Prisma Access Traffic Steering Rule Guidelines
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma Access Docs
-
5.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 4.2 Preferred
- 4.1 Preferred
- 4.0 Preferred
- 3.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 2.2 Preferred
-
-
-
-
- Allocate Licenses for Prisma Access (Managed by Strata Cloud Manager)
- Plan Service Connections for Prisma Access (Managed by Strata Cloud Manager) and Add-ons
- Add Additional Locations for Prisma Access (Managed by Strata Cloud Manager) and Add-ons
- Enable Available Add-ons for Prisma Access (Managed by Strata Cloud Manager)
- Search for Subscription Details
- Share a License for Prisma Access (Managed by Strata Cloud Manager) and Add-ons
- Increase Subscription Allocation Quantity
-
- Activate a License for Prisma Access (Managed by Strata Cloud Manager) and Prisma SD-WAN Bundle
- Activate and Edit a License for SASE 5G Through Common Services
-
- Prisma Access Onboarding Workflow
-
3.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 4.0 & Later
- 3.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 2.2 Preferred
- Prisma Access China
-
- Prisma Access
- Prisma Access Infrastructure Management
- Cadence for Software and Content Updates for Prisma Access
- Use the Prisma Access App to Get Upgrade Alerts and Updates
- View Prisma Access Software Versions
- Zone Mapping
- Prisma Access APIs
- Prisma Access Deployment Progress and Status
- Troubleshoot the Prisma Access Deployment
-
- Prisma Access Mobile User Deployments
- How the GlobalProtect App Selects a Prisma Access Location for Mobile Users
- Integrate Prisma Access with On-Premises Gateways
-
- Set Equal Gateway Priorities for On-Premises and Prisma Access Gateways
- Set a Higher Gateway Priority for an On-Premises Gateway
- Set Higher Priorities for Multiple On-Premises Gateways
- Configure Priorities for Prisma Access and On-Premises Gateways
- Allow Mobile Users to Manually Select Specific Prisma Access Gateways
- Report Prisma Access Website Access Issues
-
- Multitenancy Overview
- Multitenancy Configuration Overview
- Plan Your Multitenant Deployment
- Create an All-New Multitenant Deployment
- Enable Multitenancy and Migrate the First Tenant
- Add Tenants to Prisma Access
- Delete a Tenant
- Create a Tenant-Level Administrative User
- Sort Logs by Device Group ID in a Multitenant Deployment
-
-
-
- Default Routes With Prisma Access Traffic Steering
- Traffic Steering in Prisma Access
- Traffic Steering Requirements
- Default Routes with Traffic Steering Example
- Default Routes with Traffic Steering Direct to Internet Example
- Default Routes with Traffic Steering and Dedicated Service Connection Example
- Prisma Access Traffic Steering Rule Guidelines
- Configure Zone Mapping and Security Policies for Traffic Steering Dedicated Connections
- Configure Traffic Steering in Prisma Access
-
-
-
