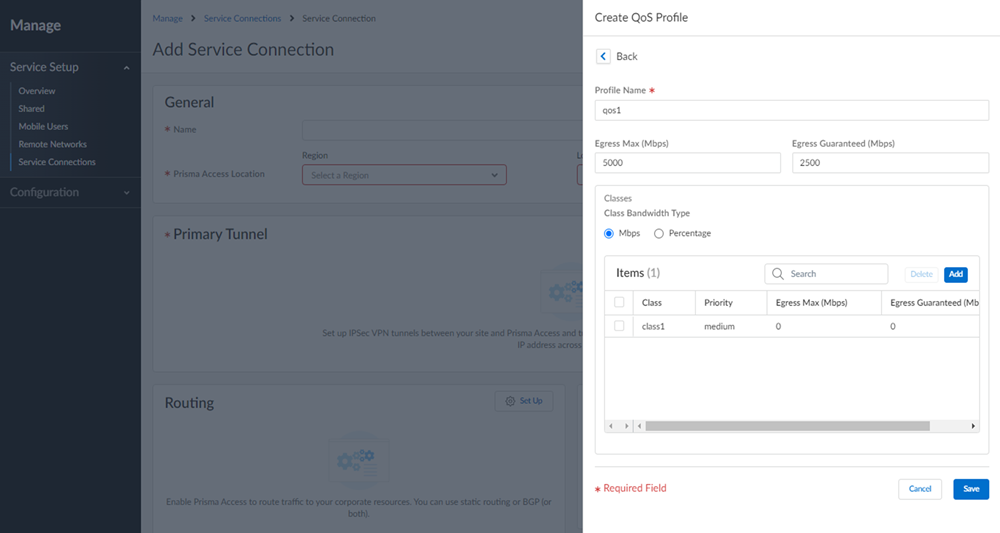
![]() (Optional) Configure QoS.To start, add a QoS Profile to define the QoS classes that will shape traffic between the HQ or data center and Prisma Access. You’ll then create a QoS policy rule and add the profile to the rule, to enforce QoS on matching HQ or data center traffic.
(Optional) Configure QoS.To start, add a QoS Profile to define the QoS classes that will shape traffic between the HQ or data center and Prisma Access. You’ll then create a QoS policy rule and add the profile to the rule, to enforce QoS on matching HQ or data center traffic.![]()
- Enter a name for your QoS Profile.Select Create New.Set the maximum throughput (in Mbps) for traffic leaving the HQ or data center service connection as the Egress Max.You can specify a value up to the maximum licensed bandwidth of your HQ or data center.Set the guaranteed bandwidth as the Egress Guaranteed (in Mbps).Any traffic that exceeds the Egress Guaranteed value is best effort but not guaranteed. Any bandwidth that is guaranteed but unused remains available to all traffic.Define each QoS Class and attach it to a policy rule.A QoS class determines the priority and bandwidth for traffic matching a QoS policy rule. There are up to eight definable QoS classes in a single QoS Profile. Unless otherwise configured, traffic that does not match a QoS class is assigned a class of 4.Configure the Priority of a QoS Class.Priorities include real-time, high, medium, or low.Configure the Egress Max value.The egress max value for a QoS class, or the combined egress max values for multiple QoS classes, must not exceed the egress max value for the QoS Profile.Configure the Egress Guaranteed value.The guaranteed bandwidth assigned to the QoS class isn't reserved for that class; unused bandwidth remains available to all traffic. Any class traffic that exceeds the egress-guaranteed value is best effort but not guaranteed.Configure Advanced Settings for your service connection.
