Prisma SD-WAN
Enable IoT Device Visibility in Prisma SD-WAN
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma SD-WAN Docs
-
-
- Prisma SD-WAN Key Elements
- Prisma SD-WAN Releases and Upgrades
- Use Copilot in Prisma SD-WAN
- Prisma SD-WAN Summary
- Prisma SD-WAN Application Insights
- Device Activity Charts
- Site Summary Dashboard
- Prisma SD-WAN Predictive Analytics Dashboard
- Prisma SD-WAN Link Quality Dashboard
- Prisma SD-WAN Subscription Usage
-
-
- Add a Branch
- Add a Data Center
- Add a Branch Gateway
- Secure Group Tags (SGT) Propagation
- Configure Circuits
- Configure Internet Circuit Underlay Link Aggregation
- Configure Private WAN Underlay Link Quality Aggregation
- Configure Circuit Categories
- Configure Device Initiated Connections for Circuits
- Add Public IP LAN Address to Enterprise Prefixes
- Manage Data Center Clusters
- Configure Secure SD-WAN Fabric Tunnels between Data Centers
- Configure a Site Prefix
- Configure Ciphers
- Configure a DHCP Server
- Configure NTP for Prisma SD-WAN
- Configure the ION Device at a Branch Site
- Configure the ION Device at a Data Center
- Switch a Site to Control Mode
- Allow IP Addresses in Firewall Configuration
-
- Configure a Controller Port
- Configure Internet Ports
- Configure WAN/LAN Ports
- Configure a Sub-Interface
- Configure a Loopback Interface
- Add and Configure Port Channel Interface
- Configure a PoE Port
- Configure and Monitor LLDP Activity and Status
- Configure a PPPoE Interface
- Configure a Layer 3 LAN Interface
- Configure Application Reachability Probes
- Configure a Secondary IP Address
- Configure a Static ARP
- Configure a DHCP Relay
- Configure IP Directed Broadcast
- VPN Keep-Alives
-
- Configure Prisma SD-WAN IPFIX
- Configure IPFIX Profiles and Templates
- Configure and Attach a Collector Context to a Device Interface in IPFIX
- Configure and Attach a Filter Context to a Device Interface in IPFIX
- Configure Global and Local IPFIX Prefixes
- Flow Information Elements
- Options Information Elements
- Configure the DNS Service on the Prisma SD-WAN Interface
- Configure SNMP
-
-
- Prisma SD-WAN Branch Routing
- Prisma SD-WAN Data Center Routing
-
- Configure an OSPF in Prisma SD-WAN
- Enable BGP for Private WAN and LAN
- Configure BGP Global Parameters
- Global or Local Scope for BGP Peers
- Configure a Route Map
- Configure a Prefix List
- Configure an AS Path List
- Configure an IP Community List
- View Routing Status and Statistics
- Distribution to Fabric
- Host Tracking
-
- Configure Multicast
- Create, Assign, and Configure a WAN Multicast Configuration Profile
- Configure Global Multicast Parameters
- Configure a Multicast Static Rendezvous Point (RP)
- Learn Rendezvous Points (RPs) Dynamically
- View LAN Statistics for Multicast
- View WAN Statistics for Multicast
- View IGMP Membership
- View the Multicast Route Table
- View Multicast Flow Statistics
- View Routing Statistics
-
- Prisma SD-WAN Branch HA Key Concepts
-
- Configure Branch HA with Gen-1 Platforms (2000, 3000, 7000, and 9000)
- Configure Branch HA with Gen-2 Platforms (3200, 5200, and 9200)
- Configure Branch HA with Gen-2 Embedded Switch Platforms (1200-S or 3200-L2)
- Configure Branch HA for Devices with Software Cellular Bypass (1200-S-C-5G)
- Configure Branch HA for Platforms without Bypass Pairs
- Configure Branch HA in a Hybrid Topology with Gen-1 (3000) and Gen-2 (3200) Platforms
- Configure HA Groups
- Add ION Devices to HA Groups
- Edit HA Groups and Group Membership
- Prisma SD-WAN Clarity Reports
-
-
CloudBlade Integrations
- CloudBlade Integrations
- CloudBlades Integration with Prisma Access
-
-
-
-
- clear app-engine
- clear app-map dynamic
- clear app-probe prefix
- clear connection
- clear device account-login
- clear dhcplease
- clear dhcprelay stat
- clear flow and clear flows
- clear flow-arp
- clear qos-bwc queue-snapshot
- clear routing
- clear routing multicast statistics
