Network Security
Configure Post-Quantum IKEv2 VPNs with RFC 9242 and RFC 9370 Hybrid Keys
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Network Security Docs
Configure Post-Quantum IKEv2 VPNs with RFC 9242 and RFC 9370 Hybrid Keys
Post-quantum RFC 9242 and RFC 9370 hybrid keys make IKEv2 VPNs resistant to attacks
by quantum computers.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
Post-quantum IKEv2 VPNs based on RFC 9242 and RFC 9370 create a hybrid key
using two or more key exchange mechanisms (KEMs) alongside an initial peering
exchange (the IKE_SA_INIT Exchange). Hybrid keys provide quantum resistance by
preventing a compromised KEM from allowing quantum attacks using Harvest Now,
Decrypt Later (HNDL) to succeed. As long as all KEMs used to create the hybrid key
are not compromised, the data remains protected.
As the standards are still relatively new and each vendor can have
different interpretations of the standard for their implementation, keeping the
configurations identical on both sides helps to keep things simple and enable the
post-quantum VPN tunnel to come up successfully. To minimize the chances of
interoperability, make sure both sides of the VPN tunnel are configured with the
same PQCs and security strengths in each of the optional key negotiation rounds.
Also check the IKEv2 fragmentation settings on both sides to ensure they are
configured correctly.
Set up IKEv2 peering and an IPSec
tunnel before configuring your post-quantum components. Additionally,
ensure you have Security policy rules that permit the IKEv2 and IPSec traffic
between the firewalls and enable logging.
To ensure data is protected for long durations, more than two KEMs should
be used, and you can further add defense-in-depth by enabling both pre-shared key
through RFC 8784 and hybrid key through RFC 9242 and RFC 9370.
To make your IKEv2 VPNs resistant to quantum attacks:
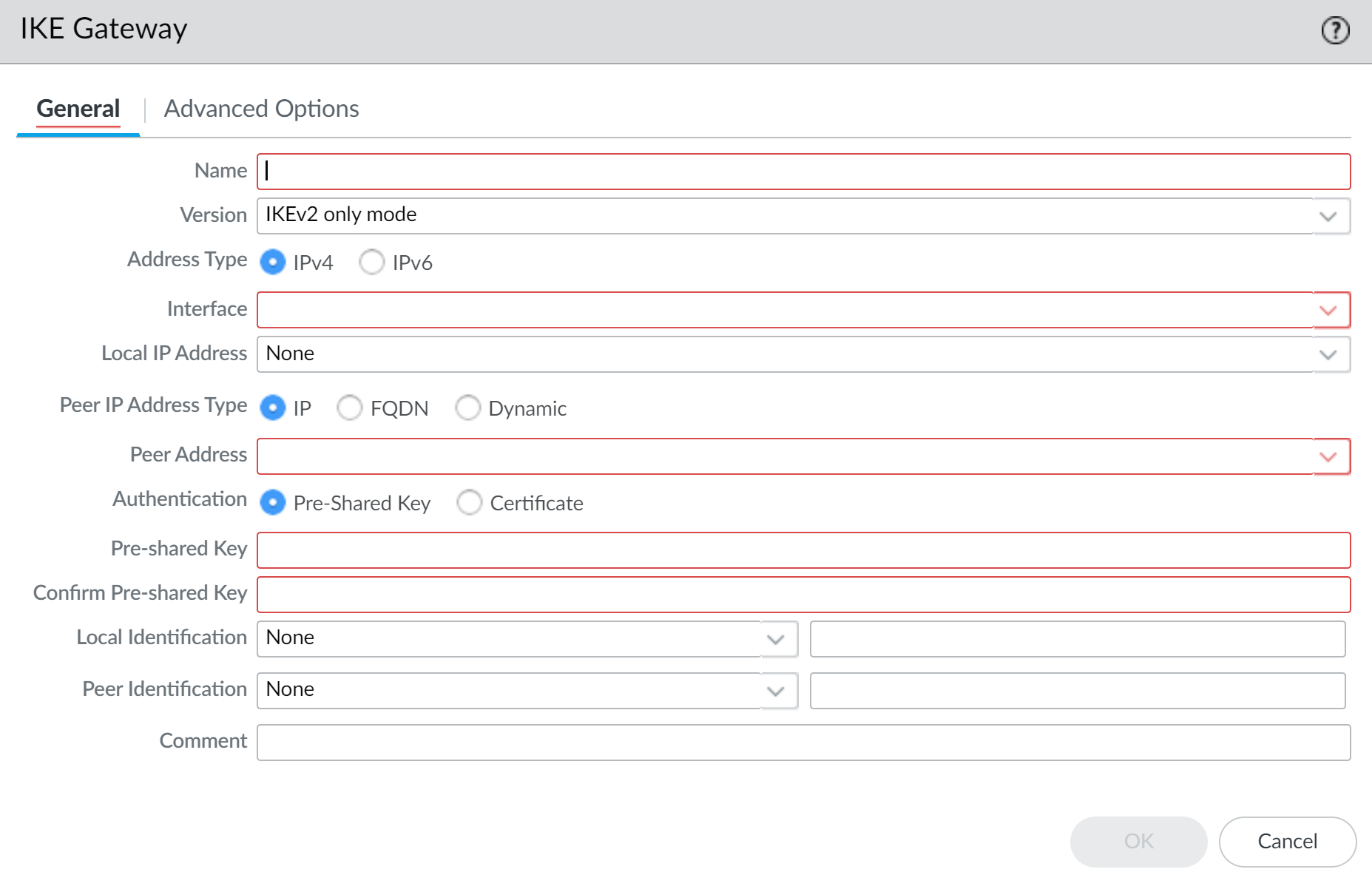
- Select NetworkNetwork ProfilesIKE Gateways and Add a new gateway.Configure the General settings and select either IKEv2 only mode or IKEv2 preferred mode as the Version.In IKEv2 only mode, if the peer does not support IKEv2, the firewall aborts the connection. In IKEv2 preferred mode, if the peer does not support IKEv2, the firewall falls back to IKEv1. However, the VPN must negotiate IKEv2 to use the post-quantum VPN features, so if the firewall falls