Create the Service Definitions on Panorama
Table of Contents
10.0 (EoL)
Expand all | Collapse all
-
- VM-Series Deployments
- VM-Series in High Availability
- Enable Jumbo Frames on the VM-Series Firewall
- Hypervisor Assigned MAC Addresses
- Custom PAN-OS Metrics Published for Monitoring
- Interface Used for Accessing External Services on the VM-Series Firewall
- PacketMMAP and DPDK Driver Support
- Enable ZRAM on the VM-Series Firewall
-
- VM-Series Firewall Licensing
- Create a Support Account
- Serial Number and CPU ID Format for the VM-Series Firewall
- Install a License API Key
- Use Panorama-Based Software Firewall License Management
-
- Maximum Limits Based on Memory
- Activate Credits
- Create a Deployment Profile
- Manage a Deployment Profile
- Register the VM-Series Firewall (Software NGFW Credits)
- Provision Panorama
- Migrate Panorama to a FW-Flex License
- Transfer Credits
- Renew Your Software NGFW Credit License
- Deactivate License (Software NGFW Credits)
- Create and Apply a Subscription-Only Auth Code
- Migrate to a Flexible VM-Series License
- What Happens When Licenses Expire?
-
- Supported Deployments on VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi)
-
- Plan the Interfaces for the VM-Series for ESXi
- Provision the VM-Series Firewall on an ESXi Server
- Perform Initial Configuration on the VM-Series on ESXi
- Add Additional Disk Space to the VM-Series Firewall
- Use VMware Tools on the VM-Series Firewall on ESXi and vCloud Air
- Use vMotion to Move the VM-Series Firewall Between Hosts
- Use the VM-Series CLI to Swap the Management Interface on ESXi
-
-
- VM-Series Firewall for NSX-V Deployment Checklist
- Install the VMware NSX Plugin
- Apply Security Policies to the VM-Series Firewall
- Steer Traffic from Guests that are not Running VMware Tools
- Dynamically Quarantine Infected Guests
- Migrate Operations-Centric Configuration to Security-Centric Configuration
- Add a New Host to Your NSX-V Deployment
- Use Case: Shared Compute Infrastructure and Shared Security Policies
- Use Case: Shared Security Policies on Dedicated Compute Infrastructure
- Dynamic Address Groups—Information Relay from NSX-V Manager to Panorama
-
- Supported Deployments of the VM-Series Firewall on VMware NSX-T (North-South)
- Components of the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (North-South)
-
- Install the Panorama Plugin for VMware NSX
- Enable Communication Between NSX-T Manager and Panorama
- Create Template Stacks and Device Groups on Panorama
- Configure the Service Definition on Panorama
- Deploy the VM-Series Firewall
- Direct Traffic to the VM-Series Firewall
- Apply Security Policy to the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T
- Use vMotion to Move the VM-Series Firewall Between Hosts
- Extend Security Policy from NSX-V to NSX-T
-
- Components of the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (East-West)
- VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (East-West) Integration
- Supported Deployments of the VM-Series Firewall on VMware NSX-T (East-West)
-
- Install the Panorama Plugin for VMware NSX
- Enable Communication Between NSX-T Manager and Panorama
- Create Template Stacks and Device Groups on Panorama
- Configure the Service Definition on Panorama
- Launch the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (East-West)
- Add a Service Chain
- Direct Traffic to the VM-Series Firewall
- Apply Security Policies to the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (East-West)
- Use vMotion to Move the VM-Series Firewall Between Hosts
-
- Install the Panorama Plugin for VMware NSX
- Enable Communication Between NSX-T Manager and Panorama
- Create Template Stacks and Device Groups on Panorama
- Configure the Service Definition on Panorama
- Launch the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (East-West)
- Create Dynamic Address Groups
- Create Dynamic Address Group Membership Criteria
- Generate Steering Policy
- Generate Steering Rules
- Delete a Service Definition from Panorama
- Migrate from VM-Series on NSX-T Operation to Security Centric Deployment
- Extend Security Policy from NSX-V to NSX-T
- Use In-Place Migration to Move Your VM-Series from NSX-V to NSX-T
- Use Migration Coordinator to Move Your VM-Series from NSX-V to NSX-T
-
-
- Deployments Supported on AWS
-
- Planning Worksheet for the VM-Series in the AWS VPC
- Launch the VM-Series Firewall on AWS
- Launch the VM-Series Firewall on AWS Outpost
- Create a Custom Amazon Machine Image (AMI)
- Encrypt EBS Volume for the VM-Series Firewall on AWS
- Use the VM-Series Firewall CLI to Swap the Management Interface
- Enable CloudWatch Monitoring on the VM-Series Firewall
-
- Use Case: Secure the EC2 Instances in the AWS Cloud
- Use Case: Use Dynamic Address Groups to Secure New EC2 Instances within the VPC
-
-
- What Components Does the VM-Series Auto Scaling Template for AWS (v2.0) Leverage?
