Enable Overlay Routing for the VM-Series on AWS
Table of Contents
11.0 (EoL)
Expand all | Collapse all
-
- VM-Series Deployments
- VM-Series in High Availability
- IPv6 Support on Public Cloud
- Enable Jumbo Frames on the VM-Series Firewall
- Hypervisor Assigned MAC Addresses
- Custom PAN-OS Metrics Published for Monitoring
- Interface Used for Accessing External Services on the VM-Series Firewall
- PacketMMAP and DPDK Driver Support
- Enable NUMA Performance Optimization on the VM-Series
- Enable ZRAM on the VM-Series Firewall
-
- VM-Series Firewall Licensing
- Create a Support Account
- Serial Number and CPU ID Format for the VM-Series Firewall
- Use Panorama-Based Software Firewall License Management
-
- Maximum Limits Based on Tier and Memory
- Activate Credits
- Create a Deployment Profile
- Activate the Deployment Profile
- Manage a Deployment Profile
- Register the VM-Series Firewall (Software NGFW Credits)
- Provision Panorama
- Migrate Panorama to a Software NGFW License
- Transfer Credits
- Renew Your Software NGFW Credits
- Deactivate License (Software NGFW Credits)
- Delicense Ungracefully Terminated Firewalls
- Set the Number of Licensed vCPUs
- Customize Dataplane Cores
- Migrate a Firewall to a Flexible VM-Series License
-
- Generate Your OAuth Client Credentials
- Manage Deployment Profiles Using the Licensing API
- Create a Deployment Profile Using the Licensing API
- Update a Deployment Profile Using the Licensing API
- Get Serial Numbers Associated with an Authcode Using the API
- Deactivate a VM-Series Firewall Using the API
- What Happens When Licenses Expire?
-
- Supported Deployments on VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi)
-
- Plan the Interfaces for the VM-Series for ESXi
- Provision the VM-Series Firewall on an ESXi Server
- Perform Initial Configuration on the VM-Series on ESXi
- Add Additional Disk Space to the VM-Series Firewall
- Use VMware Tools on the VM-Series Firewall on ESXi and vCloud Air
- Use vMotion to Move the VM-Series Firewall Between Hosts
- Use the VM-Series CLI to Swap the Management Interface on ESXi
-
-
- Supported Deployments of the VM-Series Firewall on VMware NSX-T (North-South)
- Components of the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (North-South)
-
- Install the Panorama Plugin for VMware NSX
- Enable Communication Between NSX-T Manager and Panorama
- Create Template Stacks and Device Groups on Panorama
- Configure the Service Definition on Panorama
- Deploy the VM-Series Firewall
- Direct Traffic to the VM-Series Firewall
- Apply Security Policy to the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T
- Use vMotion to Move the VM-Series Firewall Between Hosts
- Extend Security Policy from NSX-V to NSX-T
-
- Components of the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (East-West)
- VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (East-West) Integration
- Supported Deployments of the VM-Series Firewall on VMware NSX-T (East-West)
-
- Install the Panorama Plugin for VMware NSX
- Enable Communication Between NSX-T Manager and Panorama
- Create Template Stacks and Device Groups on Panorama
- Configure the Service Definition on Panorama
- Launch the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (East-West)
- Add a Service Chain
- Direct Traffic to the VM-Series Firewall
- Apply Security Policies to the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (East-West)
- Use vMotion to Move the VM-Series Firewall Between Hosts
-
- Install the Panorama Plugin for VMware NSX
- Enable Communication Between NSX-T Manager and Panorama
- Create Template Stacks and Device Groups on Panorama
- Configure the Service Definition on Panorama
- Launch the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (East-West)
- Create Dynamic Address Groups
- Create Dynamic Address Group Membership Criteria
- Generate Steering Policy
- Generate Steering Rules
- Delete a Service Definition from Panorama
