Configure Active/Passive HA
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Next-Generation Firewall Docs
-
PAN-OS 11.1 & Later
- Cloud Management of NGFWs
- PAN-OS 10.0 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 10.1
- PAN-OS 10.2
- PAN-OS 11.0 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 11.1 & Later
- PAN-OS 9.1 (EoL)
-
- Management Interfaces
-
- Launch the Web Interface
- Use the Administrator Login Activity Indicators to Detect Account Misuse
- Manage and Monitor Administrative Tasks
- Commit, Validate, and Preview Firewall Configuration Changes
- Commit Selective Configuration Changes
- Export Configuration Table Data
- Use Global Find to Search the Firewall or Panorama Management Server
- Manage Locks for Restricting Configuration Changes
-
-
- Define Access to the Web Interface Tabs
- Provide Granular Access to the Monitor Tab
- Provide Granular Access to the Policy Tab
- Provide Granular Access to the Objects Tab
- Provide Granular Access to the Network Tab
- Provide Granular Access to the Device Tab
- Define User Privacy Settings in the Admin Role Profile
- Restrict Administrator Access to Commit and Validate Functions
- Provide Granular Access to Global Settings
- Provide Granular Access to the Panorama Tab
- Provide Granular Access to Operations Settings
- Panorama Web Interface Access Privileges
-
- Reset the Firewall to Factory Default Settings
-
- Plan Your Authentication Deployment
- Pre-Logon for SAML Authentication
- Configure SAML Authentication
- Configure Kerberos Single Sign-On
- Configure Kerberos Server Authentication
- Configure TACACS+ Authentication
- Configure TACACS Accounting
- Configure RADIUS Authentication
- Configure LDAP Authentication
- Configure Local Database Authentication
- Configure an Authentication Profile and Sequence
- Test Authentication Server Connectivity
- Troubleshoot Authentication Issues
-
- Keys and Certificates
- Default Trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs)
- Certificate Deployment
- Configure the Master Key
- Export a Certificate and Private Key
- Configure a Certificate Profile
- Configure an SSL/TLS Service Profile
- Configure an SSH Service Profile
- Replace the Certificate for Inbound Management Traffic
- Configure the Key Size for SSL Forward Proxy Server Certificates
-
- HA Overview
-
- Prerequisites for Active/Active HA
- Configure Active/Active HA
-
- Use Case: Configure Active/Active HA with Route-Based Redundancy
- Use Case: Configure Active/Active HA with Floating IP Addresses
- Use Case: Configure Active/Active HA with ARP Load-Sharing
- Use Case: Configure Active/Active HA with Floating IP Address Bound to Active-Primary Firewall
- Use Case: Configure Active/Active HA with Source DIPP NAT Using Floating IP Addresses
- Use Case: Configure Separate Source NAT IP Address Pools for Active/Active HA Firewalls
- Use Case: Configure Active/Active HA for ARP Load-Sharing with Destination NAT
- Use Case: Configure Active/Active HA for ARP Load-Sharing with Destination NAT in Layer 3
- HA Clustering Overview
- HA Clustering Best Practices and Provisioning
- Configure HA Clustering
- Refresh HA1 SSH Keys and Configure Key Options
- HA Firewall States
- Reference: HA Synchronization
-
- Use the Dashboard
- Monitor Applications and Threats
- Monitor Block List
-
- Report Types
- View Reports
- Configure the Expiration Period and Run Time for Reports
- Disable Predefined Reports
- Custom Reports
- Generate Custom Reports
- Generate the SaaS Application Usage Report
- Manage PDF Summary Reports
- Generate User/Group Activity Reports
- Manage Report Groups
- Schedule Reports for Email Delivery
- Manage Report Storage Capacity