- How Does the VM-Series Auto Scaling Template for AWS (v2.0 and v2.1) Enable Dynamic Scaling?
- Plan the VM-Series Auto Scaling Template for AWS (v2.0 and v2.1)
- Customize the Firewall Template Before Launch (v2.0 and v2.1)
- Launch the VM-Series Auto Scaling Template for AWS (v2.0)
- SQS Messaging Between the Application Template and Firewall Template
- Stack Update with VM-Series Auto Scaling Template for AWS (v2.0)
- Modify Administrative Account and Update Stack (v2.0)
-
- Launch the Firewall Template (v2.1)
- Launch the Application Template (v2.1)
- Create a Custom Amazon Machine Image (v2.1)
- VM-Series Auto Scaling Template Cleanup (v2.1)
- SQS Messaging Between the Application Template and Firewall Template (v2.1)
- Stack Update with VM-Series Auto Scaling Template for AWS (v2.1)
- Modify Administrative Account (v2.1)
- Change Scaling Parameters and CloudWatch Metrics (v2.1)
-
-
- Enable the Use of a SCSI Controller
- Verify PCI-ID for Ordering of Network Interfaces on the VM-Series Firewall
-
- Deployments Supported on Azure
- Deploy the VM-Series Firewall from the Azure Marketplace (Solution Template)
- Deploy the VM-Series Firewall from the Azure China Marketplace (Solution Template)
- Create a Custom VM-Series Image for Azure
- Deploy the VM-Series Firewall on Azure Stack
- Enable Azure Application Insights on the VM-Series Firewall
- Set up Active/Passive HA on Azure
- Use the ARM Template to Deploy the VM-Series Firewall
-
- About the VM-Series Firewall on Google Cloud Platform
- Supported Deployments on Google Cloud Platform
- Prepare to Set Up VM-Series Firewalls on Google Public Cloud
- Create a Custom VM-Series Firewall Image for Google Cloud Platform
-
- Deploy the VM-Series Firewall from Google Cloud Platform Marketplace
- Management Interface Swap for Google Cloud Platform Load Balancing
- Use the VM-Series Firewall CLI to Swap the Management Interface
- Enable Google Stackdriver Monitoring on the VM Series Firewall
- Enable VM Monitoring to Track VM Changes on Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Use Dynamic Address Groups to Secure Instances Within the VPC
- Use Custom Templates or the gcloud CLI to Deploy the VM-Series Firewall
-
- Prepare Your ACI Environment for Integration
-
-
- Create a Virtual Router and Security Zone
- Configure the Network Interfaces
- Configure a Static Default Route
- Create Address Objects for the EPGs
- Create Security Policy Rules
- Create a VLAN Pool and Domain
- Configure an Interface Policy for LLDP and LACP for East-West Traffic
- Establish the Connection Between the Firewall and ACI Fabric
- Create a VRF and Bridge Domain
- Create an L4-L7 Device
- Create a Policy-Based Redirect
- Create and Apply a Service Graph Template
-
- Create a VLAN Pool and External Routed Domain
- Configure an Interface Policy for LLDP and LACP for North-South Traffic
- Create an External Routed Network
- Configure Subnets to Advertise to the External Firewall
- Create an Outbound Contract
- Create an Inbound Web Contract
- Apply Outbound and Inbound Contracts to the EPGs
- Create a Virtual Router and Security Zone for North-South Traffic
- Configure the Network Interfaces
- Configure Route Redistribution and OSPF
- Configure NAT for External Connections
-
-
- Choose a Bootstrap Method
- VM-Series Firewall Bootstrap Workflow
- Bootstrap Package
- Bootstrap Configuration Files
- Generate the VM Auth Key on Panorama
- Create the bootstrap.xml File
- Prepare the Licenses for Bootstrapping
- Prepare the Bootstrap Package
- Bootstrap the VM-Series Firewall on AWS
- Bootstrap the VM-Series Firewall on Azure
- Bootstrap the VM-Series Firewall on Google Cloud Platform
- Verify Bootstrap Completion
- Bootstrap Errors
End-of-Life (EoL)
Create the Service Definitions on Panorama
A service definition specifies the configuration
for the VM-Series firewalls installed on each host in an ESXi cluster.
The service definition must include the device group, the license
auth-codes for deploying the VM-Series firewalls, and a template
stack with one or more NSX-V service profile zones. Typically, you
create a service definition for the VM-Series firewall in an ESXi
cluster. If you have different ESXi clusters that have workloads
that require the VM-Series firewall to handle traffic differently,
you can create multiple service definitions on Panorama.