- Migrate from VM-Series on NSX-T Operation to Security Centric Deployment
- Extend Security Policy from NSX-V to NSX-T
- Use In-Place Migration to Move Your VM-Series from NSX-V to NSX-T
-
-
- Deployments Supported on AWS
-
- Planning Worksheet for the VM-Series in the AWS VPC
- Launch the VM-Series Firewall on AWS
- Launch the VM-Series Firewall on AWS Outpost
- Create a Custom Amazon Machine Image (AMI)
- Encrypt EBS Volume for the VM-Series Firewall on AWS
- Use the VM-Series Firewall CLI to Swap the Management Interface
- Enable CloudWatch Monitoring on the VM-Series Firewall
- VM-Series Firewall Startup and Health Logs on AWS
- Simplified Onboarding of VM-Series Firewall on AWS
-
- Use AWS Secrets Manager to Store VM-Series Certificates
- AWS Shared VPC Monitoring
- Use Case: Secure the EC2 Instances in the AWS Cloud
- Use Case: Use Dynamic Address Groups to Secure New EC2 Instances within the VPC
-
- Intelligent Traffic Offload
- Software Cut-through Based Offload
-
- Deployments Supported on Azure
- Deploy the VM-Series Firewall from the Azure Marketplace (Solution Template)
- Deploy the VM-Series Firewall from the Azure China Marketplace (Solution Template)
- Deploy the VM-Series with the Azure Gateway Load Balancer
- Create a Custom VM-Series Image for Azure
- Deploy the VM-Series Firewall on Azure Stack
- Deploy the VM-Series Firewall on Azure Stack HCI
- Enable Azure Application Insights on the VM-Series Firewall
- Set up Active/Passive HA on Azure
- Use Azure Key Vault to Store VM-Series Certificates
- Use the ARM Template to Deploy the VM-Series Firewall
-
- About the VM-Series Firewall on Google Cloud Platform
- Supported Deployments on Google Cloud Platform
- Create a Custom VM-Series Firewall Image for Google Cloud Platform
- Prepare to Set Up VM-Series Firewalls on Google Public Cloud
-
- Deploy the VM-Series Firewall from Google Cloud Platform Marketplace
- Management Interface Swap for Google Cloud Platform Load Balancing
- Use the VM-Series Firewall CLI to Swap the Management Interface
- Enable Google Stackdriver Monitoring on the VM Series Firewall
- Enable VM Monitoring to Track VM Changes on Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Use Dynamic Address Groups to Secure Instances Within the VPC
- Use Custom Templates or the gcloud CLI to Deploy the VM-Series Firewall
-
- Prepare Your ACI Environment for Integration
-
-
- Create a Virtual Router and Security Zone
- Configure the Network Interfaces
- Configure a Static Default Route
- Create Address Objects for the EPGs
- Create Security Policy Rules
- Create a VLAN Pool and Domain
- Configure an Interface Policy for LLDP and LACP for East-West Traffic
- Establish the Connection Between the Firewall and ACI Fabric
- Create a VRF and Bridge Domain
- Create an L4-L7 Device
- Create a Policy-Based Redirect
- Create and Apply a Service Graph Template
-
- Create a VLAN Pool and External Routed Domain
- Configure an Interface Policy for LLDP and LACP for North-South Traffic
- Create an External Routed Network
- Configure Subnets to Advertise to the External Firewall
- Create an Outbound Contract
- Create an Inbound Web Contract
- Apply Outbound and Inbound Contracts to the EPGs
- Create a Virtual Router and Security Zone for North-South Traffic
- Configure the Network Interfaces
- Configure Route Redistribution and OSPF
- Configure NAT for External Connections
-
-
- Choose a Bootstrap Method
- VM-Series Firewall Bootstrap Workflow
- Bootstrap Package
- Bootstrap Configuration Files
- Generate the VM Auth Key on Panorama
- Create the bootstrap.xml File
- Prepare the Licenses for Bootstrapping
- Prepare the Bootstrap Package
- Bootstrap the VM-Series Firewall on AWS
- Bootstrap the VM-Series Firewall on Azure
- Bootstrap the VM-Series Firewall on Azure Stack HCI
- Bootstrap the VM-Series Firewall on Google Cloud Platform
- Verify Bootstrap Completion
- Bootstrap Errors
End-of-Life (EoL)
Enable Overlay Routing for the VM-Series on AWS
Overly routing requires PAN-OS 10.0.5
or later.