- clear routing ospf
- clear routing peer-ip
- clear switch mac-address-entries
- clear user-id agent statistics
-
- arping interface
- curl
- ping
- ping6
- debug bounce interface
- debug bw-test src-interface
- debug cellular stats
- debug controller reachability
- debug flow
- debug ipfix
- debug log agent eal file log
- debug logging facility
- debug logs dump
- debug logs follow
- debug logs tail
- debug performance-policy
- debug poe interface
- debug process
- debug reboot
- debug routing multicast log
- debug routing multicast pimd
- debug servicelink logging
- debug tcpproxy
- debug time sync
- dig dns
- dig6
- file export
- file remove
- file space available
- file tailf log
- file view log
- ssh6 interface
- ssh interface
- tcpdump
- tcpping
- traceroute
- traceroute6
-
- dump appdef config
- dump appdef version
- dump app-engine
- dump app-l4-prefix table
- dump app-probe config
- dump app-probe flow
- dump app-probe prefix
- dump app-probe status
- dump auth config
- dump auth status
- dump banner config
- dump bfd status
- dump bypass-pair config
- dump cellular config
- dump cellular stats
- dump cellular status
- dump cgnxinfra status
- dump cgnxinfra status live
- dump cgnxinfra status store
- dump config network
- dump config security
- dump controller cipher
- dump controller status
- dump device accessconfig
- dump device conntrack count
- dump device date
- dump device info
- dump device status
- dump dhcp-relay config
- dump dhcprelay stat
- dump dhcp-server config
- dump dhcp-server status
- dump dhcpstat
- dump dnsservice config all
- dump dpdk cpu
- dump dpdk interface
- dump dpdk port status
- dump dpdk stats
- dump flow
- dump flow count-summary
- dump interface config
- dump interface status
- dump interface status interface details
- dump interface status interface module
- dump intra cluster tunnel
- dump ipfix config collector-contexts
- dump ipfix config derived-exporters
- dump ipfix config filter-contexts
- dump ipfix config ipfix-overrides
- dump ipfix config prefix-filters
- dump ipfix config profiles
- dump ipfix config templates
- dump lldp
- dump lldp config
- dump lldp info
- dump lldp stats
- dump lldp status
- dump log-agent eal conn
- dump log-agent eal response-time
- dump log-agent eal stats
- dump log-agent config
- dump log-agent iot snmp config
- dump log-agent iot snmp device discovery stats
- dump log-agent ip mac bindings
- dump log-agent neighbor discovery stats
- dump log-agent status
- dump ml7 mctd counters
- dump ml7 mctd session
- dump ml7 mctd version
- dump nat counters
- dump nat6 counters
- dump nat summary
- dump network-policy config policy-rules
- dump network-policy config policy-sets
- dump network-policy config policy-stacks
- dump network-policy config prefix-filters
- dump overview
- dump performance-policy config policy-rules
- dump performance-policy config policy-sets
- dump performance-policy config policy-set-stacks
- dump performance-policy config threshold-profile
- dump poe system config
- dump poe system status
- dump priority-policy config policy-rules
- dump priority-policy config policy-sets
- dump priority-policy config policy-stacks
- dump priority-policy config prefix-filters
- dump probe config
- dump probe profile
- dump radius config
- dump radius statistics
- dump radius status
- dump reachability-probe config
- dump qos-bwc config
- dump reachability-probe status
- dump routing aspath-list
- dump routing cache
- dump routing communitylist
- dump routing multicast config
- dump routing multicast igmp
- dump routing multicast interface
- dump routing multicast internal vif-entries
- dump routing multicast mroute
- dump routing multicast pim
- dump routing multicast sources
- dump routing multicast statistics
- dump routing multicast status
- dump routing ospf
- dump routing peer advertised routes
- dump routing peer config
- dump routing peer neighbor
