Create a Custom Threat Signature from a Snort Signature
Table of Contents
Expand all | Collapse all
-
- About Custom Application Signatures
- Create a Custom Application Signature
- Create a Custom L3 & L4 Vulnerability Signature
- Import a Custom Threat Signature from Snort and Suricata Rules
- Test a Custom Signature
- Custom Signature Pattern Requirements
- Testing Pattern Performance Impact
-
-
- dhcp-req-chaddr
- dhcp-req-ciaddr
- dhcp-rsp-chaddr
- dhcp-rsp-ciaddr
- dns-req-addition-section
- dns-req-answer-section
- dns-req-authority-section
- dns-req-header
- dns-req-protocol-payload
- dns-req-section
- dns-rsp-addition-section
- dns-rsp-answer-section
- dns-rsp-authority-section
- dns-rsp-header
- dns-rsp-protocol-payload
- dns-rsp-ptr-answer-data
- dns-rsp-queries-section
- email-headers
- file-data
- file-elf-body
- file-flv-body
- file-html-body
- file-java-body
- file-mov-body
- file-office-content
- file-pdf-body
- file-riff-body
- file-swf-body
- file-tiff-body
- file-unknown-body
- ftp-req-params
- ftp-req-protocol-payload
- ftp-rsp-protocol-payload
- ftp-rsp-banner
- ftp-rsp-message
- gdbremote-req-context
- gdbremote-rsp-context
- giop-req-message-body
- giop-rsp-message-body
- h225-payload
- http-req-cookie
- http-req-headers
- http-req-host-header
- http-req-host-ipv4-address-found
- http-req-host-ipv6-address-found
- http-req-message-body
- http-req-mime-form-data
- http-req-ms-subdomain
- http-req-origin-headers
- http-req-params
- http-req-uri
- http-req-uri-path
- http-req-user-agent-header
- http-rsp-headers
- http-rsp-non-2xx-response-body
- http-rsp-reason
- icmp-req-code
- icmp-req-data
- icmp-req-type
- icmp-req-protocol-payload
- icmp-rsp-data
- icmp-rsp-protocol-payload
- icmp-req-possible-custom-payload
- ike-req-headers
- ike-rsp-headers
- ike-req-payload-text
- ike-rsp-payload-text
- imap-req-cmd-line
- imap-req-first-param
- imap-req-params-after-first-param
- imap-req-protocol-payload
- imap-rsp-protocol-payload
- irc-req-params
- irc-req-prefix
- jpeg-file-scan-data
- jpeg-file-segment-data
- jpeg-file-segment-header
- ldap-req-searchrequest-baseobject
- ldap-rsp-searchresentry-objectname
- ms-ds-smb-req-share-name
- ms-ds-smb-req-v1-create-filename
- ms-ds-smb-req-v2-create-filename
- msrpc-req-bind-data
- mssql-db-req-body
- netbios-dg-req-protocol-payload
- netbios-dg-rsp-protocol-payload
- netbios-ns-req-protocol-payload
- netbios-ns-rsp-protocol-payload
- nettcp-req-context
- oracle-req-data-text
- pe-dos-headers
- pe-file-header
- pe-optional-header
- pe-section-header
- pe-body-data
- pop3-req-protocol-payload
- pop3-rsp-protocol-payload
- pre-app-req-data
- pre-app-rsp-data
- rtmp-req-message-body
- rtsp-req-headers
- rtsp-req-uri-path
- sip-req-headers
- snmp-req-community-text
- smtp-req-argument
- smtp-rsp-content
- smtp-req-protocol-payload
- smtp-rsp-protocol-payload
- ssh-req-banner
- ssh-rsp-banner
- ssl-req-certificate
- ssl-req-chello-sni
- ssl-req-client-hello
- ssl-req-protocol-payload
- ssl-req-random-bytes
- ssl-rsp-cert-subjectpublickey
- ssl-rsp-certificate