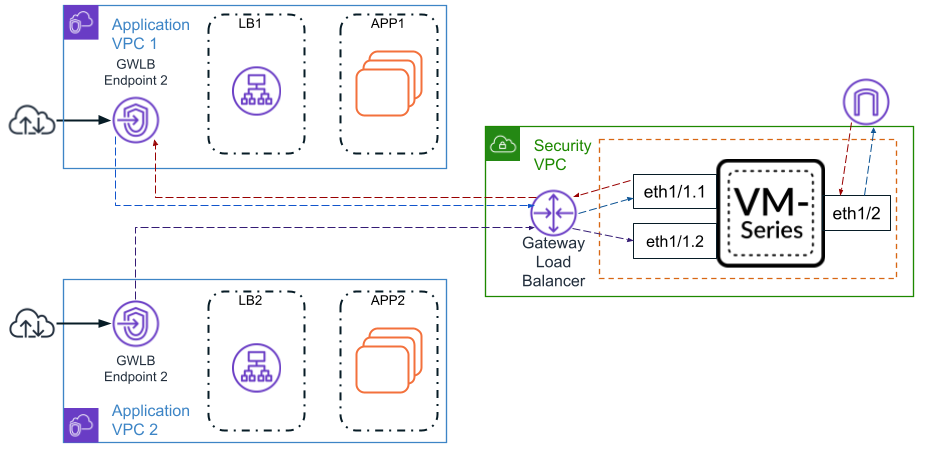
Using overlay routing in your VM-Series firewall
integration the AWS GWLB allows you to use two-zone policy to inspect
traffic leaving (egressing) your AWS environment. This allows packets
to leave the VM-Series firewall through a different interface than that
which they entered through.
When overlay routing is configured,
the firewall is able to perform a Layer 3 route lookup a packet’s
inner header. If the destination is the same as the ingress interface, the
packet will be directed as normal. All future packets in the session
are treated as vwire; as if overlay routing was not enabled. If
the packet is going to an outbound destination, the firewall decapsulates
the packet and forwards the packet to the IGW or NAT gateway. When
the packet returns, the firewall reapplies the encapsulation.
Use
the following procedure to enable overlay routing.
- Before you begin, ensure that you create different subnets for the trust and untrust interfaces.Manually Integrate the VM-Series with a Gateway Load Balancer.(Optional) Associate a VPC Endpoint with a VM-Series Interface.Use overlay routing CLI command. This CLI command is not required if you included the overlay routing op-command in the AWS user-data or the init-cfg.txt bootstrap file.
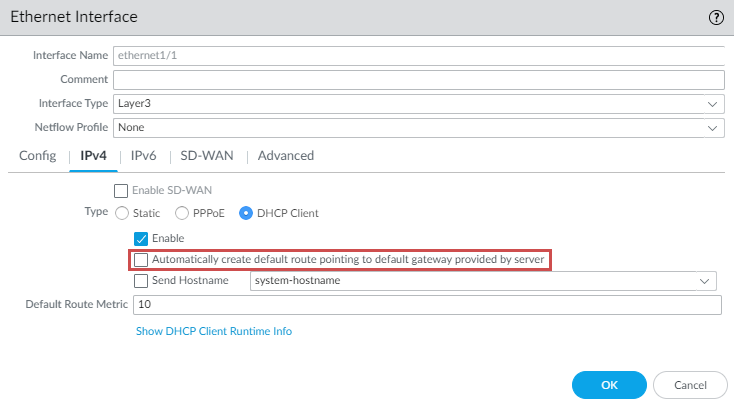
- Log in to the firewall command line interface.Execute the following command.request plugins vm_series aws gwlb overlay-routing enable yesLog in to the firewall web interface.Disable Automatically create default route pointing to default gateway provided by server on the trust (ingress) interface.
- Select NetworkInterfacesEthernet.Click on your trust interface and then the IPv4 tab.Uncheck Automatically create default route pointing to default gateway provided by server.Click OK.