- dump routing peer received-routes
- dump routing peer routes
- dump routing peer route-via
- dump routing peer status
- dump routing peer route-json
- dump routing prefixlist
- dump routing prefix-reachability
- dump routing route
- dump routing routemap
- dump routing running-config
- dump routing summary
- dump routing static-route reachability-status
- dump routing static-route config
- dump routing vpn host tracker
- dump security-policy config policy-rules
- dump security-policy config policy-set
- dump security-policy config policy-set-stack
- dump security-policy config prefix-filters
- dump security-policy config zones
- dump sensor type
- dump sensor type summary
- dump serviceendpoints
- dump servicelink summary
- dump servicelink stats
- dump servicelink status
- dump site config
- dump snmpagent config
- dump snmpagent status
- dump software status
- dump spoke-ha config
- dump spoke-ha status
- dump standingalarms
- dump static-arp config
- dump static host config
- dump static routes
- dump support details
- dump-support
- dump switch fdb vlan-id
- dump switch port status
- dump switch vlan-db
- dump syslog config
- dump syslog-rtr stats
- dump syslog status
- dump time config
- dump time log
- dump time status
- dump troubleshoot message
- dump user-id agent config
- dump user-id agent statistics
- dump user-id agent status
- dump user-id agent summary
- dump user-id groupidx
- dump user-id group-mapping
- dump user-id ip-user-mapping
- dump user-id statistics
- dump user-id status
- dump user-id summary
- dump user-id useridx
- dump vlan member
- dump vpn count
- dump vpn ka all
- dump vpn ka summary
- dump vpn ka VpnID
- dump vpn status
- dump vpn summary
- dump vrf
- dump waninterface config
- dump waninterface summary
-
- inspect app-flow-table
- inspect app-l4-prefix lookup
- inspect app-map
- inspect certificate
- inspect certificate device
- inspect cgnxinfra role
- inspect connection
- inspect dhcplease
- inspect dhcp6lease
- inspect dpdk ip-rules
- inspect dpdk vrf
- inspect fib
- inspect fib-leak
- inspect flow-arp
- inspect flow brief
- inspect flow-detail
- inspect flow internal
- inspect interface stats
- inspect ipfix exporter-stats
- inspect ipfix collector-stats
- inspect ipfix app-table
- inspect ipfix wan-path-info
- inspect ipfix interface-info
- inspect ip-rules
- inspect ipv6-rules
- inspect lqm stats
- inspect memory summary
- inspect network-policy conflicts
- inspect network-policy dropped
- inspect network-policy hits policy-rules
- inspect network-policy lookup
- inspect performance-policy fec status
- inspect policy-manager status
- inspect policy-mix lookup-flow
- inspect priority-policy conflicts
- inspect priority-policy dropped
- inspect priority-policy hits default-rule-dscp
- inspect priority-policy hits policy-rules
- inspect priority-policy lookup
- inspect performance-policy incidents
- inspect performance-policy lookup
- inspect performance-policy hits analytics
- inspect process status
- inspect qos-bwc debug-state
- inspect qos-bwc queue-history
- inspect qos-bwc queue-snapshot
- inspect routing multicast fc site-iface
- inspect routing multicast interface
- inspect routing multicast mroute
- inspect security-policy lookup
- inspect security-policy size
- inspect switch mac-address-table
- inspect system arp
- inspect system ipv6-neighbor
- inspect system vrf
- inspect vrf
- inspect wanpaths
-
-
5.6
- 5.6
- 6.1
- 6.2
- 6.3
- 6.4
- 6.5
- New Features Guide
- On-Premises Controller
- Prisma SD-WAN CloudBlades
- Prisma Access CloudBlade Cloud Managed
- Prisma Access CloudBlade Panorama Managed
-
- Features Introduced in Prisma SD-WAN ION Release 5.6
- Changes to Default Behavior in Prisma SD-WAN ION Release 5.6
- Upgrade ION 9000 Firmware for Device Version 5.6.x
- CLI Commands in Prisma SD-WAN ION Release 5.6
- Addressed Issues in Prisma SD-WAN ION Release 5.6
- Known Issues in Prisma SD-WAN ION Release 5.6