- View Policy Rule Usage
- Use External Services for Monitoring
- Configure Log Forwarding
- Configure Email Alerts
-
- Configure Syslog Monitoring
-
- Traffic Log Fields
- Threat Log Fields
- URL Filtering Log Fields
- Data Filtering Log Fields
- HIP Match Log Fields
- GlobalProtect Log Fields
- IP-Tag Log Fields
- User-ID Log Fields
- Decryption Log Fields
- Tunnel Inspection Log Fields
- SCTP Log Fields
- Authentication Log Fields
- Config Log Fields
- System Log Fields
- Correlated Events Log Fields
- GTP Log Fields
- Audit Log Fields
- Syslog Severity
- Custom Log/Event Format
- Escape Sequences
- Forward Logs to an HTTP/S Destination
- Firewall Interface Identifiers in SNMP Managers and NetFlow Collectors
- Monitor Transceivers
-
- User-ID Overview
- Enable User-ID
- Map Users to Groups
- Enable User- and Group-Based Policy
- Enable Policy for Users with Multiple Accounts
- Verify the User-ID Configuration
-
- App-ID Overview
- App-ID and HTTP/2 Inspection
- Manage Custom or Unknown Applications
- Safely Enable Applications on Default Ports
- Applications with Implicit Support
-
- Prepare to Deploy App-ID Cloud Engine
- Enable or Disable the App-ID Cloud Engine
- App-ID Cloud Engine Processing and Policy Usage
- New App Viewer (Policy Optimizer)
- Add Apps to an Application Filter with Policy Optimizer
- Add Apps to an Application Group with Policy Optimizer
- Add Apps Directly to a Rule with Policy Optimizer
- Replace an RMA Firewall (ACE)
- Impact of License Expiration or Disabling ACE
- Commit Failure Due to Cloud Content Rollback
- Troubleshoot App-ID Cloud Engine
- Application Level Gateways
- Disable the SIP Application-level Gateway (ALG)
- Maintain Custom Timeouts for Data Center Applications
-
- Decryption Overview
-
- Keys and Certificates for Decryption Policies
- SSL Forward Proxy
- SSL Forward Proxy Decryption Profile
- SSL Inbound Inspection
- SSL Inbound Inspection Decryption Profile
- SSL Protocol Settings Decryption Profile
- SSH Proxy
- SSH Proxy Decryption Profile
- Profile for No Decryption
- SSL Decryption for Elliptical Curve Cryptography (ECC) Certificates
- Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS) Support for SSL Decryption
- SSL Decryption and Subject Alternative Names (SANs)
- TLSv1.3 Decryption
- High Availability Not Supported for Decrypted Sessions
- Decryption Mirroring
- Configure SSL Forward Proxy
- Configure SSL Inbound Inspection
- Configure SSH Proxy
- Configure Server Certificate Verification for Undecrypted Traffic
- Post-Quantum Cryptography Detection and Control
- Enable Users to Opt Out of SSL Decryption
- Temporarily Disable SSL Decryption
- Configure Decryption Port Mirroring
- Verify Decryption
- Activate Free Licenses for Decryption Features
-
- Policy Types
- Policy Objects
- Track Rules Within a Rulebase
- Enforce Policy Rule Description, Tag, and Audit Comment
- Move or Clone a Policy Rule or Object to a Different Virtual System
-
- External Dynamic List
- Built-in External Dynamic Lists
- Configure the Firewall to Access an External Dynamic List
- Retrieve an External Dynamic List from the Web Server
- View External Dynamic List Entries
- Exclude Entries from an External Dynamic List
- Enforce Policy on an External Dynamic List
- Find External Dynamic Lists That Failed Authentication
- Disable Authentication for an External Dynamic List
- Register IP Addresses and Tags Dynamically
- Use Dynamic User Groups in Policy
- Use Auto-Tagging to Automate Security Actions
- CLI Commands for Dynamic IP Addresses and Tags
- Application Override Policy
- Test Policy Rules
-
- Network Segmentation Using Zones
- How Do Zones Protect the Network?