back to IKEv1, those features are not available.IKEv1 is considered to be weak. If both IKE peers can support it, upgrade your VPN connections to IKEv2 and select IKEv2 only mode to ensure adequate levels of security and the ability to use PQ VPNs.
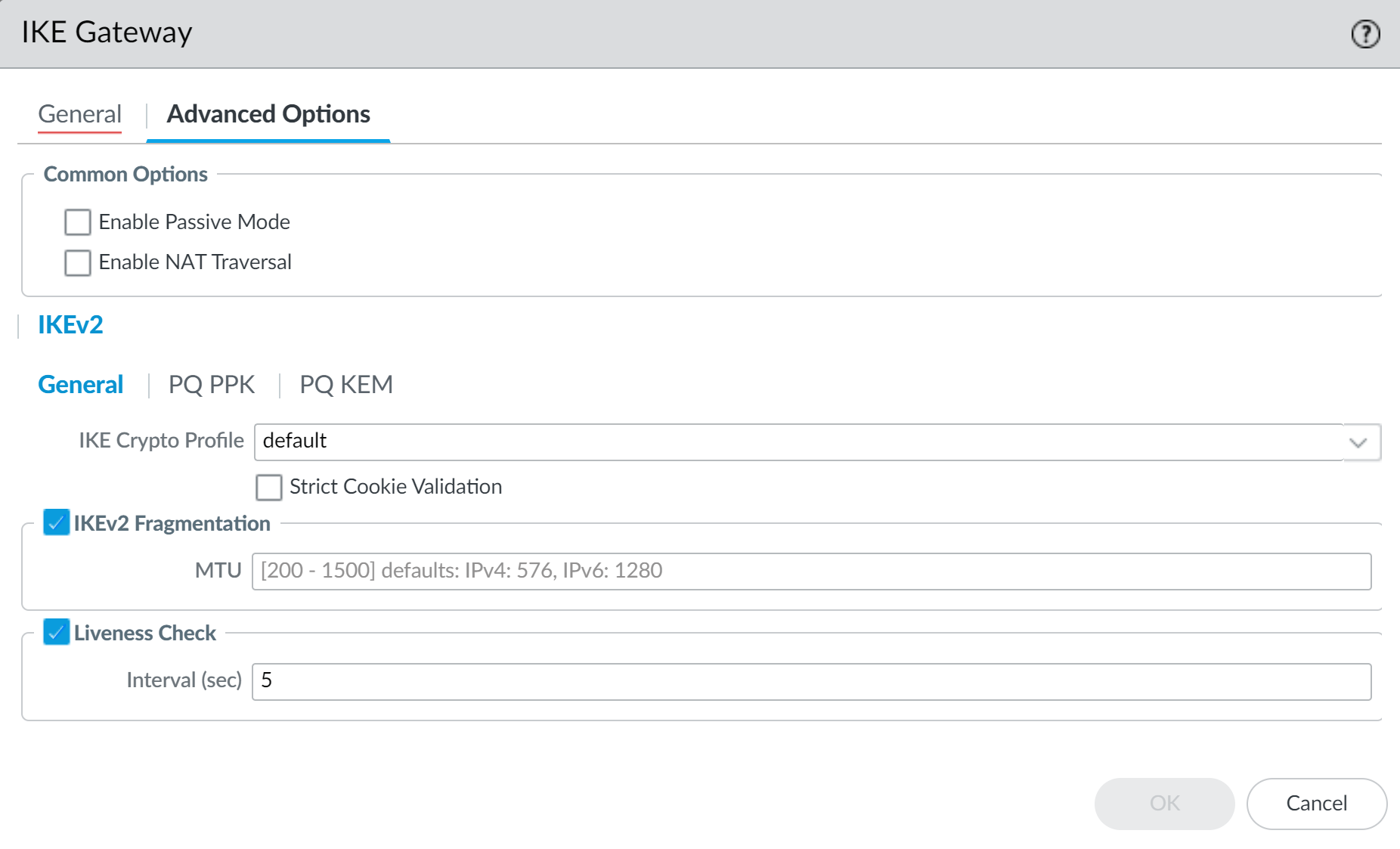
![]() Configure the non-quantum Advanced Options.Dynamic peer IKE gateways on the same local IP address must have the same IKE Crypto profile and Enable NAT Traversal and IKEv2 Fragmentation settings.Select IKEv2. From the General tab, you can specify an IKE Crypto profile, enable IKEv2 Fragmentation, and set the Liveness Check.IKEv2 Fragmentation should be enabled when using PQC KEMs as the key sizes and data payloads are larger.
Configure the non-quantum Advanced Options.Dynamic peer IKE gateways on the same local IP address must have the same IKE Crypto profile and Enable NAT Traversal and IKEv2 Fragmentation settings.Select IKEv2. From the General tab, you can specify an IKE Crypto profile, enable IKEv2 Fragmentation, and set the Liveness Check.IKEv2 Fragmentation should be enabled when using PQC KEMs as the key sizes and data payloads are larger.![]() Configure the post-quantum Advanced Options.