Enable IoT Device Visibility in Prisma SD-WAN
Learn how to enable IoT Device Visibility in Prisma SD-WAN. It also lists
details such as IP address, MAC address, vendor details, and so on, for greater
visibility.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
Prisma SD-WAN with Strata Cloud Manager supports IoT device visibility
to identify devices in your network. Prisma SD-WAN branch ION devices
inspect packets, extract information, and generate messages to send to Strata Logging Service in a specific format.
IoT Security obtains this information
from Strata Logging Service and lists all the devices discovered in its
portal. It also lists details such as IP address, MAC address, vendor details, and
so on, for greater visibility. IoT Security must have visibility into network
traffic to discover, identify, and monitor the network behaviors of devices.

When integrating IoT Security with Prisma
Access, IoT Security relies on the Traffic logs that Prisma Access provides to analyze traffic at the branch sites that Prisma Access serves. Although Prisma Access can log outbound and inbound
traffic from the sites it protects, it can't log traffic that never reaches it; that
is, the traffic between devices at the same branch site.
Of particular importance to IoT Security is network traffic with
services such as DHCP and ARP that link an IP address assigned to a device with its
MAC address. In an environment where devices are assigned IP addresses dynamically
through DHCP, it's difficult to use IP addresses alone to track the network activity
of devices because they can each have multiple IP addresses over a period of time.
By having visibility into DHCP traffic, IoT Security can update the IP address
of a device when it changes. Similarly, by having visibility into ARP traffic
(gratuitous ARP announcements, for example),IoT Security can track how IP
addresses correspond to device MAC addresses.
Once IoT Security has an IP address-to-device mapping, it can use its AI and
machine learning engines to monitor and analyze the network activities of the device
over time. It can form a baseline of the normal device network behaviors, determine
its identity, inform you of any known vulnerabilities, and detect anomalous network
behaviors indicating risk.
When a DHCP server is at a branch site, DHCP traffic will never reach Prisma Access. Neither will ARP traffic, which only occurs within a Layer 2
broadcast domain. But, it's possible for ION devices at branch sites to see DHCP
traffic. If they’re in the same Layer 2 broadcast domain, then the branch ION
devices can also see the ARP traffic that devices generate. When integrated with IoT Security, Prisma SD-WAN ION devices log this traffic and
forward their logs to Strata Logging Service where IoT Security
accesses them for analysis.
To support IoT device visibility in Prisma SD-WAN, you need
the following licenses and subscriptions in the same tenant service group (TSG) that Prisma SD-WAN belongs to:
IoT Security depends on the information extracted from the
IoT device traffic, such as DHCP & ARP, for device classification and risk
assessment. Prior to Release 6.3.1, users adopting IoT Security lacked
visibility into the traffic generated by IoT devices that was local to the branch,
or traveled via WAN links outside of Prisma Access. This limited the scope of
visibility to directly connected devices or to packets that traversed the Prisma SD-WAN branch ION device.
Starting with Release 6.3.1, Prisma SD-WAN supports the discovery of devices not directly
connected to the Prisma SD-WAN branch ION devices. The system uses
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) with LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol)
to discover IoT devices within a branch network.
Prisma SD-WAN does not support Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) to
discover devices.