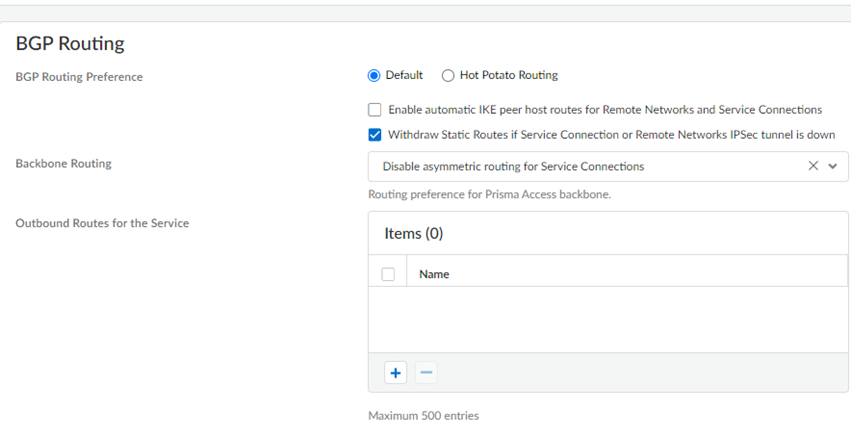
![]()
- Specify the BGP Routing Preferences to use with service connections.You can specify network preferences to use either your organization’s network, or the Prisma Access network, to process the service connection traffic.
- Default—Prisma Access uses default routing in its internal network.
- Hot potato routing—Prisma Access hands off service connection traffic to your organization’s WAN as quickly as possible.
Changing the Prisma Access service connection routing method requires a thorough understanding of your organization’s topology and routing devices, along with an understanding of how Prisma Access routing works. We recommend that you read Routing for Service Connection Traffic carefully before changing the routing method from default.Withdraw Static Routes if Service Connection or Remote Network IPSec tunnel is down if you want Prisma Access to remove static routes when a tunnel goes down without a backup tunnel.This functionality is enabled by default for Prisma Access (Managed by Strata Cloud Manager) deployments.Prisma Access removes the route in the following situations:- The primary tunnel goes down and there is no secondary tunnel.
- If a primary and secondary tunnel are configured, but both go down.
You cannot apply this change if tunnel monitoring is not enabled.Note the behavior of tunnels if this feature is enabled or disabled and that the behavior for dual tunnel deployments is unchanged.Withdraw Static Routes Enabled Withdraw Static Routes Disabled Single tunnel deployments: The static route is withdrawn.Dual tunnel deployments: The static route is withdrawn for failover purposes between the primary and secondary Tunnel.Single tunnel deployments: The static route is not withdrawn.Dual tunnel deployments: The static route is withdrawn for failover purposes between the primary and secondary Tunnel.Configure the Backbone Routing to use for the service connections.By default, the Prisma Access backbone requires that you have a symmetric network path for the traffic returning from the data center or headquarters location by way of a service connection. If you want to use ECMP or another load balancing mechanism for service connections from your CPE, you can enable asymmetric flows through the Prisma Access backbone.- Select Disable asymmetric routing for Service Connections to require symmetric flows across the service connection backbone.
- Select Allow asymmetric routing for Service Connections to allow Prisma Access to use asymmetric flows across the service connection backbone.
- If you have multiple service connections to a location, you can take advantage of load balancing in your Prisma Access deployment by selecting Allow asymmetric routing and load sharing across Service Connections (the default setting). However, load balancing is done on a best-effort basis, and load balancing will fail if one of the service connections goes down.When you select Allow asymmetric routing and load sharing across Service Connections, Prisma Access enables network redundancy between the GlobalProtect portals and gateways and service connections. This functionality provides redundant network paths between the mobile user dataplane and service connections in different compute locations. Enabling redundancy provides users with more resilient access to resources behind service connections in a data center or headquarters locations. Because a service connection is required for mobile users to access resources from remote networks, users also have more resiliency in accessing resources in remote network locations.