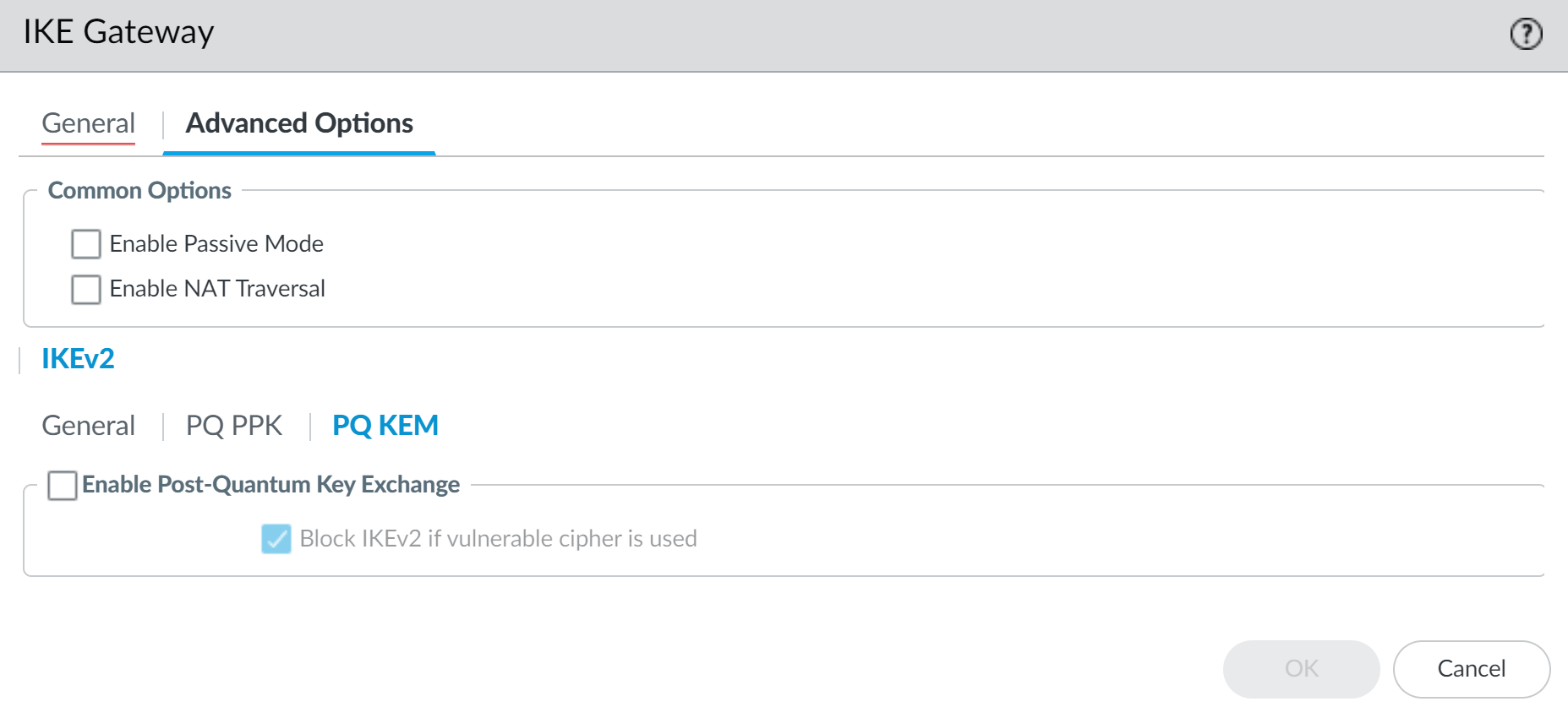
Configure the post-quantum Advanced Options.- Select PQ KEM, and then Enable Post-Quantum Key Exchange. This option is disabled by default.Select (or deselect) this option for all dynamic peer IKE gateways on the same local IP address.
- (Optional) Select Block IKEv2 if vulnerable cipher is used. If this option is enabled, the firewall blocks all new IKEv2 peerings if it detects a vulnerable KEM is being used in the IKE Crypto profile. Existing VPN tunnels that came up beforehand can continue.