With LLDP, each IoT device transmits its device
information to its neighboring networking devices (such as switches and routers).
This information is available in the Management Information databases (MIBs). The
ION device launches an SNMP MIB (management information base) query to retrieve the
IP address and MAC address entries of the IoT devices.
The ION device then retrieves the LLDP neighbors of
the neighboring devices, one at time to get their IP or MAC address bindings. This
process of recursively discovering the devices known as “crawling” continues until
the ION device discovers all its neighbors.
The ION device sends the discovered IP or MAC address
bindings (along with information such as VLAN, subnets, and so on) as part of the
Enhanced Application logs (EAL) to Strata Logging Service. IoT Security
consumes these logs and provides visibility in the IoT Security portal.
You might need to modify security in the IoT devices to
allow SNMP from a new source.
The following steps explain how to onboard IoT Security and Prisma SD-WAN to Prisma Access as add-ons and how Prisma SD-WAN ION devices extend IoT Security visibility into
their branch sites.
- Add IoT Security and Prisma SD-WAN as Prisma Access add-ons.Follow the steps in Activate a License for Panorama-Managed , and ensure to include IoT Security and Prisma SD-WAN as add-ons. You can onboard them together or at different times.When you onboard and enable both IoT Security and Prisma SD-WAN to a Prisma Access (Managed by Panorama) account, the Prisma SD-WAN Controller automatically enables IoT device