Enable Communication Between the NSX-V Manager and Panorama
Table of Contents
10.0 (EoL)
Expand all | Collapse all
-
- VM-Series Deployments
- VM-Series in High Availability
- Enable Jumbo Frames on the VM-Series Firewall
- Hypervisor Assigned MAC Addresses
- Custom PAN-OS Metrics Published for Monitoring
- Interface Used for Accessing External Services on the VM-Series Firewall
- PacketMMAP and DPDK Driver Support
- Enable ZRAM on the VM-Series Firewall
-
- VM-Series Firewall Licensing
- Create a Support Account
- Serial Number and CPU ID Format for the VM-Series Firewall
- Install a License API Key
- Use Panorama-Based Software Firewall License Management
-
- Maximum Limits Based on Memory
- Activate Credits
- Create a Deployment Profile
- Manage a Deployment Profile
- Register the VM-Series Firewall (Software NGFW Credits)
- Provision Panorama
- Migrate Panorama to a FW-Flex License
- Transfer Credits
- Renew Your Software NGFW Credit License
- Deactivate License (Software NGFW Credits)
- Create and Apply a Subscription-Only Auth Code
- Migrate to a Flexible VM-Series License
- What Happens When Licenses Expire?
-
- Supported Deployments on VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi)
-
- Plan the Interfaces for the VM-Series for ESXi
- Provision the VM-Series Firewall on an ESXi Server
- Perform Initial Configuration on the VM-Series on ESXi
- Add Additional Disk Space to the VM-Series Firewall
- Use VMware Tools on the VM-Series Firewall on ESXi and vCloud Air
- Use vMotion to Move the VM-Series Firewall Between Hosts
- Use the VM-Series CLI to Swap the Management Interface on ESXi
-
-
- VM-Series Firewall for NSX-V Deployment Checklist
- Install the VMware NSX Plugin
- Apply Security Policies to the VM-Series Firewall
- Steer Traffic from Guests that are not Running VMware Tools
- Dynamically Quarantine Infected Guests
- Migrate Operations-Centric Configuration to Security-Centric Configuration
- Add a New Host to Your NSX-V Deployment
- Use Case: Shared Compute Infrastructure and Shared Security Policies
- Use Case: Shared Security Policies on Dedicated Compute Infrastructure
- Dynamic Address Groups—Information Relay from NSX-V Manager to Panorama
-
- Supported Deployments of the VM-Series Firewall on VMware NSX-T (North-South)
- Components of the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (North-South)
-
- Install the Panorama Plugin for VMware NSX
- Enable Communication Between NSX-T Manager and Panorama
- Create Template Stacks and Device Groups on Panorama
- Configure the Service Definition on Panorama
- Deploy the VM-Series Firewall
- Direct Traffic to the VM-Series Firewall
- Apply Security Policy to the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T
- Use vMotion to Move the VM-Series Firewall Between Hosts
- Extend Security Policy from NSX-V to NSX-T
-
- Components of the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (East-West)
- VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (East-West) Integration
- Supported Deployments of the VM-Series Firewall on VMware NSX-T (East-West)
-
- Install the Panorama Plugin for VMware NSX
- Enable Communication Between NSX-T Manager and Panorama
- Create Template Stacks and Device Groups on Panorama
- Configure the Service Definition on Panorama
- Launch the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (East-West)
- Add a Service Chain
- Direct Traffic to the VM-Series Firewall
- Apply Security Policies to the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (East-West)
- Use vMotion to Move the VM-Series Firewall Between Hosts
-
- Install the Panorama Plugin for VMware NSX
- Enable Communication Between NSX-T Manager and Panorama
- Create Template Stacks and Device Groups on Panorama
- Configure the Service Definition on Panorama
- Launch the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (East-West)
- Create Dynamic Address Groups
- Create Dynamic Address Group Membership Criteria
- Generate Steering Policy
- Generate Steering Rules
- Delete a Service Definition from Panorama
- Migrate from VM-Series on NSX-T Operation to Security Centric Deployment
- Extend Security Policy from NSX-V to NSX-T
- Use In-Place Migration to Move Your VM-Series from NSX-V to NSX-T
- Use Migration Coordinator to Move Your VM-Series from NSX-V to NSX-T
-
-
- Deployments Supported on AWS
-
- Planning Worksheet for the VM-Series in the AWS VPC
- Launch the VM-Series Firewall on AWS
- Launch the VM-Series Firewall on AWS Outpost
- Create a Custom Amazon Machine Image (AMI)
- Encrypt EBS Volume for the VM-Series Firewall on AWS
- Use the VM-Series Firewall CLI to Swap the Management Interface
- Enable CloudWatch Monitoring on the VM-Series Firewall
-
- Use Case: Secure the EC2 Instances in the AWS Cloud
- Use Case: Use Dynamic Address Groups to Secure New EC2 Instances within the VPC
-
-
- What Components Does the VM-Series Auto Scaling Template for AWS (v2.0) Leverage?
- How Does the VM-Series Auto Scaling Template for AWS (v2.0 and v2.1) Enable Dynamic Scaling?