(Optional) Specify Outbound Routes for the Service by adding up to 500 prefixes for which Prisma Access adds static routes on all service connections and remote network connections. Prisma Access then routes traffic to these prefixes over the internet.![]()
More IKE Options
Based on the IPSec device type you selected, Prisma Access provides a recommended set of ciphers and a key lifetime for the IKE Phase 1 key exchange process between the device at your HQ/DC and Prisma Access. You can use the recommended settings, or customize the settings as needed for your environment.- Select an IKE Protocol Version for your IPSec device and Prisma Access to use for IKE negotiation.If you select IKEv1 Only Mode, Prisma Access can use only the IKEv1 protocol for the negotiation. If you select IKEv2 Only Mode, Prisma Access can use only the IKEv2 protocol for the negotiation. If you select IKEv2 Preferred Mode, Prisma Access uses the IKEv2 protocol only if your IPSec device also supports IKEv2. If your IPSec device does not support IKEv2, Prisma Access falls back to using the IKEv1 protocol.Add an IKEv1 Crypto Profile to customize the IKE crypto settings that define the encryption and authentication algorithms used for the key exchange process in IKE Phase 1.Prisma Access automatically uses a default IKE Crypto profile based on the Branch Device Type that’s being used to establish this tunnel.
- Encryption—Specify the encryption algorithm used in the IKE SA negotiation.Prisma Access supports the following encryption algorithms: 3des (168 bits), aes-128-cbc (128 bits), aes-192-cbc (192 bits), aes-256-cbc (256 bits), and DES (56 bits). You can also select null (no encryption).
- Authentication—Specify the authentication algorithm used in the IKE SA negotiation.Prisma Access supports the following authentication algorithms: sha1 (160 bits), sha256 (256 bits), sha384 (384 bits), sha512 (512 bits), and md5 (128 bits). You can also select null (no authentication).
- DH Group—Specify the Diffie-Hellman (DH) groups used to generate symmetrical keys for IKE in the IKE SA negotiation. The Diffie-Hellman algorithm uses the private key of one party and the public key of the other to create a shared secret, which is an encrypted key that both VPN tunnel peers share.Prisma Access supports the following DH groups: Group 1 (768 bits), Group 2 (1,024 bits—default), Group 5 (1,536 bits), Group 14 (2,048 bits), Group 19 (256-bit elliptic curve group), and Group 20 (384-bit elliptic curve group). For the strongest security, select the group with the highest number.
- Lifetime—Specify the unit and amount of time for which the IKE Phase 1 key is valid (default is 8 hours). For IKEv1, the security association (SA) isn't actively re-keyed before the key lifetime expires. The IKEv1 Phase 1 re-key triggers only when the SA expires. For IKEv2, the SA must be re-keyed before the key lifetime expires. If the SA isn't re-keyed upon expiration, the SA must begin a new Phase 1 key.
- IKEv2 Authentication Multiple—Specify the value that is multiplied by the key lifetime to determine the authentication count (range is 0-50; default is 0). The authentication count is the number of times that the security processing node can perform IKEv2 IKE SA re-key before it must start over with IKEv2 reauthentication. The default value of 0 disables the reauthentication feature.
Enable IKE Passive Mode so that Prisma Access only response to IKE connections and does not initiate them.IKE NAT Traversal is turned on by default.This means that UDP encapsulation is used on IKE and UDP protocols, enabling them to pass-through network address translation (NAT) devices that are between the IPSec VPN tunnel endpoints.More IPSec Options
Based on the IPSec device type you selected, Prisma Access provides a recommended set of IPSec protocol and key lifetime settings to secure data within the IPSec tunnel between your IPSec device and Prisma Access in IKE Phase 2 for the security association (SA). You can use the recommended settings, or customize the settings as needed for your environment.- Customize the IPSec Crypto Profile to define how data is secured within the tunnel when Auto Key IKE automatically generates keys for the IKE SAs during IKE Phase 2.Prisma Access automatically configures a default IPSec Crypto profile based on the Branch Device Type vendor. You can either use the default profile or create a custom profile.
- IPSec Protocol—Secure the data that traverses the VPN tunnel. The Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) protocol encrypts the data, authenticates the source, and verifies the data integrity. The Authentication Header (AH) protocol authenticates the source and verifies the data integrity.If you use ESP as the IPSec protocol, also specify the Encryption algorithm used in the IPSec SA negotiation.Prisma Access supports the following encryption algorithms: aes-256-gcm (256 bits), aes-256-cbc (256 bits), aes-192-cbc (192 bits), aes-128-gcm (128 bits), aes-128-cbc (128 bits), 3des (168 bits), and DES (56 bits). You can also select null (no encryption).