- ssl-rsp-protocol-payload
- ssl-rsp-server-hello
- tcp-context-free
- telnet-req-client-data
- telnet-rsp-server-data
- udp-context-free
- unknown-req-tcp-payload
- unknown-rsp-tcp-payload
- unknown-req-udp-payload
- unknown-rsp-udp-payload
-
- dnp3-req-func-code
- dnp3-req-object-type
- dns-rsp-tcp-over-dns
- dns-rsp-txt-found
- ftp-req-params-len
- http-req-connect-method
- http-req-content-length
- http-req-cookie-length
- http-req-dst-port
- http-req-header-length
- http-req-param-length
- http-req-no-host-header
- http-req-no-version-string-small-pkt
- http-req-simple-request
- http-req-uri-path-length
- http-req-uri-tilde-count-num
- http-rsp-code
- http-rsp-content-length
- http-rsp-total-headers-len
- iccp-req-func-code
- ike-req-payload-type
- ike-rsp-payload-type
- ike-req-payload-length
- ike-rsp-payload-length
- ike-version
- imap-req-cmd-param-len
- imap-req-first-param-len
- imap-req-param-len-from-second
- irc-req-protocol-payload
- irc-rsp-protocol-payload
- ntlm-req-auth-v1
- ntlm-req-auth-v2
- open-vpn-req-protocol-payload
- pfcp-req-msg-type
- pfcp-rsp-msg-type
- smtp-req-helo-argument-length
- smtp-req-mail-argument-length
- smtp-req-rcpt-argument-length
- sctp-req-ppid
- ssl-req-client-hello-ext-type
- ssl-req-client-hello-missing-sni
- ssl-rsp-version
- stun-req-attr-type
- panav-rsp-zip-compression-ratio
- Context Qualifiers
-
Create a Custom Threat Signature from a Snort Signature
Convert a third-party signature a custom PAN-OS threat
signature.
The following steps illustrate the process
for converting a Snort signature into a custom spyware signature
compatible with Palo Alto Networks firewalls. The use case below
uses a Snort rule for a North Korean Trojan malware variant as identified
by the Department of Homeland Security, the Federal Bureau of Investigation,
and other US government partners.
With Panorama version 10.0 or later or Strata Cloud Manager, you can use
the IPS Signature Converter to automatically convert Snort and Suricata rules into
custom Palo Networks threat signatures instead of manually performing the following
procedure.
Snort
rule:
alert tcp any any -> any any (msg:"Malformed_UA"; content:"User-Agent: Mozillar/"; depth:500; sid:99999999;)
In
this example you can:
- Use the IP addresses provided as part of the IOC List to detect if a possible infection already exists by searching the firewall logs.
- The IP addresses provided can be part of an EDL or Address group and added to a Policy to block traffic to and from the suspicious list.
- Use the provided Snort signature and convert it to a custom spyware signature. This signature will become part of the spyware profile added to the appropriate policy.
For
other use cases, see our companion article.
- NGFW
- Create a Custom Spyware or Vulnerability Object. For this example, a custom Spyware object will be created.
- Navigate to ObjectsCustom ObjectsSpyware or Vulnerability.
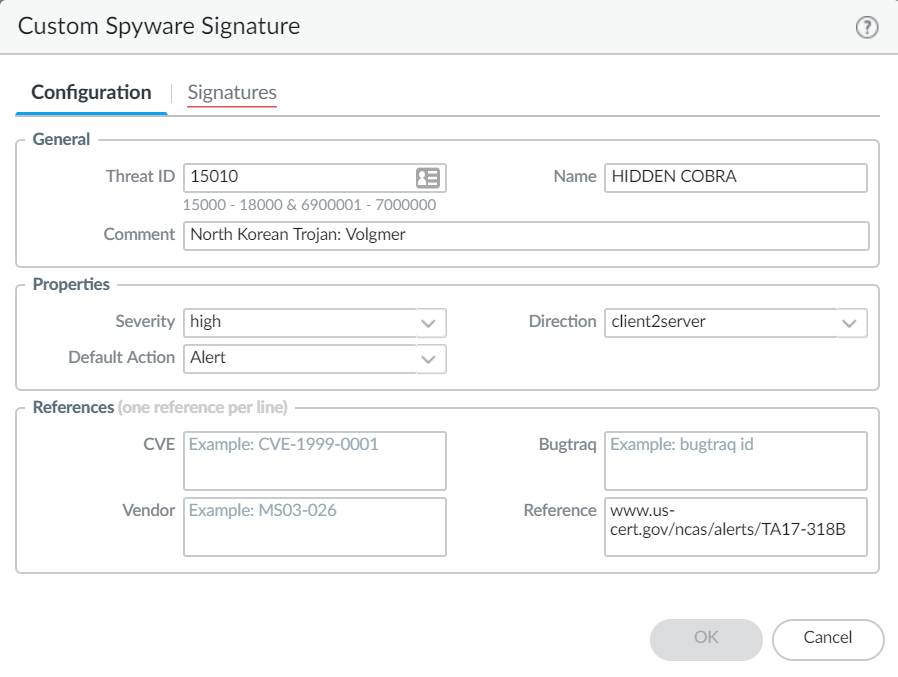
- Click Add and provide a Threat ID, an optional comment, and fill out the Properties section.