On
a Panorama commit, each service definition is registered on the
NSX-V Manager. On registration with the NSX-V Manager, the NetX
API implementation makes each zone (defined within the template
stack) available for redirecting traffic. When you deploy the VM-Series
firewalls, you can select the profile name for the VM-Series firewall(s)
to which you want to redirect traffic from the objects in NSX-V
security groups. The appropriately configured firewall can then
inspect the traffic and enforce policy from the virtual machines
that belong to the NSX-V security groups.
- (Optional) Configure a Notify GroupCreate a notify group by specifying devices groups that should be notified of changes in the virtual environment. The firewalls included in the specified device groups receive a real-time update of security groups and IP addresses of guest VMs in them. The firewalls use this update to determine the most current list of members that constitute dynamic address groups referenced in policy
- Select PanoramaVMwareNSX-VNotify Group and click Add.
- Give your Notify Group a descriptive Name.
- Select the boxes of all devices groups that should be notified of changes to the virtual environment. If a device group does not have a check box available, it means that the device group is automatically included by virtue of the device group hierarchy.
- Click OK.
- Add a new service definition.You can create up to 32 service definitions on Panorama.
- Select PanoramaVMwareNSX-VService Definitions.
- Select Add to create a new
service definition. The maximum number of characters in a service
definition name is 40.On the NSX-V Manager, this service definition name displays in the Services column on Networking & SecurityService DefinitionsServices.
- (Optional) Add a Description that identifies the function or purpose for the VM-Series firewalls that will be deployed using this service definition.
- Assign a device group and a template stack to the service
definition.Make sure to Create the zone(s) for each template stack.Because the firewalls deployed in this solution will be centrally administered from Panorama, you must specify the Device Group and the Template Stack that the firewalls belong to. All the firewalls that are deployed using this service definition belong to the specified template stack and device group.
- Select the device group or device group hierarchy in the Device Group drop-down.
- Select the template stack in the Template drop-down.You cannot reuse a template stack or a device group assigned to one service definition in another service definition.
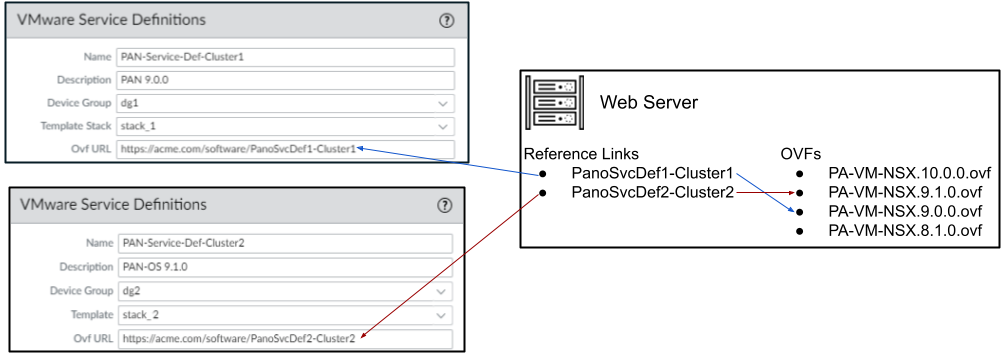
- Specify the location of the OVF file.Download the zip file, unzip it to extract and save the .ovf, mf and .vmdk files to the same directory. Both the files are used to deploy each instance of the firewall.If needed, modify the security settings on the server so that you can download the file types. For example, on the IIS server modify the Mime Types configuration; on an Apache server edit the .htaccess file.Do not change the Panorama service definition OVF path after a successful NSX Service Deployment of VM-Series firewalls. Changing the OVF path, after a successful VM-Series firewall deployment, can result in a NSX Service Deployment failed state. You may resolve this failure in NSX-V Manager, however this may cause all VM-Series firewalls to redeploy.It is recommended that you use an OVF path name that scales and allows you to change the base image without impacting your deployed firewalls. Instead of a path such as https://acme.com/software/PA-VM-NST.9.1.0.ovf, use something such as https://acme.com/software/PanoSvcDef1-Cluster1.ovf. Using a static path reference will eliminate any future need to change the OVF path. It is recommended to create a path for each Panorama service definition (vSphere cluster) in your deployment and change the PAN-OS base images references on the web server as needed.To use a different OVF for an existing Service Definition, change the reference link on the web server to point to another OVF. Changing the web server OVF reference links will not impact existing NSX Service Deployments. The new OVF path will take affect on new service deployments or any hosts introduced into the vSphere Cluster.