-
PAN-OS 10.1
- PAN-OS 10.1
- PAN-OS 10.2
- PAN-OS 11.0 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 11.1 & Later
-
- Tap Interfaces
-
- Layer 2 and Layer 3 Packets over a Virtual Wire
- Port Speeds of Virtual Wire Interfaces
- LLDP over a Virtual Wire
- Aggregated Interfaces for a Virtual Wire
- Virtual Wire Support of High Availability
- Zone Protection for a Virtual Wire Interface
- VLAN-Tagged Traffic
- Virtual Wire Subinterfaces
- Configure Virtual Wires
- Configure an Aggregate Interface Group
- Configure Bonjour Reflector for Network Segmentation
- Use Interface Management Profiles to Restrict Access
-
- DNS Overview
- DNS Proxy Object
- DNS Server Profile
- Multi-Tenant DNS Deployments
- Configure a DNS Proxy Object
- Configure a DNS Server Profile
- Use Case 1: Firewall Requires DNS Resolution
- Use Case 2: ISP Tenant Uses DNS Proxy to Handle DNS Resolution for Security Policies, Reporting, and Services within its Virtual System
- Use Case 3: Firewall Acts as DNS Proxy Between Client and Server
- DNS Proxy Rule and FQDN Matching
-
- NAT Rule Capacities
- Dynamic IP and Port NAT Oversubscription
- Dataplane NAT Memory Statistics
-
- Translate Internal Client IP Addresses to Your Public IP Address (Source DIPP NAT)
- Enable Clients on the Internal Network to Access your Public Servers (Destination U-Turn NAT)
- Enable Bi-Directional Address Translation for Your Public-Facing Servers (Static Source NAT)
- Configure Destination NAT with DNS Rewrite
- Configure Destination NAT Using Dynamic IP Addresses
- Modify the Oversubscription Rate for DIPP NAT
- Reserve Dynamic IP NAT Addresses
- Disable NAT for a Specific Host or Interface
-
- Network Packet Broker Overview
- How Network Packet Broker Works
- Prepare to Deploy Network Packet Broker
- Configure Transparent Bridge Security Chains
- Configure Routed Layer 3 Security Chains
- Network Packet Broker HA Support
- User Interface Changes for Network Packet Broker
- Limitations of Network Packet Broker
- Troubleshoot Network Packet Broker
-
-
Cloud Management and AIOps for NGFW
- Cloud Management and AIOps for NGFW
- PAN-OS 10.0 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 10.1
- PAN-OS 10.2
- PAN-OS 11.0 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 11.1
- PAN-OS 11.2
- PAN-OS 8.1 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 9.0 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 9.1 (EoL)
Configure Active/Passive HA
Learn how to configure an active/passive HA pair of firewalls, including setting up
physical connections, enabling ping, setting HA mode and group ID, establishing control and
data link connections, and enabling HA.
The following procedure shows how to configure
a pair of firewalls in an active/passive deployment as depicted
in the following example topology.