- Integrate Prisma Access With Other Palo Alto Networks Apps
- Integrate Third-Party Enterprise Browser with Explicit Proxy
- Integrate Third-Party NDRs with Prisma Access
- Juniper Mist Integration for SASE Health
-
-
- Connect your Mobile Users in Mainland China to Prisma Access Overview
- Configure Prisma Access for Mobile Users in China
- Configure Real-Name Registration and Create the VPCs in Alibaba Cloud
- Attach the CEN and Specify the Bandwidth
- Create Linux Instances in the Alibaba Cloud VPCs
- Configure the Router Instances
- Onboard the GlobalProtect Gateway and Configure the Prisma Access Portal
-
-
-
- INC_MU_APP_EXPERIENCE_UNREACHABLE_ ALL_PA_LOCATIONS
- INC_MU_APP_EXPERIENCE_UNREACHABLE_ PER_PA_LOCATION
- INC_RN_APP_EXPERIENCE_UNREACHABLE_ ALL_PA_LOCATIONS
- INC_RN_APP_EXPERIENCE_UNREACHABLE_ ONE_PA_LOCATION
- INC_CIE_AGENT_DISCONNECT
- INC_CIE_DIRECTORY_DISCONNECT
- INC_GLOBALPROTECT_GW_USER_AUTH_ TIMEOUT_FAILURES_COUNT_EXCEEDED_ ABOVE_BASELINE_ALL_PA_LOCATIONS
- INC_GLOBALPROTECT_GW_USER_AUTH_ TIMEOUT_FAILURES_COUNT_EXCEEDED_ ABOVE_BASELINE_PER_PA_LOCATION
- INC_GLOBALPROTECT_PORTAL_AUTH_ TIMEOUT_FAILURES_COUNT_EXCEEDED_ ABOVE_BASELINE_ALL_PA_LOCATIONS
- INC_GLOBALPROTECT_PORTAL_AUTH_ TIMEOUT_FAILURES_COUNT_EXCEEDED_ ABOVE_BASELINE_PER_PA_LOCATION
- INC_MU_AUTH_SERVER_UNREACHABLE_ALL_ PA_LOCATIONS
- INC_MU_AUTH_SERVER_UNREACHABLE_PER_ PA_LOCATION
- INC_MU_DNS_SERVER_UNREACHABLE_ALL_ PA_LOCATIONS
- INC_MU_DNS_SERVER_UNREACHABLE_ PER_PA_LOCATION
- INC_PORTAL_CLIENTLESS_VPN_AUTH_ TIMEOUT_FAILURES_COUNT_EXCEEDED_ ABOVE_BASELINE_ALL_PA_LOCATIONS
- INC_PORTAL_CLIENTLESS_VPN_AUTH_ TIMEOUT_FAILURES_COUNT_EXCEEDED_ ABOVE_BASELINE_PER_PA_LOCATION
- INC_RN_AUTH_SERVER_UNREACHABLE_ALL_ PA_LOCATIONS
- INC_RN_AUTH_SERVER_UNREACHABLE_PER_ PA_LOCATION
- INC_RN_DNS_SERVER_UNREACHABLE_ALL_ PA_LOCATIONS
- INC_RN_DNS_SERVER_UNREACHABLE_PER_ PA_LOCATION
- INC_RN_ECMP_TUNNEL_RTT_EXCEEDED_ BASELINE
- INC_RN_PRIMARY_WAN_TUNNEL_RTT_ EXCEEDED_BASELINE
- INC_RN_SECONDARY_TUNNEL_DOWN
- INC_RN_SECONDARY_WAN_TUNNEL_RTT_ EXCEEDED_BASELINE
- INC_RN_SITE_CAPACITY_PREDICTION
- INC_SC_PRIMARY_WAN_TUNNEL_RTT_ EXCEEDED_BASELINE
- INC_SC_SECONDARY_WAN_TUNNEL_RTT_ EXCEEDED_BASELINE
- INC_SC_SITE_CAPACITY_PREDICTION
-
- INC_CERTIFICATE_EXPIRY
- INC_GP_CLIENT_VERSION_UNSUPPORTED
- INC_MU_IP_POOL_BLOCK_UTILIZATION_ EXCEEDED_CAPACITY
- INC_MU_IP_POOL_BLOCK_UTILIZATION_ EXCEEDED_THRESHOLD
- INC_PA_INFRA_DEGRADATION
- INC_PA_SERVICE_DEGRADATION_PA_LOCATION
- INC_PA_SERVICE_DEGRADATION_RN_ SITE_CONNECTIVITY
- INC_PA_SERVICE_DEGRADATION_SC_ CONNECTIVITY
- INC_RN_ECMP_BGP_DOWN
- INC_RN_ECMP_BGP_FLAP
- INC_RN_ECMP_PROXY_TUNNEL_DOWN
- INC_RN_ECMP_PROXY_TUNNEL_FLAP
- INC_RN_ECMP_TUNNEL_DOWN
- INC_RN_ECMP_TUNNEL_FLAP
- INC_RN_PRIMARY_WAN_BGP_FLAP
- INC_RN_PRIMARY_WAN_PROXY_TUNNEL_DOWN
- INC_RN_PRIMARY_WAN_PROXY_TUNNEL_FLAP
- INC_RN_PRIMARY_WAN_TUNNEL_DOWN
- INC_RN_PRIMARY_WAN_TUNNEL_FLAP
- INC_RN_SECONDARY_WAN_BGP_DOWN