![]() In VM-Series OVF URL, add the location of the web server that hosts the ovf file. Both http and https are supported protocols. For example, enter https://acme.com/software/PA-VM-NSX.9.1.0.ovfSelect the ovf file that matches the VM-Series model you plan to deploy. For the VM-200, use vm100.ovf. For the VM-1000-HV, use vm300.ovf.You can use the same ovf version or different versions across service definitions. Using different ovf versions across service definitions allows you to vary the PAN-OS version on the VM-Series firewalls in different ESXi clusters.
In VM-Series OVF URL, add the location of the web server that hosts the ovf file. Both http and https are supported protocols. For example, enter https://acme.com/software/PA-VM-NSX.9.1.0.ovfSelect the ovf file that matches the VM-Series model you plan to deploy. For the VM-200, use vm100.ovf. For the VM-1000-HV, use vm300.ovf.You can use the same ovf version or different versions across service definitions. Using different ovf versions across service definitions allows you to vary the PAN-OS version on the VM-Series firewalls in different ESXi clusters. - (Optional) Select a Notify Group.To create context awareness between the virtual and security environments so that policy is consistently applied to all traffic steered to the firewalls, select the device groups to notify when there are changes in the virtual environment.Select each device group to which you want to enable notifications in the Notify Device Groups drop-down. If a device group does not have a checkbox available, it means that the device group is automatically included by virtue of the device group hierarchy.The firewalls included in the specified device groups receive a real-time update of security groups and IP addresses. The firewalls use this update to determine the most current list of members that constitute dynamic address groups referenced in policy.
- To automatically retrieve a device certificate when the
VM-Series firewall is deployed by NSX Manager, configure the device
certificate.
- If you have not done so already, log in to the Customer Support Portal and generate a Registration PIN and PIN ID.
- Under Device Certificate, click Enable.
- Copy the PIN ID and enter it into the Device Certificate PIN ID field.
- Reenter the PIN ID into the Confirm Device Certificate PIN ID field.
- Copy the Registration ID and enter it into the Device Certificate PIN Value field.
- Reenter the Registration ID into the Confirm Device Certificate PIN Value field.
- Save the service definition and attach it to the service
manager.
- Click OK.
- Select PanoramaVMwareNSX-VService Manager and click the link of the service manager name.
- Under Service Definitions, click Add and select your service definition from the drop-down.
- Click OK.
- Select Commit and Commit Type: Panorama.Committing the changes triggers the process of registering each service definition as a security service on the NSX-V Manager.
- Add the authorization code to license the firewalls.The auth-code must be for the VM-Series model NSX bundle; for example, PAN-VM-300-PERP- BND-NSX.Verify that the order quantity/ capacity is adequate to support the number of firewall you need to deploy in your network.
- Select PanoramaDevice Groups and choose the device group you associated with the service definition you just created.
- Under Dynamically Added Device Properties, add the
authorization code you received with your order fulfillment email
and select a PAN-OS software version from the SW Version drop-down.When a new firewall is deployed under NSX-V and added to the selected device group, the authorization code is applied and the firewall is upgraded to the select version of PAN-OS.On the support portal, you can view the total number of firewalls that you are authorized to deploy and the ratio of the number of licenses that have been used to the total number of licenses enabled by your auth-code.
- Synchronize the configuration between Panorama and
the NSX-V Manager.
- Select PanoramaVMwareNSX-VService Managers.
- Select NSX Config-Sync under the Actions column.
- Click Yes to confirm the sync.
- Verify that the service definition and the NSX-V service
profile that you defined on Panorama are registered on the NSX-V
Manager.
- On the NSX-V Manager, to verify that the
service definition is available, select Networking
& SecurityService DefinitionsServices. The service definition
is listed as a Service on the NSX-V Manager.
- To verify that the zones are available on the NSX-V
Manager:
- Select Networking and SecurityService ComposerSecurity Policies, and click Create Security Policy.
- Select Network Introspection Services, and click Add.
- In the Service Name drop-down, select a Palo Alto Networks service that you verified in the step above.
- In the Profile drop-down, verify that you can view all the zones you defined for that service definition on Panorama.
- On the NSX-V Manager, to verify that the
service definition is available, select Networking
& SecurityService DefinitionsServices. The service definition
is listed as a Service on the NSX-V Manager.
- (Optional)
Synchronize the configuration between Panorama and the NSX-V Manager.If you add or update the service definitions configured on Panorama, select NSX Config Sync in the Action column under PanoramaVMwareNSX-VService Managers to synchronize the changes on the NSX-V Manager.This link is not available if you have any pending commits on Panorama.If the synchronization fails, view the details to know whether to fix the error on Panorama or on the NSX-V Manager. For example, if you delete a service definition on Panorama, but the service definition cannot be deleted from the NSX-V Manager because it is referenced in a rule on the NSX-V Manager, the synchronization will fail with an error message that indicates the reason for failure.