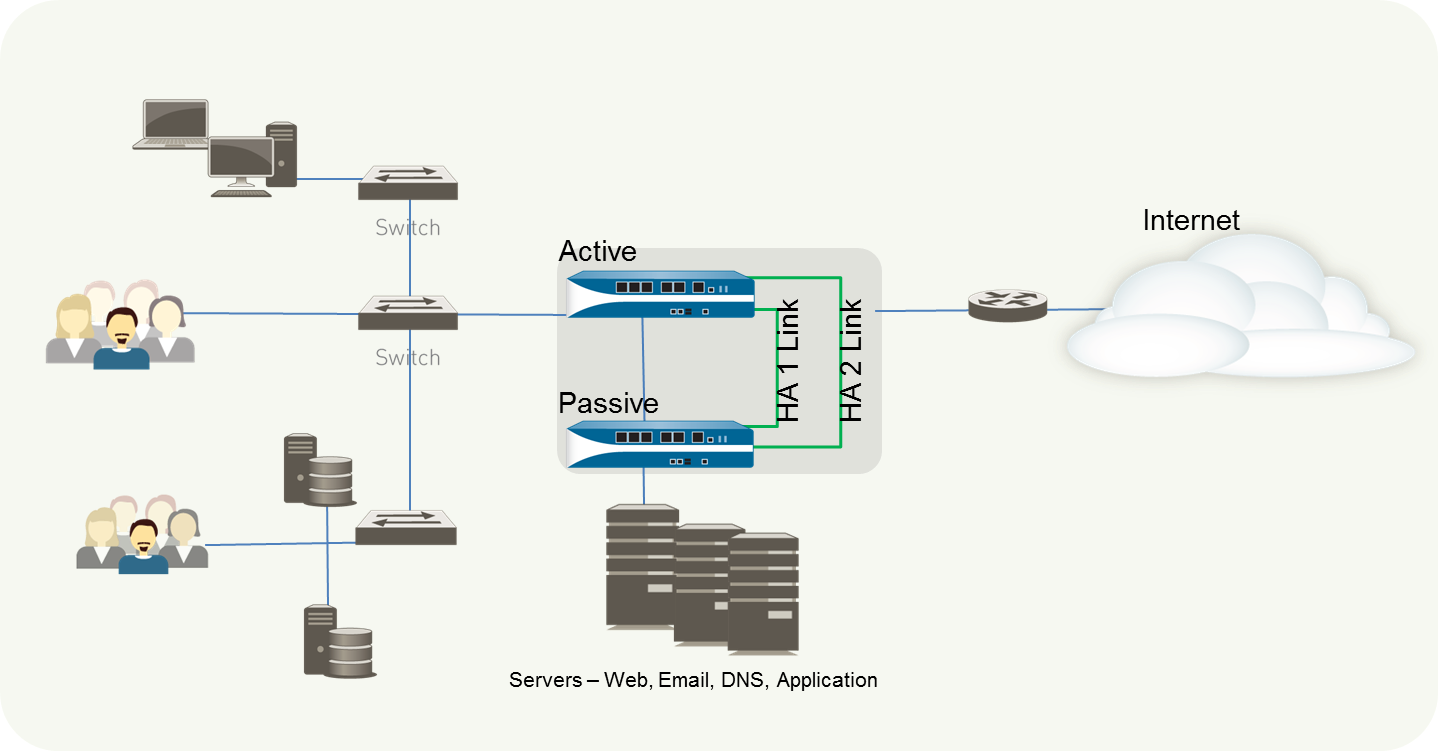
To configure
an active/passive HA pair, first complete the following workflow on
the first firewall and then repeat the steps on the second firewall.
- Connect the HA ports to set up a physical connection between the firewalls.
- For firewalls with dedicated HA ports, use an Ethernet cable to connect the dedicated HA1 ports and the HA2 ports on peers. Use a crossover cable if the peers are directly connected to each other.
- For firewalls without dedicated HA ports, select two data interfaces for the HA2 link and the backup HA1 link. Then, use an Ethernet cable to connect these in-band HA interfaces across both firewalls.
Use the management port for the HA1 link and ensure that the management ports can connect to each other across your network. - Enable ping on the management port.Enabling ping allows the management port to exchange heartbeat backup information.
- Select DeviceSetupInterfacesManagement.
- Select Ping as a service that is permitted on the interface.
- If the firewall does not have dedicated HA ports, set up the data ports to function as HA ports.For firewalls with dedicated HA ports continue to the next step.
- Select NetworkInterfaces.
- Confirm that the link is up on the ports that you want to use.
- Select the interface and set Interface Type to HA.
- Set the Link Speed and Link Duplex settings, as appropriate.
- Set the HA mode and group ID.
- Select DeviceHigh AvailabilityGeneral and edit the Setup section.