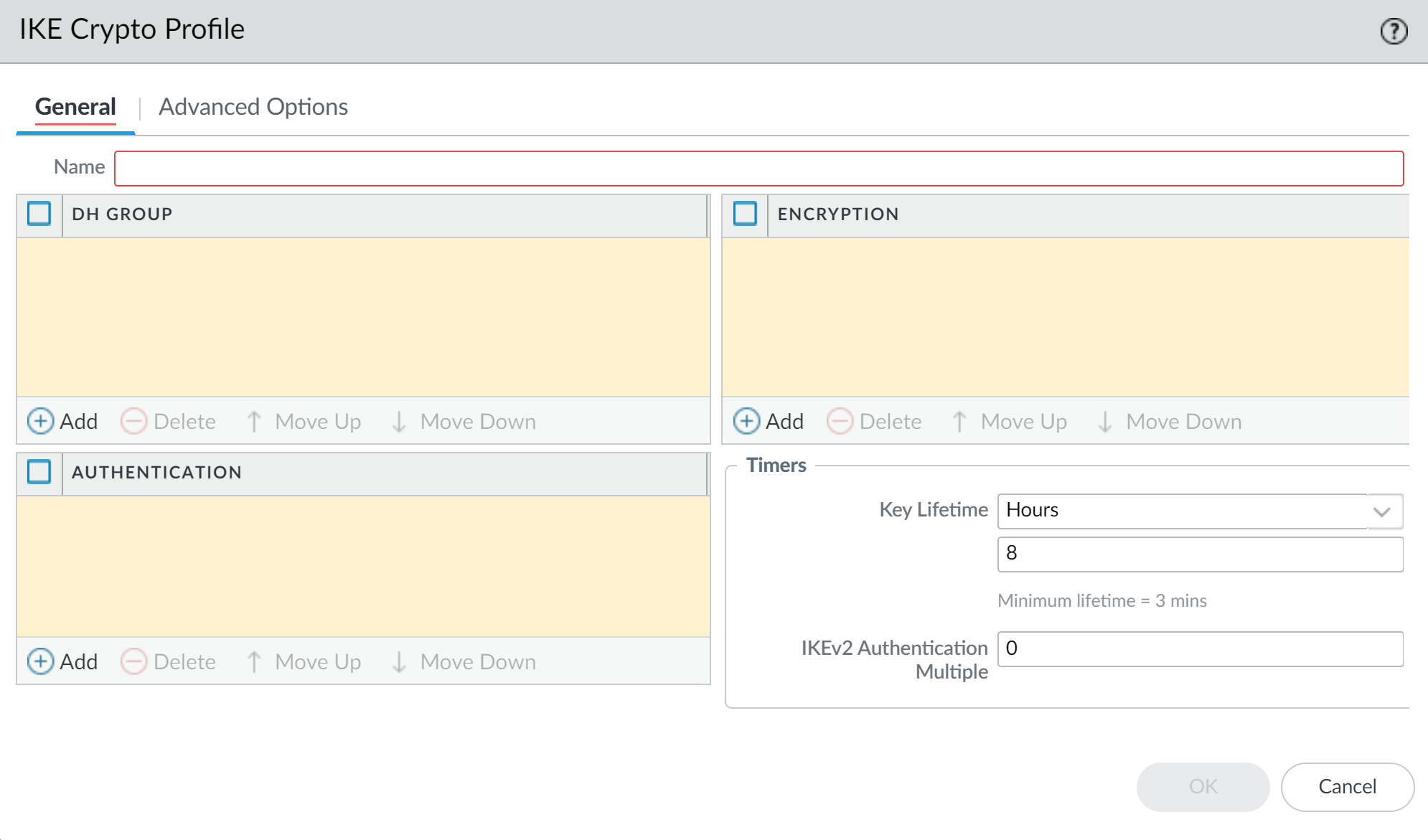
![]() Click OK to create the IKE Gateway.Select NetworkNetwork ProfilesIKE Crypto and Add a new profile.Configure the General settings and select the cryptographic components (DH Group, Encryption, Authentication, Timers) for the default IKEv2 key exchange.Select a strong classic key exchange configuration to raise quantum resistance. DH Group 20 or higher, AES-256-GCM, and refresh the keys more frequently using the key lifetime. To completely regenerate the key at specific intervals, enable the IKEv2 Authentication Multiple by setting a value higher than zero. The key is regenerated after the multiple of the Key Lifetime is reached.
