Set Up Credential Phishing Prevention
Table of Contents
End-of-Life (EoL)
Set Up Credential Phishing Prevention
After you have decided which of the Methods
to Check for Corporate Credential Submissions you want to
use, take the following steps to enable the firewall to detect when
users submit corporate credentials to web pages and either alert
on this action, block the credential submission, or require users
to acknowledge the dangers of phishing before continuing with credential
submission.
- If you have not done so already, Enable User-ID.Each of the Methods to Check for Corporate Credential Submissions requires a different User-ID configuration to check for corporate credential submissions:
- If you plan to use the group mapping method, which detects whether a user is submitting a valid corporate username, Map Users to Groups.
- If you plan to use the IP user mapping method, which detects whether a user is submitting a valid corporate username and that username is the same as the login username, Map IP Addresses to Users.
- If you plan to use the domain credential filter method, which detects whether a user is submitting a valid username and password and that those credentials belong to the logged-in user, Configure Credential Detection with the Windows-based User-ID Agent and Map IP Addresses to Users.
If you have not done so already, configure a best practice URL Filtering profile to ensure protection against URLs that have been observed hosting malware or exploitive content.- Select ObjectsSecurity ProfilesURL Filtering and Add or modify a URL Filtering profile.Block access to all known dangerous URL categories: malware, phishing, dynamic-dns, unknown, command-and-control, extremism, copyright-infringement, proxy-avoidance-and-anonymizers, newly-registered-domain, grayware, and parked.Add a decryption policy rule to decrypt the traffic you want to monitor for user credential submissions.Configure the URL Filtering profile to detect corporate credential submissions to websites that are in allowed URL categories.The firewall does not check credential submissions for trusted sites, even if you enable the checks for the URL categories for these sites, to provide best performance. The trusted sites represent sites where Palo Alto Networks has not observed any malicious or phishing attacks. Updates for this trusted site list are delivered through Application and Threat content updates. For a list of App-IDs that are exempt from credential detection, see Trusted App-IDs That Skip Credential Submission Detection on live.paloaltonetworks.com.
- Select User Credential Detection.Select one of the Methods to Check for Corporate Credential Submissions to web pages from the User Credential Detection drop-down:Confirm that the format for the primary username is the same as the username format that the User-ID source provides.
- Use IP User Mapping—Checks for valid corporate username submissions and verifies that the login username maps to the source IP address of the session. To do this, the firewall matches the submitted username and source IP address of the session against its IP-address-to-username mapping table. To use this method you can use any of the user mapping methods described in Map IP Addresses to Users.
- Use Domain Credential Filter—Checks for valid corporate usernames and password submissions and verifies that the username maps to the IP address of the logged in user. See Configure Credential Detection with the Windows-based User-ID Agent for instructions on how to set up User-ID to enable this method.
- Use Group Mapping—Checks for valid username submissions based on the user-to-group mapping table populated when you configure the firewall to Map Users to Groups.With group mapping, you can apply credential detection to any part of the directory, or for specific groups that have access to your most sensitive applications, such as IT.
This method is prone to false positives in environments that do not have uniquely structured usernames. Because of this, you should only use this method to protect your high-value user accounts.Set the Valid Username Detected Log Severity the firewall uses to log detection of corporate credential submissions. By default, the firewall logs these events as medium severity.Block (or alert) on credential submissions to allowed sites.- Select Categories.For each Category to which Site Access is allowed, select how you want to treat User Credential Submissions:
- alert—Allow users to submit credentials to the website, but generate a URL Filtering log each time a user submits credentials to sites in this URL category.
- allow—(default) Allow users to submit credentials to the website.
- block—Block users from submitting credentials to the website. When a user tries to submit credentials, the firewall displays the Anti-Phishing Block Page, preventing the credential submission.
- continue—Present the Anti-Phishing Continue Page response page to users when they attempt to submit credentials. Users must select Continue on the response page to continue with the submission.
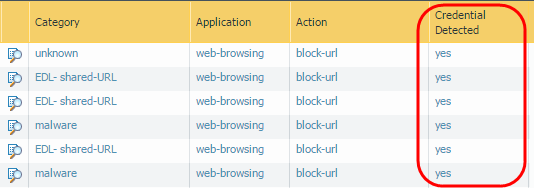
Select OK to save the URL Filtering profile.Apply the URL Filtering profile with the credential detection settings to your Security policy rules.- Select PoliciesSecurity and Add or modify a Security policy rule.On the Actions tab, set the Profile Type to Profiles.Select the new or updated URL Filtering profile to attach it to the Security policy rule.Select OK to save the Security policy rule.Commit the configuration.Monitor credential submissions the firewall detects.Select ACCHosts Visiting Malicious URLs to see the number of users who have visited malware and phishing sites.Select MonitorLogsURL Filtering.The new Credential Detected column indicates events where the firewall detected a HTTP post request that included a valid credential:
![]() To display this column, hover over any column header and click the arrow to select the columns you’d like to display.Log entry details also indicate credential submissions:
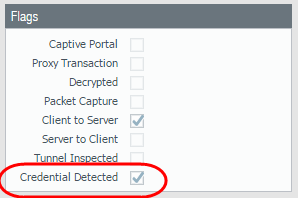
To display this column, hover over any column header and click the arrow to select the columns you’d like to display.Log entry details also indicate credential submissions:![]() Validate and troubleshoot credential submission detection.
Validate and troubleshoot credential submission detection.- Use the following CLI command to view credential detection statistics:
> show user credential-filter statisticsThe output for this command varies depending on the method configured for the firewall to detect credential submissions. For example, if the Domain Credential Filter method is configured in any URL Filtering profile, a list of User-ID agents that have forwarded a bloom filter to the firewall is displayed, along with the number of credentials contained in the bloom filter.- (Group
Mapping method only) Use the following CLI command
to view group mapping information, including the number of URL Filtering
profiles with Group Mapping credential detection enabled and the usernames
of group members that have attempted to submit credentials to a restricted
site.
> show user group-mapping statistics
- (Domain
Credential Filter method only) Use the following
CLI command to see all Windows-based User-ID agents that are sending mappings
to the firewall:
> show user user-id-agent state allThe command output now displays bloom filter counts that include the number of bloom filter updates the firewall has received from each agent, if any bloom filter updates failed to process, and how many seconds have passed since the last bloom filter update. - (Domain Credential Filter method only) The Windows-based User-ID agent displays log messages that reference BF (bloom filter) pushes to the firewall. In the User-ID agent interface, select MonitoringLogs.