- Plan the VM-Series Auto Scaling Template for AWS (v2.0 and v2.1)
- Customize the Firewall Template Before Launch (v2.0 and v2.1)
- Launch the VM-Series Auto Scaling Template for AWS (v2.0)
- SQS Messaging Between the Application Template and Firewall Template
- Stack Update with VM-Series Auto Scaling Template for AWS (v2.0)
- Modify Administrative Account and Update Stack (v2.0)
-
- Launch the Firewall Template (v2.1)
- Launch the Application Template (v2.1)
- Create a Custom Amazon Machine Image (v2.1)
- VM-Series Auto Scaling Template Cleanup (v2.1)
- SQS Messaging Between the Application Template and Firewall Template (v2.1)
- Stack Update with VM-Series Auto Scaling Template for AWS (v2.1)
- Modify Administrative Account (v2.1)
- Change Scaling Parameters and CloudWatch Metrics (v2.1)
-
-
- Enable the Use of a SCSI Controller
- Verify PCI-ID for Ordering of Network Interfaces on the VM-Series Firewall
-
- Deployments Supported on Azure
- Deploy the VM-Series Firewall from the Azure Marketplace (Solution Template)
- Deploy the VM-Series Firewall from the Azure China Marketplace (Solution Template)
- Create a Custom VM-Series Image for Azure
- Deploy the VM-Series Firewall on Azure Stack
- Enable Azure Application Insights on the VM-Series Firewall
- Set up Active/Passive HA on Azure
- Use the ARM Template to Deploy the VM-Series Firewall
-
- About the VM-Series Firewall on Google Cloud Platform
- Supported Deployments on Google Cloud Platform
- Prepare to Set Up VM-Series Firewalls on Google Public Cloud
- Create a Custom VM-Series Firewall Image for Google Cloud Platform
-
- Deploy the VM-Series Firewall from Google Cloud Platform Marketplace
- Management Interface Swap for Google Cloud Platform Load Balancing
- Use the VM-Series Firewall CLI to Swap the Management Interface
- Enable Google Stackdriver Monitoring on the VM Series Firewall
- Enable VM Monitoring to Track VM Changes on Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Use Dynamic Address Groups to Secure Instances Within the VPC
- Use Custom Templates or the gcloud CLI to Deploy the VM-Series Firewall
-
- Prepare Your ACI Environment for Integration
-
-
- Create a Virtual Router and Security Zone
- Configure the Network Interfaces
- Configure a Static Default Route
- Create Address Objects for the EPGs
- Create Security Policy Rules
- Create a VLAN Pool and Domain
- Configure an Interface Policy for LLDP and LACP for East-West Traffic
- Establish the Connection Between the Firewall and ACI Fabric
- Create a VRF and Bridge Domain
- Create an L4-L7 Device
- Create a Policy-Based Redirect
- Create and Apply a Service Graph Template
-
- Create a VLAN Pool and External Routed Domain
- Configure an Interface Policy for LLDP and LACP for North-South Traffic
- Create an External Routed Network
- Configure Subnets to Advertise to the External Firewall
- Create an Outbound Contract
- Create an Inbound Web Contract
- Apply Outbound and Inbound Contracts to the EPGs
- Create a Virtual Router and Security Zone for North-South Traffic
- Configure the Network Interfaces
- Configure Route Redistribution and OSPF
- Configure NAT for External Connections
-
-
- Choose a Bootstrap Method
- VM-Series Firewall Bootstrap Workflow
- Bootstrap Package
- Bootstrap Configuration Files
- Generate the VM Auth Key on Panorama
- Create the bootstrap.xml File
- Prepare the Licenses for Bootstrapping
- Prepare the Bootstrap Package
- Bootstrap the VM-Series Firewall on AWS
- Bootstrap the VM-Series Firewall on Azure
- Bootstrap the VM-Series Firewall on Google Cloud Platform
- Verify Bootstrap Completion
- Bootstrap Errors
End-of-Life (EoL)
Enable Communication Between the NSX-V Manager and Panorama
To automate the provisioning of the VM-Series
firewall for NSX-V, enable communication between the NSX-V Manager and
Panorama. This is a one-time setup, and only needs to be modified
if the IP address of the NSX-V Manager changes or if the capacity
license for deploying the VM-Series firewall is exceeded.
- (Optional) Bypass proxy server settings,
configured on Panorama under PanoramaSetupServicesProxy
Server, for communication between Panorama
and NSX-V Manager. This command allows Panorama to communicate directly
with NSX-V Manager while maintaining proxied communication for other
services. This feature requires Panorama plugin for VMware NSX 2.0.5.
- Log in to the Panorama CLI.
- Execute the following command to enable or disable
proxy bypass.admin@Panorama> request plugins vmware_nsx global proxy bypass {yes | no}Select yes to enable proxy bypass and no to disable proxy bypass.
- Log in to the Panorama web interface.Using a secure connection (https) from a web browser, log in using the IP address and password you assigned during initial configuration (https://<IP address>).
- Set up access to the NSX-V Manager.
- Select PanoramaVMwareNSX-VService Managers and click Add.