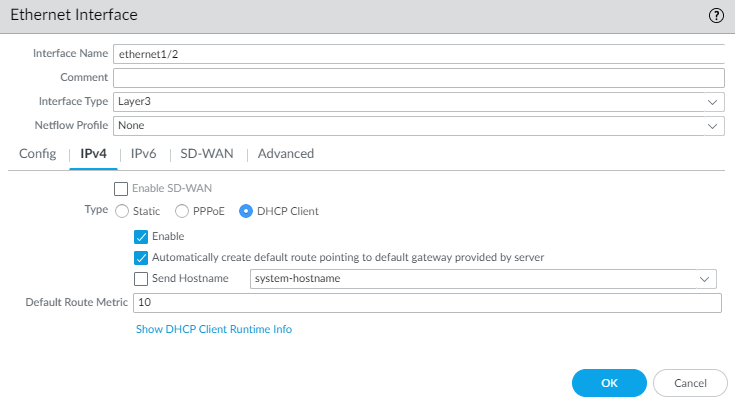
![]() Configure interface Ethernet 1/2.
Configure interface Ethernet 1/2.- Select NetworkInterfacesEthernet.Select the Interface Type—Layer 3.On the Config tab, expand the Security Zone drop-down and select New Zone. This zone will act as your untrust zone and directing outbound traffic out of your security VPC. Define the new zone, such as VM-Series-untrust, and then click OK.On the IPv4 tab, select DHCP Client.Select Automatically create default route pointing to default gateway provided by server.Click OK.
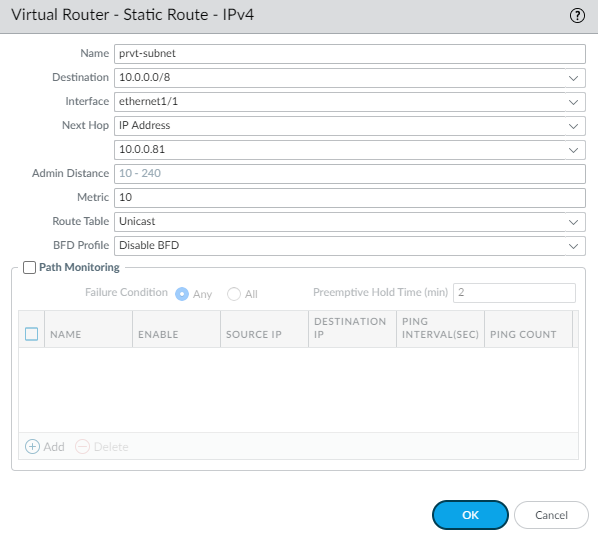
![]() Configure a virtual router.
Configure a virtual router.- Select NetworkVirtual RoutersAdd.Enter a descriptive Name for the virtual router.Under Interfaces, Add Ethernet1/1, any subinterfaces under Ethernet1/1, and Ethernet1/2.Click Static RoutesAdd.
- Enter a descriptive name for the static route.
- As the Destination, enter the private IP address of the application VPC subnet.
- Select the trust (ingress) interface from the Interface drop-down.
- For Next Hop, select IP Address and enter the IP address of the gateway of the trust interface. You can find the gateway IP address on NetworkInterfacesEthernetDynamic-DHCP Client.
![]()
- Click OK.
![]()
Ensure that the static routes can reach all application VPC in your deployment. You can either make a few large aggregated routes (covering all RFC1918) or application VPC specific routes. If you use subinterfaces, you do not need to route back to the sub-interface. The egress check looks only for the matching interface instead of the matching subinterface.Click OK.Create a NAT policy for traffic egressing Ethernet1/2.- Select PoliciesNATAdd.Enter a descriptive Name for the NAT policy rule.Select ipv4 from the NAT Type drop-down.On the Original Packet tab, set the Source Zone to any and the Destination Zone to your untrust (egress) zone.On the Translated Packet tab, set the following parameters.
- Translation Type: Dynamic IP and Port
- Address Type: Interface Address
- Interface: Select your untrust (egress) port from the drop-down.
- IP Address: None
Click OK.Commit your changes.