visibility on ION devices at all branch sites that belong to the corresponding tenant service group (TSG). The Prisma SD-WAN Controller learns the ID and FQDN of the Strata Logging Service instance in its TSG and automatically gets the device certificate and distributes it to ION devices to use when authenticating themselves to Strata Logging Service. The controller then instructs the ION devices to log the DHCP and ARP traffic they detect on their networks and forward their logs to Strata Logging Service.ION devices send ARP Traffic logs by default but you must configure them as either a DHCP relay agent or DHCP server to send DHCP Traffic logs to Strata Logging Service.IoT Security accesses the log data in Strata Logging Service and uses machine learning algorithms to analyze it. Through its analysis, IoT Security discovers and identifies devices on the network and deduces their usual network behaviors. IoT Security generates alerts when there is anomalous network activity and detects device vulnerabilities and potential threats. You can view the results of its analysis in the IoT Security portal.
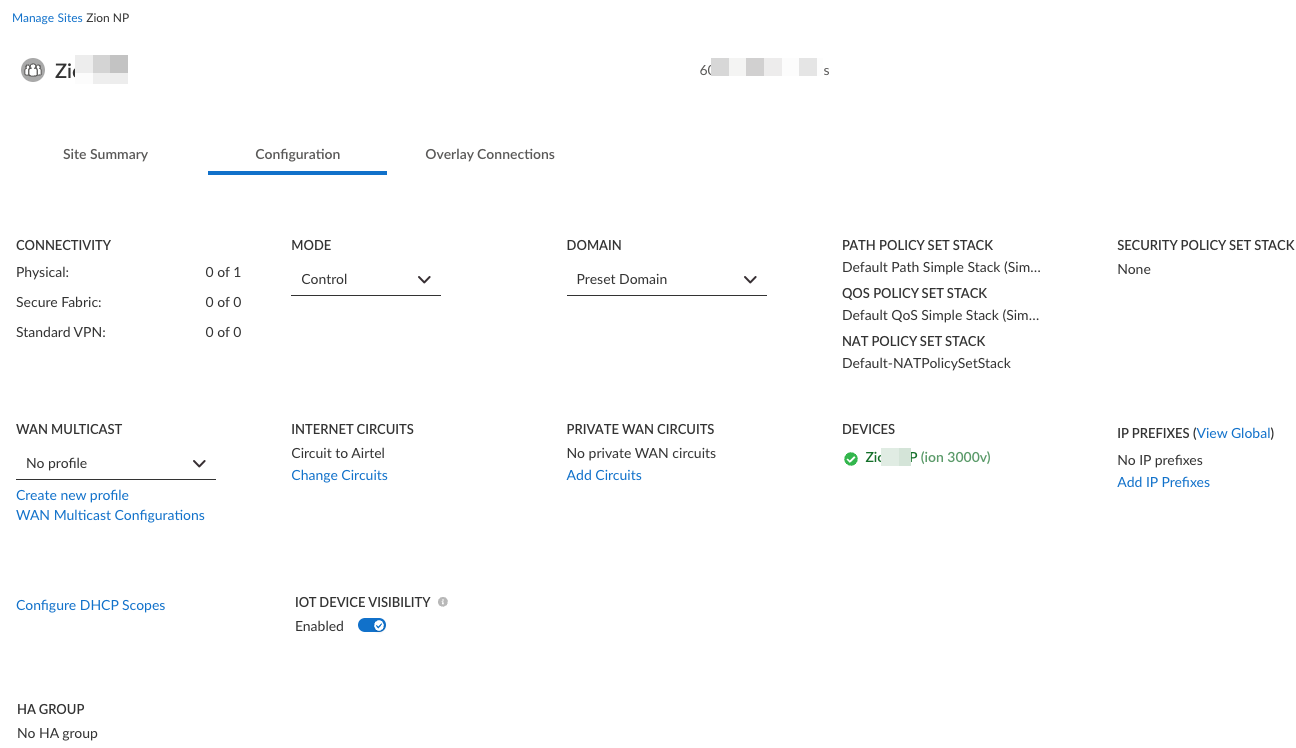
- Optional Control the sites that can forward logs to the Strata Logging Service from the Prisma SD-WAN web interface.When a TSG for Prisma Access includes both IoT Security and Prisma SD-WAN add-ons, it Prisma SD-WAN enables IoT Security visibility by default on the ION devices at all the branch sites.However, if you want to disable it on a particular site, pre-logon to Prisma SD-WAN, select WorkflowsSites, select the site, and toggle IoT Device Visibility off. This disables IoT Device Visibility on all ION devices at that site.