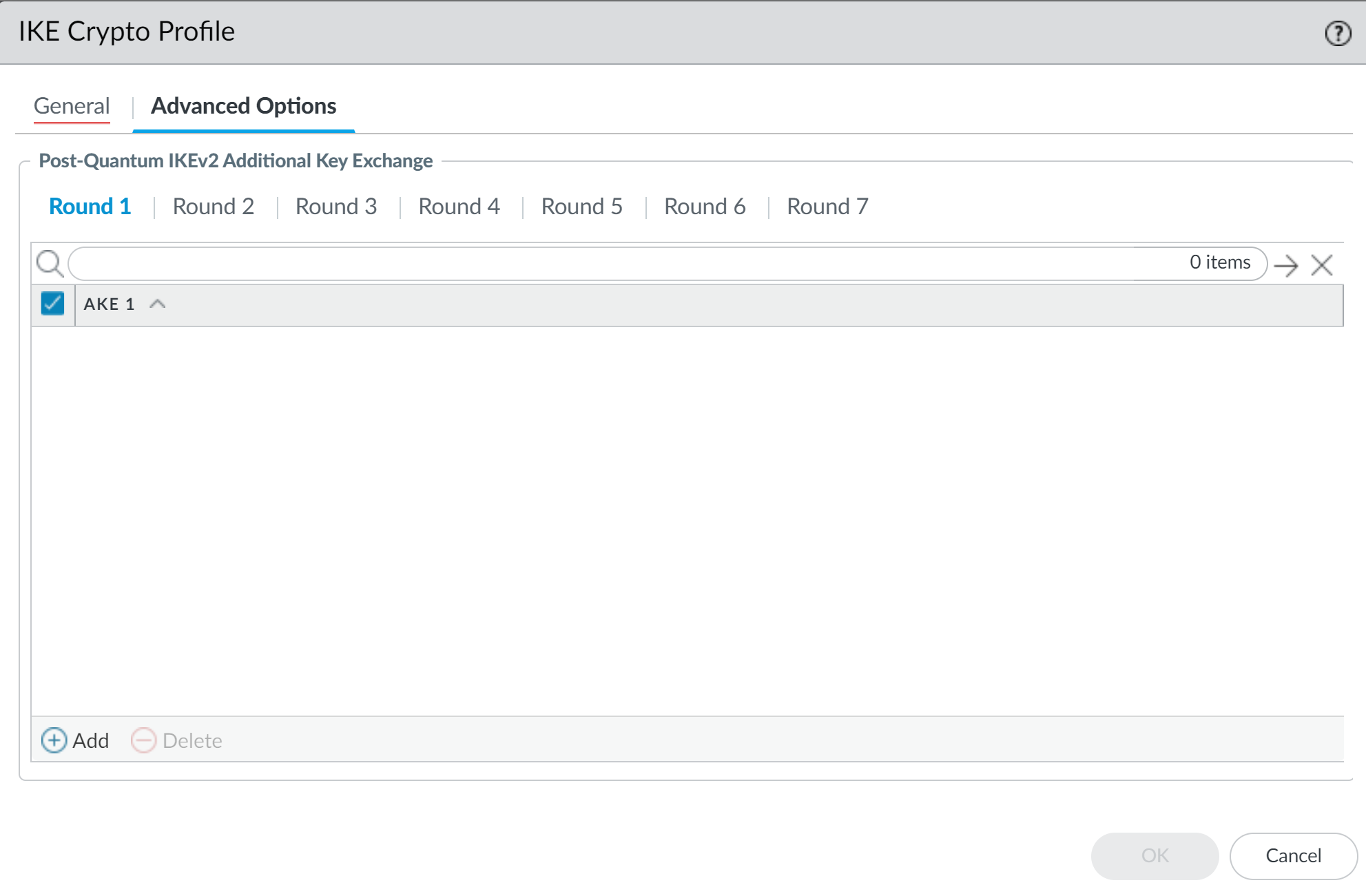
Click OK to create the IKE Gateway.Select NetworkNetwork ProfilesIKE Crypto and Add a new profile.Configure the General settings and select the cryptographic components (DH Group, Encryption, Authentication, Timers) for the default IKEv2 key exchange.Select a strong classic key exchange configuration to raise quantum resistance. DH Group 20 or higher, AES-256-GCM, and refresh the keys more frequently using the key lifetime. To completely regenerate the key at specific intervals, enable the IKEv2 Authentication Multiple by setting a value higher than zero. The key is regenerated after the multiple of the Key Lifetime is reached.![]() Select Advanced Options and configure the optional Post-Quantum IKEv2 Additional Key Exchange rounds.A maximum of seven Additional Key Exchange Rounds (Round 1-7) are permitted in RFC 9370. At a minimum, one PQC KEM is required to add quantum resistance. Adding additional PQC KEMs further raises quantum resistance, but adds negotiation overhead and increases the size of the IKEv2 packets.RFC 9370 allows additional key exchange rounds to be skipped. For skipped rounds, they can be left blank or set to None.The order of the PQCs in the Additional Key Exchange Round sets the preference. The PQC listed at the top is preferred and is selected if the VPN termination device on the other side of the tunnel supports it. If you want to negotiate the strongest PQC that both sides can support, place the highest security level PQC at the top of the list in each Additional Key Exchange Round.The VPN termination devices on both sides of the tunnel should be configured to the same PQC and security strength to minimize interoperability issues. To secure sensitive information for long periods of time, select a PQC with a security strength equivalent to Level 3 or higher.