- Enter the Service Manager Name.On the NSX-V Manager, this name displays in the Service Manager column on Networking & SecurityService DefinitionsService Managers.
- (Optional) Add a Description that identifies the VM-Series firewall as a service.
- Enter the NSX Manager URL—IP address or FQDN—at which to access the NSX-V Manager.
- Enter the NSX Manager Login credentials—the
username and password for your Enterprise Administrator role on
NSX Manager. This allows Panorama to authenticate with the NSX-V
Manager.The ampersand (&) special character is not supported in the NSX-V manager account password. If a password includes an ampersand, the connection between Panorama and NSX-V manager fails.If you change your NSX-V Manager login password, ensure that you update the password on Panorama immediately. An incorrect password breaks the connection between Panorama and NSX-V Manager. Panorama does not receive updates about changes to your deployment while disconnected from NSX-V Manager.
- Click OK.
- Commit your changes to Panorama.Select Commit and Commit Type: Panorama.
- Verify the connection status on Panorama.To view the connection status between Panorama and the NSX-V Manager.
- Select PanoramaVMwareNSX-VService Managers.
- Verify the message in the Status column.When the connection is successful, the status displays as Registered. This indicates that Panorama and the NSX-V Manager are in sync and the VM-Series firewall is registered as a service on the NSX-V Manager.The unsuccessful status messages are:
- Not connected: Unable to reach/establish a network connection to the NSX-V Manager.
- Invalid Credentials: The access credentials (username and/or password) are incorrect.
- Out of sync: The configuration settings defined on Panorama are different from what is defined on the NSX-V Manager.Click the link for details on the reasons for failure. For example, NSX-V Manager may have a service definition with the same name as defined on Panorama. To fix the error, use the service definition name listed in the error message to validate the service definition on the NSX-V Manager. Until the configuration on Panorama and the NSX-V Manager is synchronized, you cannot add a new service definition on Panorama.
- No service/ No service profile: Indicates an incomplete configuration on the NSX-V Manager.
If you make a change and need to manually sync, see 10
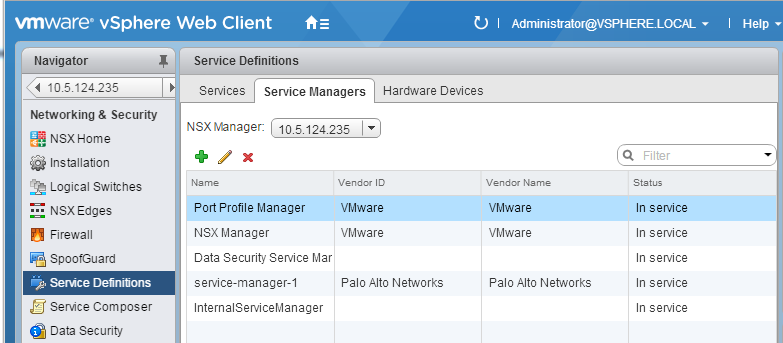
- Verify that the firewall is registered as a service on
the NSX-V Manager.
- On the vSphere web client, select Networking & SecurityService
DefinitionsService Managers.
![]()
- Verify that Palo Alto Networks displays as a vendor in the list of services available for installation.
- On the vSphere web client, select Networking & SecurityService
DefinitionsService Managers.
- If you are running VMware NSX plugin 2.0.4 or later,
you can configure Panorama to automatically synchronize dynamic
objects with NSX-V manager as if you issued an Synchronize
Dynamic Objects. By default, the DAG Sync interval is
disabled and the value is set to zero (0). To enable the DAG Sync,
set the interval between one hour and 72 hours. Setting a value
of zero hours disables the DAG sync. To configure or disable the
interval, complete the following procedure.
- Log in to the Panorama CLI.
- Execute the following command.request plugins vmware_nsx nsx_v dag-sync-interval interval <interval-in-hours>You can view the configured value with the following show command.show plugins vmware_nsx nsx_v dag-sync-interval
- (Optional) In large NSX-V environments with
tens of thousands of IP addresses, allowing Panorama enough time to
retrieve IP address updates from NSX-V Manager is essential. You
can now configure the amount of time—up to 10 minutes—Panorama has
to retrieve updates from NSX-V Manager. By default, Panorama waits
up to two minutes (120 seconds) to get IP address updates from NSX-V
Manager. However, if Panorama does not retrieve all the IP address
updates within the alloted two minutes, Panorama times out and the
update fails. You can determine if you are experiencing curl call failures through the Panorama error log. Curl call failures return the following message.
2019-05-23 06:50:15.780 -0700 ERROR: Curl call to NSX Manager failed
Complete the following procedure to increase the amount of time Panorama has to process updates. This feature requires Panorama plugin for VMware NSX 2.0.5.- Log in to the Panorama CLI.
- Execute the following command to set the curl call
timeout. You can set the time out from 30 seconds to 600 seconds (10
minutes).admin@Panorama> request plugins vmware_nsx global curl-timeout timeout <seconds>If Panorama is part of an HA pair, configure the same timeout value on the active and passive Panorama peers.