- View device information learned from Prisma SD-WAN sites in the IoT Security portal.
- Navigate to the IoT Security portal and select the Devices tab to view device details.
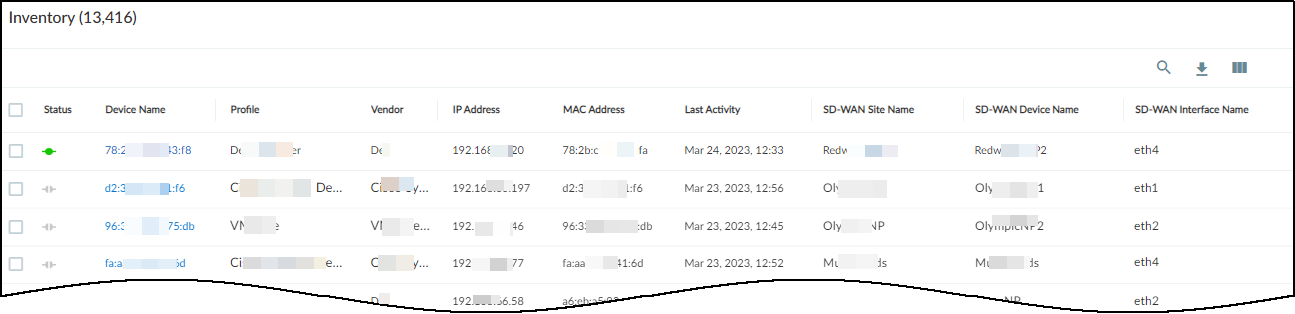
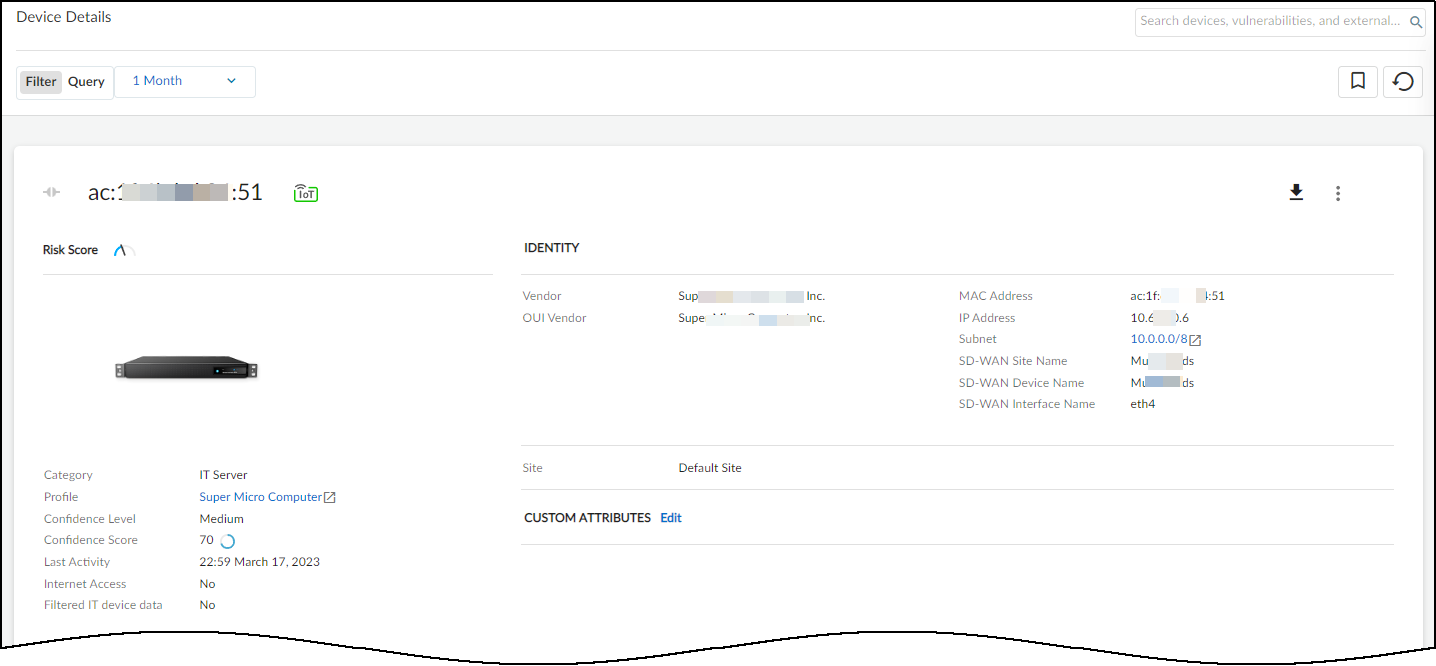
 After IoT Security receives data in Traffic logs from Prisma SD-WAN ION devices and starts discovering and identifying network-connected devices at branch sites, it displays its findings in the Inventory table on the Devices page in the IoT Security portal. For each device thatIoT Security learned from Prisma SD-WAN, it displays various device attributes such as its IP and MAC address, device category, vendor, model, and OS as well as several identifying attributes of the ION devices that provided the logs such as:
After IoT Security receives data in Traffic logs from Prisma SD-WAN ION devices and starts discovering and identifying network-connected devices at branch sites, it displays its findings in the Inventory table on the Devices page in the IoT Security portal. For each device thatIoT Security learned from Prisma SD-WAN, it displays various device attributes such as its IP and MAC address, device category, vendor, model, and OS as well as several identifying attributes of the ION devices that provided the logs such as:- Prisma SD-WAN site name
- Prisma SD-WAN device name
- Prisma SD-WAN interface name

- Optional Click a device to view details such as Prisma SD-WAN site, device, and interface names.