Select Advanced Options and configure the optional Post-Quantum IKEv2 Additional Key Exchange rounds.A maximum of seven Additional Key Exchange Rounds (Round 1-7) are permitted in RFC 9370. At a minimum, one PQC KEM is required to add quantum resistance. Adding additional PQC KEMs further raises quantum resistance, but adds negotiation overhead and increases the size of the IKEv2 packets.RFC 9370 allows additional key exchange rounds to be skipped. For skipped rounds, they can be left blank or set to None.The order of the PQCs in the Additional Key Exchange Round sets the preference. The PQC listed at the top is preferred and is selected if the VPN termination device on the other side of the tunnel supports it. If you want to negotiate the strongest PQC that both sides can support, place the highest security level PQC at the top of the list in each Additional Key Exchange Round.The VPN termination devices on both sides of the tunnel should be configured to the same PQC and security strength to minimize interoperability issues. To secure sensitive information for long periods of time, select a PQC with a security strength equivalent to Level 3 or higher.![]() Click OK to create the IKE Crypto profile.Select NetworkNetwork ProfilesIPSec Crypto and Add a new profile.Configure the General settings and select the cryptographic components for the IPSec ESP protocol (Encryption, Authentication, DH Group, Lifetime).Select a strong classic cryptographic configuration to raise quantum resistance. DH Group 20 or higher, AES-256-GCM, SHA384 or higher, and refresh the keys more frequently using the key lifetime.
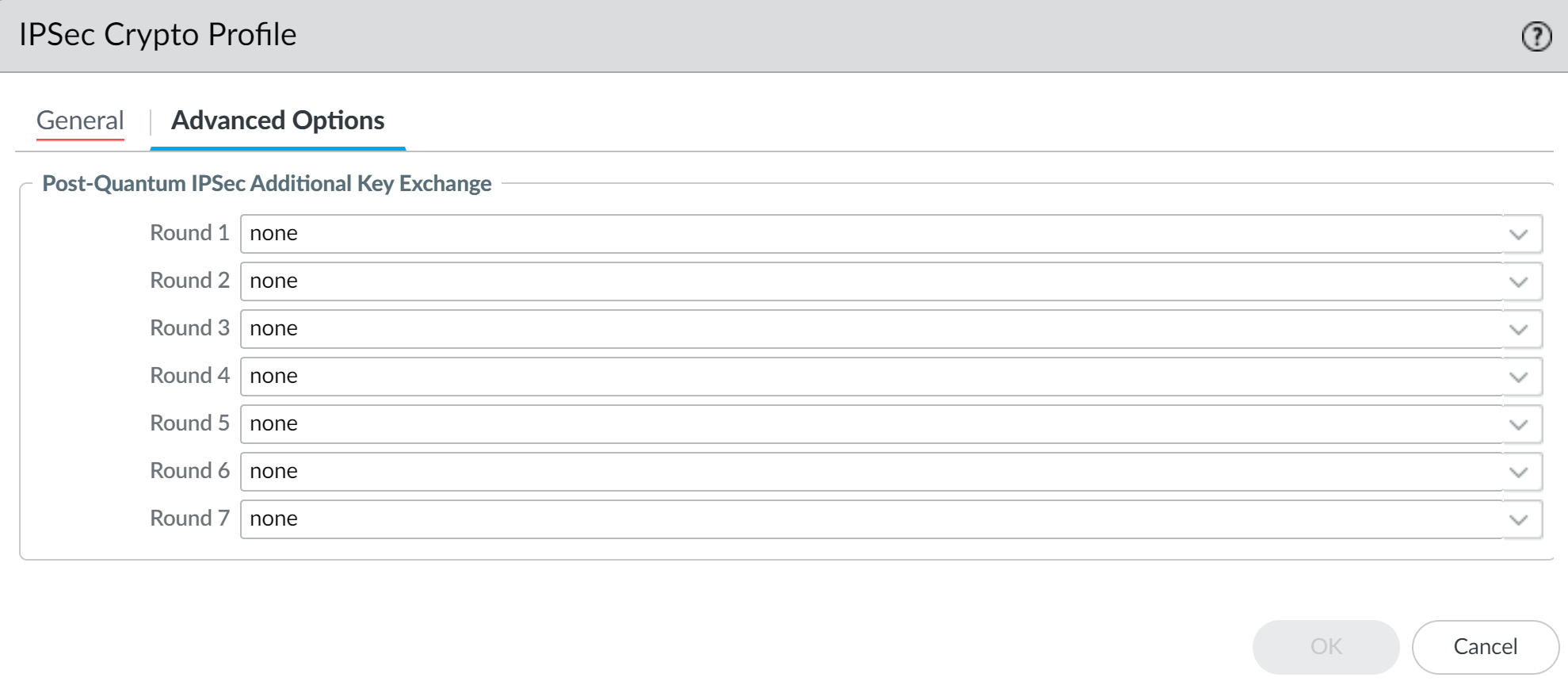
Click OK to create the IKE Crypto profile.Select NetworkNetwork ProfilesIPSec Crypto and Add a new profile.Configure the General settings and select the cryptographic components for the IPSec ESP protocol (Encryption, Authentication, DH Group, Lifetime).Select a strong classic cryptographic configuration to raise quantum resistance. DH Group 20 or higher, AES-256-GCM, SHA384 or higher, and refresh the keys more frequently