Authentication—Specify the authentication algorithm used in the IPSec SA negotiation.Prisma Access supports the following authentication algorithms: sha1 (160 bits), sha256 (256 bits), sha384 (384 bits), sha512 (512 bits), and md5 (128 bits). If you set the IPSec Protocol to ESP, you can also select none (no authentication).DH Group—Specify the Diffie-Hellman (DH) groups for IKE in the IPSec security association (SA) negotiation.Prisma Access supports the following DH groups: Group 1 (768 bits), Group 2 (1,024 bits—default), Group 5 (1,536 bits), Group 14 (2,048 bits), Group 19 (256-bit elliptic curve group), and Group 20 (384-bit elliptic curve group). For the strongest security, select the group with the highest number. If you don’t want to renew the key that Prisma Access creates during IKE phase 1, select no-pfs (no perfect forward secrecy). If you select this option, Prisma Access reuses the current key for the IPSec SA negotiation.Lifetime—Specify the unit and amount of time during which the negotiated key is valid (default is 1 hour).Lifesize—Specify the unit and amount of data that the key can use for encryption.Verify Service Connection Status
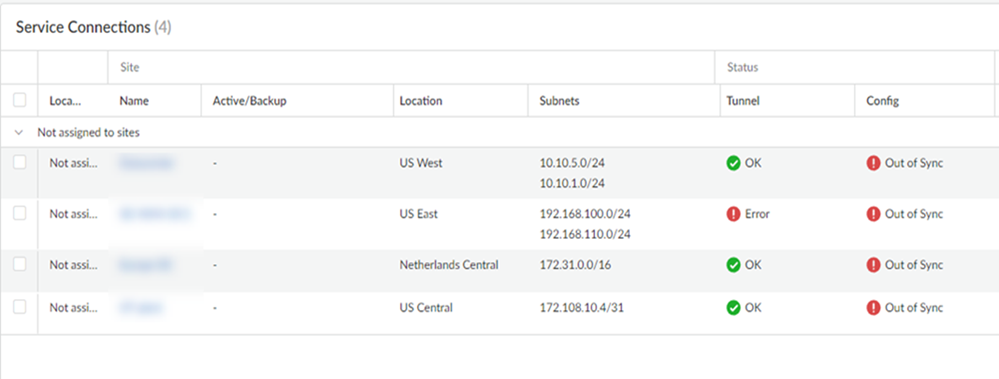
To verify that the service connection has been successfully set up, select ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessConfiguration ScopePrisma AccessService Connectionsand check that the Status is OK.If the status isn't OK, hover over the Status icon to view any errors.![]() The Sites area allows you to view all onboarded service connections, along with their status and other details about them.Site
The Sites area allows you to view all onboarded service connections, along with their status and other details about them.Site- Name—The name of the service connection.
- Active/Backup—The active and backup locations of the service connection.
- Subnets—The assigned infrastructure subnets of the service connection.
Status- Tunnel—The operational status of the connection between Prisma Access and your service connection.
- Config—The status of your last configuration push to service. If the local configuration and the configuration in the cloud match, the Config Status is In sync. If you have made a change locally, and not yet pushed the configuration to the cloud, this may display the status Out of sync. Hover over the status indicator for more detailed information. After committing and pushing the configuration to Prisma Access, the Config Status changes to In sync.
Prisma Access- Location—The location where the service connection is deployed.
- Service IP—The IP address of the service connection.
- EBGP Router—The IP address of the EBGP Router in the service connection.
Links- BGP IPv4—The status of the BGP IPv4 routing in the service connection.
- BGP IPv6—The status of the BGP IPv6 routing in the service connection.
- IPSec Tunnel—The IPSec tunnel of your service connection. The first IPSec tunnel you establish will be the (Primary) tunnel. If you established a second IPSec tunnel it will be the (Secondary) tunnel.
- Peer IP Address—The gateway IP address of the service connection.