![]()
- Under Signatures, press Add.
- Specify the following information:
- Standard—Enter a name to identify the signature in the field.
- Comment—Enter an optional description.
- If the order in which the firewall attempts to match the signature definitions is important, keep Ordered Condition Match selected.
- Scope—Indicate whether this signature applies to a full Session or a single Transaction.
- Add a condition by clicking Add And Condition or Add Or Condition.
- Select an Operator from the drop-down menu to define the conditions that must be true for the signature to match traffic.
- If you select Pattern Match, identify a Context in the Snort pattern that matches our available contexts, provide a regular expression Pattern, and optionally, Add a qualifier/value pair. Select Negate to specify conditions under which the custom signature does not trigger.
- If you select Equal To, Less Than, or Greater Than, select a Context and enter a Value.
- Click OK to finish creating the Spyware object.
- Verify that the custom Spyware object is part of your Anti-Spyware Profile.
- Go to Security ProfilesAnti-Spyware. Click an existing profile, then under Exceptions, search for your signature’s Threat ID and Enable it.
- Create an EDL object.
- Navigate to ObjectsExternal Dynamic Lists. Click Add.
- Add the suspicious IP address provided from the IOC list to a previously created EDL or a new EDL as shown below.
- Add the EDL and Anti-Spyware profiles to appropriate Policy Objects.
- Test policy is working as expected by looking at Threat logs.
- Change the action for the spyware object from alert to drop/reset after verification. Also, change the severity of the object created as needed.
- Commit your signature(s).
- Strata Cloud Manager
- Create a custom Anti-Spyware or Vulnerability Protection signature.
- Log in to the Strata Cloud Manager on the hub.
- Select ManageConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessSecurity Services and then select Anti-Spyware or Vulnerability Protection, depending on the signature type.
- From the Custom Signatures tab, select Add Custom Signature and then Import Signature.
- Under Signatures, press Add.
- Specify the following information:
- Standard—Enter a name to identify the signature in the field.
- Comment—Enter an optional description.
- If the order in which the firewall attempts to match the signature definitions is important, keep Ordered Condition Match selected.
- Scope—Indicate whether this signature applies to a full Session or a single Transaction.
- Add a condition by clicking Add And Condition or Add Or Condition.
- Select an Operator from the drop-down menu to define the conditions that must be true for the signature to match traffic.
- If you select Pattern Match, identify a Context in the Snort pattern that matches our available contexts, provide a regular expression Pattern, and optionally, Add a qualifier/value pair. Select Negate to specify conditions under which the custom signature does not trigger.
- If you select Equal To, Less Than, or Greater Than, select a Context and enter a Value.
- Click OK to finish creating the Spyware object.
- Verify that the custom Spyware object is part of your Anti-Spyware Profile.
- Go to Security ProfilesAnti-Spyware. Click an existing profile, then under Exceptions, search for your signature’s Threat ID and Enable it.
- Create an EDL object.
- Navigate to ObjectsExternal Dynamic Lists. Click Add.
- Add the suspicious IP address provided from the IOC list to a previously created EDL or a new EDL as shown below.
- Add the EDL and Anti-Spyware profiles to appropriate Policy Objects.
- Test policy is working as expected by looking at Threat logs.
- Change the action for the spyware object from alert to drop/reset after verification. Also, change the severity of the object created as needed.
- Commit your signature(s).