using the key lifetime.![]() Select the Advanced Options and configure the optional Post-Quantum IPSec Additional Key Exchange rounds.A maximum of seven Additional Key Exchange Rounds (Round 1-7) are permitted and only one PQC KEM is permitted per round. At a minimum, one PQC KEM is required to add quantum resistance. Adding additional PQC KEMs further raises quantum resistance, but adds negotiation overhead and increases the size of the IPSec re-key packets.Both sides of the IPSec tunnel must be configured with the same PQC and security strength level in each Additional Key Exchange Round. If there is a mismatch, the re-key operation fails.To secure sensitive information for long periods of time, select a PQC with a security strength equivalent to Level 3 or higher.
Select the Advanced Options and configure the optional Post-Quantum IPSec Additional Key Exchange rounds.A maximum of seven Additional Key Exchange Rounds (Round 1-7) are permitted and only one PQC KEM is permitted per round. At a minimum, one PQC KEM is required to add quantum resistance. Adding additional PQC KEMs further raises quantum resistance, but adds negotiation overhead and increases the size of the IPSec re-key packets.Both sides of the IPSec tunnel must be configured with the same PQC and security strength level in each Additional Key Exchange Round. If there is a mismatch, the re-key operation fails.To secure sensitive information for long periods of time, select a PQC with a security strength equivalent to Level 3 or higher.![]() Click OK to create the IPSec Crypto profile.Commit the configuration.If you are not the administrator of both IKEv2 peers, communicate the IKEv2 gateway, IKE Crypto profile, and IPSec Crypto profile information to the peer's administrator for installation on their peer device.
Click OK to create the IPSec Crypto profile.Commit the configuration.If you are not the administrator of both IKEv2 peers, communicate the IKEv2 gateway, IKE Crypto profile, and IPSec Crypto profile information to the peer's administrator for installation on their peer device.