- Set a Group ID and optionally a Description for the pair. The Group ID uniquely identifies each HA pair on your network. If you have multiple HA pairs that share the same broadcast domain you must set a unique Group ID for each pair.
- Set the mode to Active Passive.
- Set up the control link connection.This example shows an in-band port that is set to interface type HA.For firewalls that use the management port as the control link, the IP address information is automatically pre-populated.
- In DeviceHigh AvailabilityHA Communications, edit Control Link (HA1).
- Select the Port that you have cabled for use as the HA1 link.
- Set the IPv4/IPv6 Address and Netmask.If the HA1 interfaces are on separate subnets, enter the IP address of the Gateway. Do not add a gateway address if the firewalls are directly connected or are on the same VLAN.
- (Optional) Enable encryption for the control link connection.This is typically used to secure the link if the two firewalls are not directly connected, that is if the ports are connected to a switch or a router.
- Export the HA key from one firewall and import it into the peer firewall.
- Select DeviceCertificate ManagementCertificates.
- Select Export HA key. Save the HA key to a network location that the peer can access.
- On the peer firewall, select DeviceCertificate ManagementCertificates, and select Import HA key to browse to the location that you saved the key and import it in to the peer.
- Repeat this process on the second firewall to exchange HA keys on both devices.
- Select DeviceHigh AvailabilityHA Communications, edit the Control Link (HA1) section.
- Select Encryption Enabled.If you enable encryption, after you finish configuring the HA firewalls, you can Refresh HA1 SSH Keys and Configure Key Options.
- Set up the backup control link connection.
- In DeviceHigh AvailabilityHA Communications, edit Control Link (HA1 Backup).
- Select the HA1 backup interface and set the IPv4/IPv6 Address and Netmask.PA-3200 Series firewalls don’t support an IPv6 address for the HA1 backup control link; use an IPv4 address.
- Set up the data link connection (HA2) and the backup HA2 connection between the firewalls.
- In DeviceHigh AvailabilityHA Communications, edit the Data Link (HA2) section.
- Select the Port to use for the data link connection.
- Select the Transport method. The default is ethernet, and will work when the HA pair is connected directly or through a switch. If you need to route the data link traffic through the network, select IP or UDP as the transport mode.UPD is the only supported transport mode in Azure environments. UDP is the preferred transport mode for PA-1400 Series and PA-3400 Series firewalls.
- If you use IP or UDP as the transport method, enter the IPv4/IPv6 Address and Netmask.
- Verify that Enable Session Synchronization is selected.
- Select HA2 Keep-alive to enable monitoring on the HA2 data link between the HA peers. If a failure occurs based on the threshold that is set (default is 10000 ms), the defined action will occur. For active/passive configuration, a critical system log message is generated when an HA2 keep-alive failure occurs.You can configure the HA2 keep-alive option on both firewalls, or just one firewall in the HA pair. If the option is only enabled on one firewall, only that firewall will send the keep-alive messages. The other firewall will be notified if a failure occurs.
- Edit the Data Link (HA2 Backup) section, select the interface, and add the IPv4/IPv6 Address and Netmask.
- Enable heartbeat backup if your control link uses a dedicated HA port or an in-band port.You do not need to enable heartbeat backup if you are using the management port for the control link.
- In DeviceHigh AvailabilityGeneral, edit the Election Settings.
- Select Heartbeat Backup.To allow the heartbeats to be transmitted between the firewalls, you must verify that the management port across both peers can route to each other.Enabling heartbeat backup also allows you to prevent a split-brain situation. Split brain occurs when the HA1 link goes down causing the firewall to miss heartbeats, although the firewall is still functioning. In such a situation, each peer believes that the other is down and attempts to start services that are running, thereby causing a split brain. When the heartbeat backup link is enabled, split brain is prevented because redundant heartbeats and hello messages are transmitted over the management port.