- INC_RN_SECONDARY_WAN_BGP_FLAP
- INC_RN_SECONDARY_WAN_PROXY_TUNNEL_DOWN
- INC_RN_SECONDARY_WAN_PROXY_TUNNEL_FLAP
- INC_RN_SECONDARY_WAN_TUNNEL_DOWN
- INC_RN_SECONDARY_WAN_TUNNEL_FLAP
- INC_RN_SITE_DOWN
- INC_RN_SITE_LONG_DURATION_CAPACITY_ EXCEEDED_THRESHOLD
- INC_RN_SITE_LONG_DURATION_EXCEEDED_ CAPACITY
- INC_RN_SPN_LONG_DURATION_CAPACITY_EXCEEDED _THRESHOLD
- INC_RN_SPN_LONG_DURATION_EXCEEDED_ CAPACITY
- INC_SC_PRIMARY_WAN_BGP_DOWN
- INC_SC_PRIMARY_WAN_BGP_FLAP
- INC_SC_PRIMARY_WAN_PROXY_TUNNEL_DOWN
- INC_SC_PRIMARY_WAN_PROXY_TUNNEL_FLAP
- INC_SC_PRIMARY_WAN_TUNNEL_DOWN
- INC_SC_PRIMARY_WAN_TUNNEL_FLAP
- INC_SC_SECONDARY_WAN_BGP_DOWN
- INC_SC_SECONDARY_WAN_BGP_FLAP
- INC_SC_SECONDARY_WAN_PROXY_TUNNEL_DOWN
- INC_SC_SECONDARY_WAN_PROXY_TUNNEL_FLAP
- INC_SC_SECONDARY_WAN_TUNNEL_DOWN
- INC_SC_SECONDARY_WAN_TUNNEL_FLAP
- INC_SC_SITE_DOWN
- INC_SC_SITE_LONG_DURATION_CAPACITY_ EXCEEDED_THRESHOLD
- INC_SC_SITE_LONG_DURATION_EXCEEDED_ CAPACITY
- INC_ZTNA_CONNECTOR_APP_STATUS_DOWN
- INC_ZTNA_CONNECTOR_APP_STATUS_DOWN_PARTIAL
- INC_ZTNA_CONNECTOR_CPU_HIGH
- INC_ZTNA_CONNECTOR_MEMORY_HIGH
- INC_ZTNA_CONNECTOR_TUNNEL_DOWN
-
- AL_CIE_AGENT_DISCONNECT
- AL_CIE_DIRECTORY_DISCONNECT
- AL_MU_IP_POOL_CAPACITY
- AL_MU_IP_POOL_USAGE
- AL_RN_ECMP_BGP_DOWN
- AL_RN_ECMP_BGP_FLAP
- AL_RN_PRIMARY_WAN_BGP_DOWN
- AL_RN_PRIMARY_WAN_BGP_FLAP
- AL_RN_PRIMARY_WAN_TUNNEL_DOWN
- AL_RN_PRIMARY_WAN_TUNNEL_FLAP
- AL_RN_SECONDARY_WAN_BGP_DOWN
- AL_RN_SECONDARY_WAN_BGP_FLAP
- AL_RN_SECONDARY_WAN_TUNNEL_DOWN
- AL_RN_SECONDARY_WAN_TUNNEL_FLAP
- AL_RN_SITE_DOWN
- AL_RN_SITE_LONG_DURATION_CAPACITY_ EXCEEDED_THRESHOLD
- AL_RN_SITE_LONG_DURATION_EXCEEDED_ CAPACITY
- AL_RN_SPN_LONG_DURATION_CAPACITY_ EXCEEDED_THRESHOLD
- AL_SC_PRIMARY_WAN_BGP_DOWN
- AL_SC_PRIMARY_WAN_BGP_FLAP
- AL_SC_PRIMARY_WAN_TUNNEL_DOWN
- AL_SC_PRIMARY_WAN_TUNNEL_FLAP
- AL_SC_SECONDARY_WAN_BGP_DOWN
- AL_SC_SECONDARY_WAN_BGP_FLAP
- AL_SC_SECONDARY_WAN_TUNNEL_DOWN
- AL_SC_SECONDARY_WAN_TUNNEL_FLAP
- AL_SC_SITE_DOWN
- AL_SC_SITE_LONG_DURATION_CAPACITY_ EXCEEDED_THRESHOLD
- AL_SC_SITE_LONG_DURATION_EXCEEDED_CAPACITY
- AL_ZTNA_CONNECTOR_APP_STATUS_DOWN
- AL_ZTNA_CONNECTOR_APP_STATUS_DOWN_PARTIAL
- AL_ZTNA_CONNECTOR_CPU_HIGH
- AL_ZTNA_CONNECTOR_MEMORY_HIGH
- AL_ZTNA_CONNECTOR_TUNNEL_DOWN
- New Features in Incidents and Alerts
- Known Issues
Prisma Access Traffic Steering Rule Guidelines
Learn about the guidelines you need to follow when you
configure Prisma Access traffic steering.
Traffic steering can process a wide variety of possible
configurations; however, it is important to understand how Prisma
Access processes rules, so you can create rules are easy to maintain
and manage. To help you create the rules that work best for your
deployment, follow these guidelines:
- Prisma Access evaluates rules in the order that you create them (from top to bottom). Specify more specific rules at the top and more general rules at the bottom.