- Set the device priority and enable preemption.This setting is only required if you wish to make sure that a specific firewall is the preferred active firewall. For information, see Device Priority and Preemption.
- In DeviceHigh AvailabilityGeneral, edit the Election Settings.
- Set the numerical value in Device Priority. Make sure to set a lower numerical value on the firewall that you want to assign a higher priority to.If both firewalls have the same device priority value, the firewall with the lowest MAC address on the HA1 control link will become the active firewall.
- Select Preemptive.You must enable preemptive on both the active firewall and the passive firewall.
- (Optional) Modify the HA Timers.By default, the HA timer profile is set to the Recommended profile and is suited for most HA deployments.
- In DeviceHigh AvailabilityGeneral, edit the Election Settings.
- Select the Aggressive profile for triggering failover faster; select Advanced to define custom values for triggering failover in your set up.To view the preset value for an individual timer included in a profile, select Advanced and click Load Recommended or Load Aggressive. The preset values for your hardware model will be displayed on screen.
- (Optional) Modify the link status of the HA ports on the passive firewall.The passive link state is shutdown, by default. After you enable HA, the link state for the HA ports on the active firewall will be green and those on the passive firewall will be down and display as red.Setting the link state to Auto allows for reducing the amount of time it takes for the passive firewall to take over when a failover occurs and it allows you to monitor the link state.To enable the link status on the passive firewall to stay up and reflect the cabling status on the physical interface:
- In DeviceHigh AvailabilityGeneral, edit the Active Passive Settings.
- Set the Passive Link State to Auto.The auto option decreases the amount of time it takes for the passive firewall to take over when a failover occurs.Although the interface displays green (as cabled and up) it continues to discard all traffic until a failover is triggered.When you modify the passive link state, make sure that the adjacent devices do not forward traffic to the passive firewall based only on the link status of the firewall.
- Enable HA.
- Select DeviceHigh AvailabilityGeneral and edit the Setup section.
- Select Enable HA.
- Select Enable Config Sync. This setting enables the synchronization of the configuration settings between the active and the passive firewall.
- Enter the IP address assigned to the control link of the peer in Peer HA1 IP Address.For firewalls without dedicated HA ports, if the peer uses the management port for the HA1 link, enter the management port IP address of the peer.
- Enter the Backup HA1 IP Address.
- (Optional) Enable LACP and LLDP Pre-Negotiation for Active/Passive HA for faster failover if your network uses LACP or LLDP.
- Ensure that in Step12you set the link state to Auto.
- Select NetworkInterfacesEthernet.
- To enable LACP active pre-negotiation:
- Select an AE interface in a Layer 2 or Layer 3 deployment.
- Select the LACP tab.
- Select Enable in HA Passive State.
- Click OK.You cannot also select Same System MAC Address for Active-Passive HA because pre-negotiation requires unique interface MAC addresses on the active and passive firewalls.
- To enable LACP passive pre-negotiation:
- Select an Ethernet interface in a virtual wire deployment.
- Select the Advanced tab.
- Select the LACP tab.
- Select Enable in HA Passive State.
- Click OK.
- To enable LLDP active pre-negotiation:
- Select an Ethernet interface in a Layer 2, Layer 3, or virtual wire deployment.
- Select the Advanced tab.
- Select the LLDP tab.
- Select Enable in HA Passive State.
- Click OK.If you want to allow LLDP passive pre-negotiation for a virtual wire deployment, perform Step14.ebut do not enable LLDP itself.
- Save your configuration changes.Click Commit.
- After you finish configuring both firewalls, verify that the firewalls are paired in active/passive HA.
- Access the Dashboard on both firewalls, and view the High Availability widget.
- On the active firewall, click the Sync to peer link.
- Confirm that the firewalls are paired and synced, as shown as follows:
- On the passive firewall: the state of the local firewall should display passive and the Running Config should show as synchronized.
- On the active firewall: The state of the local firewall should display active and the Running Config should show as synchronized.