- Create multiple rules with fewer matching criteria, instead of creating fewer rules with multiple types of criteria. Creating simpler rules both speeds up rule creation and makes it easier to modify a rule.
- Since you cannot move a rule up or down in a list after you create it, carefully plan your rule order before you create the rules.
- Rules that specify Any source address and User, Any source destination and URL Category, and Any service are not supported. Use more specific rules; for example, specify a rule with Any source or destination traffic and a service of service-http and service-https.
- If you are going to specify rules for users in the Source User field, make sure that Prisma Access can distinguish between users if the same username is shared between users who authenticate locally and users who authenticate using LDAP by authenticating LDAP users in the format of domain/username and authenticating local users in the format of username (without the domain name).
- If you have configured an on-premises next-generation firewall as a master device, you can auto-populate user and group information for mobile user device groups in traffic steering and security policy rules by selecting PanoramaCloud ServicesConfigurationMobile Users, clicking the gear icon to edit the Settings, and selecting the Master Device in the Device Group area. While this populates the master device in every device group, it only populates the user and group information for mobile users in security policy rules.
- If an EDL (type IP List) is used in a Traffic Steering Rule, and the EDL source URL of the EDL is updated to a URL that is not accessible, Prisma Access may continue to use the cached IP list from the previous URL.
- Prisma Access bypasses Traffic Steering for rules with a service type of HTTP or HTTPS if you use an application override policy for TCP ports 80 and 443.In addition, traffic steering does not work for URLs from URL categories referenced in the traffic steering rule if you have configured an application override policy for TCP ports 80 or 443.
- You can specify destination IP addresses and URL categories in the same rule. If you do, Prisma Access uses a logical OR to process the destination criteria in the rule, but processes the URLs and URL category traffic based on TCP ports 80 and 8080 for HTTP and TCP port 443 for HTTPS.For a rule with IP addresses and URL categories, traffic matches the rule if either the IP address or the URL category matches, but processes the URL category traffic based on ports 80, 443, and 8080 only. Palo Alto Networks does not recommend creating a rule of this type; instead, create simpler rules.
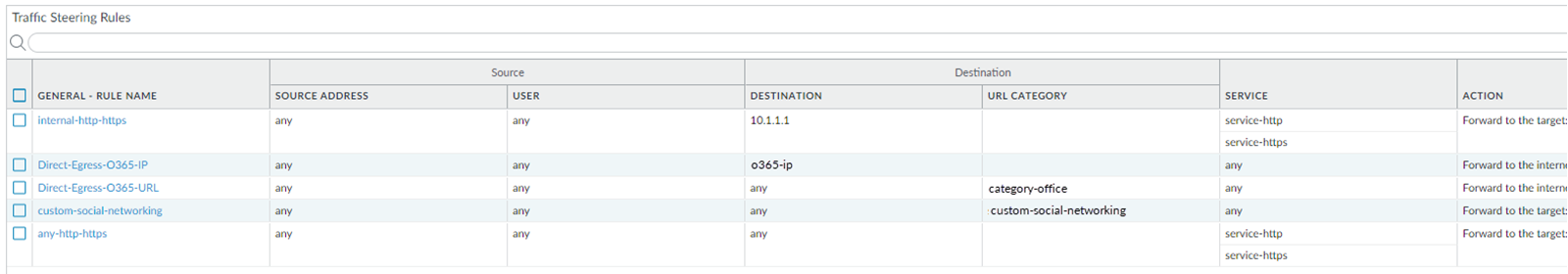
For example, you want to enforce the following rules for your
network traffic:
- You have an internal HTTP server with an IP address of 10.1.1.1 in the data center, and you want to direct internal HTTP and HTTPS traffic to this server. The IP address of the server is 10.1.1.1.Traffic to this server should not go to the internet and should be processed internally; therefore, choose a non-dedicated target for this traffic, because this type of target processes both internal and internet-bound traffic.
- You want office365.com traffic to be routed directly to the internet.
- You want traffic from *.example.com or any traffic defined in a custom URL category of custom-social-networking to be routed to a dedicated connection.
- You want any other HTTP and HTTPS traffic to use the same non-dedicated service connection target as that used for the internal HTTP server.
For this example, create the rules from the most specific to
the least specific, as shown in the following screenshot. Do not
add the rule that allows all HTTP and HTTPS traffic first, or Prisma
Access would direct all HTTP and HTTPS traffic to the non-dedicated
connection without evaluating any of the other rules.